* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Lecture #25
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
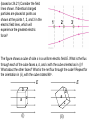
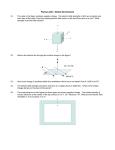
Tue. Feb. 3 – Physics Lecture #25 Gauss’s Law I: Field Lines and Flux 1. Electric Field Vectors and Electric Field Lines 2. Electric Field and Electric Flux Think about This: Discuss with neighbors (based on 24.21) Consider the field lines shown. If identical charged particles are placed at points as shown at the points 1, 2, and 3 in the electric field lines, which will experience the greatest electric force? 1 2 3 The figure shows a cube of side s in a uniform electric field E. What is the flux through each of the cube faces a, b, and c with the cube oriented as in (i)? What about the other faces? What is the net flux through the cube? Repeat for the orientation in (ii), with the cube rotated 60o. E E b a (i) b c a c (ii) A spherical surface surrounds an isolated positive charge, as shown (in crosssection). If a second (positive) charge is placed outside the surface: a) What happens to the electric field on the surface a the point P between the charges? b) What happens to the total electric flux through the surface? + + P + c) Return to just the single positive charge. Calculate the flux through the spherical surface.