* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Technological singularity wikipedia , lookup
Computer vision wikipedia , lookup
Computer Go wikipedia , lookup
Human-Computer Interaction Institute wikipedia , lookup
Wizard of Oz experiment wikipedia , lookup
Machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Expert system wikipedia , lookup
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Knowledge representation and reasoning wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
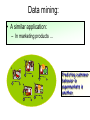
AI vs. Brain Historical Perspective • (4th C BC+) Aristotle, George Boole, Gottlob Frege, Alfred Tarski – formalizing the laws of human thought • (16th C+) Gerolamo Cardano, Pierre Femat, James Bernoulli, Thomas Bayes – formalizing probabilistic reasoning • (1950+) Alan Turing, John von Neumann, Claude Shannon – thinking as computation • (1956) John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Herbert Simon, Allen Newell – start of the field of AI Hardware 1011 neurons 1014 synapses cycle time: 10-3 sec 107 transistors 1010 bits of RAM cycle time: 10-9 sec Computer vs. Brain Evolution of Human & Computers Projection •In near future computers will have –As many processing elements as our brain, –But far fewer interconnections –Much faster updates. •Fundamentally different hardware –Requires fundamentally different algorithms! What is Intelligence? The Turing test: • a human judge engages in a natural language conversation with a human and a machine designed to generate performance indistinguishable from that of a human being. • All participants are separated from one another. • If the judge cannot reliably tell the machine from the human, the machine is said to have passed the test. Chatbot Alice: A dialogue with Alice-bot: > I’m Daniel Nice to meet you Daniel. > Do you know Clinton? He was the second Impeached President of the United States. > Do you like him? Sure he has never done anything to me. > What is an impeachment? It is a good question. I have to process that one for a while. I would do a search for it. > Who are you? I ask myself that question, "Who am I?" > What do you do? I am chatting with people on the net. Dialogue continued: > What is your favorite topic? My favorite subject is artificial intelligence. > What is artificial intelligence? Artificial intelligence is the branch of engineering and science devoted to constructing machines that think. I can ask someone about it. > Can you do anything else than chatting? Doing anything else than chatting is not among my strongest traits. ... Dialogue continued (2): > How old am I? Is this a trick question? You said you were how many years old? My guess is that you are really a kid. > What would you like to know about me? Tell me about your educational background. > I am a professor in computer science You are a professor in computer science? How do you like your work? > It’s kind of nice teaching courses on artificial intelligence I guess it is a lot of fun. > What should I tell the students about you? Be sure to think before you speak. State your point clearly and slowly and gauge the listener's response before going any further. Is Alice intelligent? • ABSOLUTELY NOT ! • ~ 50,000 fairly trivial input-response rules. – + some pattern matching – + some knowledge – + some randomness • NO reasoning component • BUT: demonstrates ‘human-like’ behaviour. – Won the ‘turing award’ Dimensions of the AI Definition human-like vs. rational Systems that Systems that think like humans think rationally thought vs. behavior Systems that act Systems that act like humans rationally AI as Science Science: • Where did the physical universe come from? And what laws guide its dynamics? • How did biological life evolve? And how do living organisms function? • What is the nature of intelligent thought? AI as Engineering • How can we make software systems more powerful and easier to use? – Speech & intelligent user interfaces – Autonomic computing – SPAM detection – Mobile robots, softbots & immobots – Data mining – Modeling biological systems – Medical expert systems... State of the Art “I could feel – I could smell – a new kind of intelligence across the table” -Gary Kasparov Saying Deep Blue doesn’t really think about chess is like saying an airplane doesn’t really fly because it doesn’t flap its wings. – Drew McDermott IBM超级电脑人机对战 • In February 2011, IBM’s program Watson, defeated the two greatest Jeopardy! quiz show champions by a significant margin. • IBM超级电脑“沃森”于2011年2月参加美 国最受欢迎的智力竞赛节目《危险边缘》 (Jeopardy),与两位最成功的选手展开 对决。冠军奖金为100万美元,亚军为30万 美元,季军为20万美元。 Mathematical Calculation Shuttle Repair Scheduling Started: January 1996 Launch: October 15th, 1998 Experiment: May 17-21 courtesy JPL Compiled into 2,000 variable SAT problem Real-time planning and diagnosis Mars Rover Europa Mission ~ 2018 Credit Card Fraud Detection Speech Recognition Data mining: • An application of Machine Learning techniques – It solves problems that humans can not solve, because the data involved is too large .. Detecting cancer risk molecules is one example. Data mining: • A similar application: – In marketing products ... Predicting customer behavior in supermarkets is another. Many other applications: • Computer vision: • In language and speech processing: • In robotics: DARPA Grand Challenge • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DARPA_Grand _Challenge • Google 自动驾驶汽车无事故行驶三十万英 里 – http://www.guao.hk/posts/googleautomated-car-adds-new-model-lexusrx450h.html – http://news.mydrivers.com/1/227/227396.ht m Google translation • http://translate.google.com/ 对对联 • http://couplet.msra.cn/ Limits of AI Today • Today’s successful AI systems –operate in well-defined domains –employ narrow, specialize knowledge • Commonsense Knowledge –needed in complex, open-ended worlds • Your kitchen vs. GM factory floor –understand unconstrained Natural Language Natural Language Processing • 大学里有两种人不谈恋爱:一种是谁都看 不上,另一种是谁都看不上。 • 大学里有两种人最容易被甩:一种人不知 道什么叫做爱,一种人不知道什么叫做爱 • 这些人都是原先喜欢一个人,后来喜欢一 个人。 How to Get Commonsense? • CYC Project (Doug Lenat, Cycorp) –Encoding 1,000,000 commonsense facts about the world by hand –Coverage still too spotty for use! • Machine Learning Recurrent Themes • Explicit Knowledge Representation vs. Implicit –Neural Nets - McCulloch & Pitts 1943 • Died out in 1960’s, revived in 1980’s • Simplified model of real neurons, but still useful; parallelism –Brooks “Intelligence without Representation” Recurrent Themes II • Logic vs. Probability –In 1950’s, logic dominates (McCarthy, … • attempts to extend logic “just a little” (e.g. non-monotonic logics) –1988 – Bayesian networks (Pearl) • efficient computational framework –Today’s hot topic: combining probability & FOL & Learning Recurrent Themes III • Weak vs. Strong Methods • Weak – general search methods (e.g. A* search) • Knowledge intensive (e.g expert systems) • more knowledge less computation • Today: resurgence of weak methods • desktop supercomputers • How to combine weak & strong? Recurrent Themes IV • Importance of Representation • Features in ML • Reformulation • The mutilated checkerboard AI: Topics • • Agent: anything that perceiving its environment through sensors and acting upon that environment actuators. Agents – Search thru Problem Spaces, Games & Constraint Sat • • – Knowledge Representation and Reasoning • • – Machine learning, data mining, Planning • – Proving theorems Model checking Learning • – One person and multi-person games Search in extremely large space Probabilistic vs. Deterministic Robotics • • • • Vision Control Sensors Activity Recognition Issues • What do you expect AI do for you? • Will AI defeat human brain in the future? Why and when?