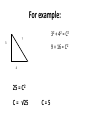* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vector Fill-in Notes
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Minkowski space wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
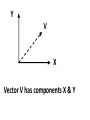
10-31-11 Agenda HOMEWORK CHECK Place on your desk: *Calculator & Protractor *Orange Homework Chart *Protractor/Angle Packet (graph paper) 1) Vector components in a right triangle θ are named relative to____. 1) Warm-Up 5 min 2) Finish Vocab. Words 10 min 3) Vocab. Quiz 15 min 4) Vector fill-in notes 15 min 5) Examples of Fnet 15 min 6) “In the Park” worksheet 15 min 7) Physics Test Review 20 min 2) The process of resolving a vector into resolution its components is called____________. 8) Pre-Vector Worksheet II Vocab. 1. Equilibrant: the one force that brings the net force to equal zero. The equilibrant is equal to but opposite the resultant. 2. Graphical Representation: using a vector diagram to represent either forces acting on an object or velocity/ acceleration vectors. Review: -Vectors requite magnitude (how much) and direction & or orientation. -Scalar quantities (speed, time, mass, etc) do not require direction but do have magnitude. -Direction of vectors on paper: top of page is NORTH, bottom of the page is SOUTH, to the right is EAST and the left is WEST OR A COMBINATION. -Types of vectors which have been studied and will be covered in this unit: •Weight vectors which are always drawn 90˚ from the middle of the object which has the weight. •Friction vectors will be drawn horizontal OR against the other force that is acting AGAINST •Force vectors are drawn based on the NET FORCE which will cause the motion. •Velocity vectors are drawn exactly as any force vectors but 2 terms are used: -Tailwind which means the wind is from behind or also moving in the same direction. -Headwind means head-on so that the object is moving against the direction; opposite direction. -Relative to the ground= horizontal direction and can also be used with an angle that is “relative to the ground. PARTS OF A VECTOR: -Component & or composition of vectors: finding the diagonal. [resultant/diagonal/hypotenuse or NET FORCE of the 2 quantities given] which will form the right triangle. Component vectors are the horizontal and vertical vectors which make the 2 sides of the triangle. The unknown angle called theta is used to find the diagonal based on where the angle is located. -Resolution of vectors: the diagonal is known and you “resolve” the diagonal to find the 2 sides of the triangle based on the given angle (theta). METHODS USED TO SOLVE FOR VECTORS: •GRAPHIC METHOD: the horizontal and vertical lines are drawn to scale and the hypotenuse is solved by measurement based on the scale. •Trig. Functions: Use of sine, cosine and tangent •Parallelogram Method: 4 sided shape in which the opposite sides are parallel and equal in length—the resultant is the diagonal of the parallelogram—used with the graphic and Trig method. Pythagorean theorem: A2+B2=C2 **Can ONLY be used when “direction” is not an issue---so, NOT with Vectors!!! EQUILIBRIUM VECTORS– When forces are opposite but equal and so the displacement is ZERO. If motion is involved, it will be constant. Static equilibrium: where there are NO unbalanced forces acting on a body, the vector sum of all forces acting on the body is zero—called the equilibrant force. So if each force is equal to the other then, the body is either at rest or moving at a constant speed in a straight line. Special Case: If you are ONLY solving for the equilibrant force, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the magnitude of the resultant. **Use only, if 2 sides are known and direction is NOT needed! PYTHAGOREAM THEOREM 2 A + 2 B = 2 C C (hypotenuse) side A side B For example: 32 + 42 = C2 ? 3 9 + 16 = C2 4 25 = C2 C = √25 C=5 Y V X Vector V has components X & Y DUE TODAY: • Vector Fill-in Notes (KEEP) • Practice Problems & In the Park “The person lives twice who lives the first life well.” Robert Herrick DUE NEXT CLASS: • Study for Vector Quiz • Bring Calculator & Protractor!