* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11-4-10 Aim: What are the apparent motions of the stars and planets?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
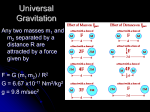
11-4-10 Aim: What are the apparent motions of the stars and planets? Do Now: 1. If there was another planet (Z) that was in between Mercury and Venus, estimate its distance from the sun, diameter, period of revolution. Also tell me if it would be terrestrial or jovian? 2. List the planets in order of increasing eccentricity of their orbits. 3. HW: R&H pp. 60-62, A&E #1-14 Celestial Sphere- an imaginary dome showing the portion of the sky visible from your location. Parts of the Celestial Sphere Meridian • Zenith – point directly overhead. • Meridian – line connecting north to south passing through your zenith. • Horizon – where the ground meets the sky 360 deg. around you. Daily Motion of Stars and Planets • Because the earth rotates 15deg/hr from west to east all celestial objects will appear to rise in the east and set in the west. This includes all stars, including the sun, the moon and the planets. Retrograde Motion- the apparent backward motion of the planets as the earth passes them in their orbit Earth’s elliptical orbit about the sun 11-5-10 Aim: What causes the seasons? • Do Now: • 1. Draw a celestial sphere for New York. Be sure to label meridian, zenith, horizon, compass directions and the location of Polaris. • 2. What is a direct ray? • 3. What is aphelion and perihelion? www.brainpop.com/science#885B39 • Google “Randy Russell portfolio on seasons” www.msu.edu/.webloc 11-8-10 Aim: What are the models that help explain celestial motion? • Do Now: • 1. I see the sun directly overhead at noon on June 21, where am I and what compass direction did I look to see the sunrise? • 2. As altitude of the sun increases, intenstiy___. • 3. Explain retrograde motion. • HW R&H pp.63-64, A&E #15-19, Finish Lab. 11-9-10 How is the earth moving? • Do Now: QUIZ • For each lettered position on the board, indicate the date, location of the direct rays, name of the day and the # of daylight hours at the North Pole, N.Y., Equator, and the South Pole. • • HW: R&H pp.65-70, A&E #20-40 Evidence of the earth’s rotation • 1. Night and day- as the earth rotates 15 deg./hour from west to east all locations will experience light and dark in 24 hours. • 2. Apparent rising and setting of all celestial objects. • 3. Motions of the Foucault Pendulum- a freely swinging pendulum appears to change direction as a result of the earth’s rotation. • 4. The Coriolis Effect- winds and water will be deflected to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere as result of earth’s rotation. • 5. Star Trails- time lapse photos taken of stars seem to make circular trails around Polaris. Foucault Pendulum Coriolis Effect Evidence of Earth’s Revolution • Different constellations visible at different times of the year • Ecliptic- the apparent path that the sun makes through the stars as a result of the earth’s revolution. (p.67) 11-10-10 Aim: What causes the phases of the moon? • • • • • • • • • • Do Now: Name the thing responsible for each: A. Night/day B. Retrograde motion C. Different constellations visible at different times of year. D. Star Trails E. Motions of Foucault Pendulum F. Ecliptic G. Seasons H. Apparent path of the sun during the day. • HW- R&H pp. 71-74, A&E # 41-57 Moon’s Revolution and Phases of the Moon Moon Facts Rotation = 27.3 days Revolution = 27.3 days (Seiderial Month) *because the moon rotates and revolves at the same speed we always see the same side of the moon. Full Cycle of Phases = 29.5 days (Sonadal Month) Reason- because the earth revolves around the sun at the same time the moon revolves around the earth, it takes 2 extra days for the moon to catch up to earth in its orbit. The moon’s revolution around the earth is what causes us to see different phases of the moon. Orbit = counterclockwise in an ellipse and on a 5 degree tilt. 11-12-10 Aim: What causes tides? • Do Now: • 1. What is the difference between a siderial and a sonadal month? • 2. Because the moon rotates and revolves at the same speed, what does this cause to happen? • HW: p.76 #1-29 A&E, Finish Lab. Spring Tides and Neap Tidescontrolled by the gravitational pull of the moon but enhanced by the gravitaional pull of the sun. Tides Animation • Spring Tide – when the moon and the sun pull in the same direction creating the highest high tides and the lowest low tides for the month. • Neap Tide – when the sun and the moon are at right angles to the earth, high tide stays with the moon creating the lowest high and highest low tides for the month. www.mmscrusaders.com/.webloc Eclipses Caused when the moon’s shadow blocks out the sun or when the earth’s shadow blocks out the moon. Solar Eclipse Lunar Eclipse The reason we do not experience eclipses every month is because the moon’s orbit is on a 5 deg. Tilt causing the earth, sun and moon not to lign up perfectly. What a lunar eclipse looks like