* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab 1 - UTeM
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
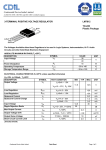
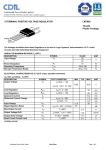
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA FAKULTI KEJURUTERAAN ELEKTRONIK DAN KEJURUTERAAN KOMPUTER BENP 2183 ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTATION LAB SESSION 1 MEASUREMENT ERROR Prepared by: Norizan bin Mohamad / Zahriladha Zakaria Industrial Electronics Department, FKEKK (December 2004) 1.0 OBJECTIVES This experiment is designed to help students to : a) use DMM to measure DC voltage and current of a circuit. b) analyze and understand the error introduced during measurement. c) explain the causes of measurement errors. 2.0 EQUIPMENTS 1) 2) 3) 4) Digital Multimeter (DMM) DC Power Supply Resistor : 1 k - 2 units Project Board 3.0 PROCEDURES : 3.1 PART A : DC Voltage Measurement 1. Measure and record the expected resistance values of the two resistors using DMM. 2. Construct the circuit in Figure 1. R1 A Vin I2 R2 Vout B Figure 1 3. Set the input voltage Vin = 1 V. Using DMM, measure and record the output voltage across R2 . 4. Increase Vin by 1 V. Measure and record the output voltage across R2 . 5. Repeat Step 4 until Vin = 10 V. (Write down your measurement in a table) 6. Calculate the expected voltage across R2 for all the input voltages, Vin in Step 5 . (use the expected resistance value of R1 and R2 ) 7. For each measurement and expected values in Step 5 and 6, calculate the absolute error, % error, relative accuracy, and % accuracy. What is the average % accuracy of your DMM ? 8. Draw a graph of measured output voltage vs. input voltage from your data in Step 5. How is the relationship between the measured output voltage and input voltage ? Is there any obvious error seen on your graph ? Is there any systematic error shown on your graph ? Discuss your observations and findings. 3.2 PART B : DC Current Measurement 1. Use the resistors and circuit in Part A. 2. Set the input voltage Vin = 1 V. Using DMM, measure and record the current flow through R2 . 3. Increase Vin by 1 V. Measure and record the current flow through R2 . 4. Repeat Step 3 until Vin = 10 V. (Write down your measurement in a table). 5. Calculate the expected current flow through R2 for all the input voltages, Vin in Step 4 . (use the expected resistance value of R1 and R2 ) 6. For each measurement and expected values in Step 4 and 5, calculate the absolute error, % error, relative accuracy, and % accuracy. 7. Draw a graph of measured current vs. input voltage from your data in Step 4. How is the relationship between the measured current and input voltage ? Is there any obvious error seen on your graph ? Is there any systematic error shown on your graph ? Discuss your observations and findings. 8. Make conclusion on your observations and findings for the measurement error in Part A and Part B. Give your opinions on how to reduce the errors.