* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.1 The Nature of Heat
Radiator (engine cooling) wikipedia , lookup
Cutting fluid wikipedia , lookup
Vapor-compression refrigeration wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
Space Shuttle thermal protection system wikipedia , lookup
Passive solar building design wikipedia , lookup
Solar water heating wikipedia , lookup
Heat exchanger wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Solar air conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Intercooler wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Insulated glazing wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conduction wikipedia , lookup
Copper in heat exchangers wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthermia wikipedia , lookup
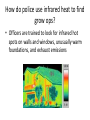
Chapter 6 Controlling Heat Transfer 6.1 Absorbing and Losing Heat Science 14 and 10-4 with Mrs. M Specific Heat Capacity Can’t take the heat? Get out of the kitchen! Just kidding, water can take the heat • Water can absorb a lot of heat without raising its temperature a lot • It takes a lot more heat energy to increase the temperature of water • Water has a HIGH specific heat which means a LOW temperature compared to other substances Water Can Take the Heat • Heat absorption: the rate at which materials absorb heat • Specific heat capacity: measures a substance’s ability to absorb or lose heat – Water has a high specific heat so it can take on a lot of heat energy without increasing it’s temperature too much Oceans moderate climate • • • • Oceans store thermal energy (heat) Water can absorb heat on a hot day Water can release heat on a cool day Water’s specific heat capacity is larger than that of oil, sand, or metal Fire walkers • Socks make their feet sweat before performing the walk. How might this help to protect their feet from burning? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-iBFwpKV6ak Lab Report • Heat absorption and specific heat capacity • There are equal amounts of water, vegetable oil, and vinegar in beakers on a hot plate. If all are given the same amount of heat, which will heat up fastest? Which will stay hot the longest? • Analysis: Considering water’s specific heat capacity is 4.19 J/g°C and oil’s is 1.97 J/g°C, why do you think that you saw the difference in heating? Check Your Understanding Page 110 #3. Why does water at a beach feel cooler than sand during the day and warmer at night? #4. Use your knowledge of specific heat capacity to explain why water is a better coolant than vegetable oil. Relate your knowledge of specific heat capacity to coolant in a car radiator. #5. You plan to make French fries. It’s best to use very hot oil with a higher or lower specific heat capacity better? Why? Air vs. Water Heat Capacity https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hyPLusD-tyM 6.2 Keeping Heat at Home • During winter, Canadian houses lose heat because hot air escapes to the cold outside • Insulation can help this problem Conductors vs Insulators • Metal • Ceramic • Electrical wire • • • • • Glass Wood Plastic Fabrics Reflective foil Conductors vs Insulators • Metal • Ceramic • Electrical wire • • • • • Glass Wood Plastic Fabrics Reflective foil Why wrap food in aluminum/tin foil? Why do welders need equipment? 6.2 Insulation • Insulation slows heat transfer • R-value is a measure of how well an insulating material slows heat transfer • High R-value means better insulation R-value • The total R-value is the sum of the R-values of each material used • Example: What is the total R-value if you have 25mm of expanded polystyrene and rigid urethane? – expanded polystyrene 3.96 – rigid urethane 7.50 – Total = 3.96 + 7.50 = R-11.46 Check Your Understanding • Page 119 #1a Use Table 6.2 on page 111 to help you calculate the R-values of the following insulation materials: a) 25 mm of air space + 25 mm of expanded polystyrene Cavity Walls • Walls often have a cavity of air in between the layers • This air gap can be filled with insulation to eliminate convection currents within walls What has a higher R-value? • Double wall • Double wall with insulation Check Your Understanding • Page 119 #1 Guest Speaker: Firefighter Facts about fire: • Can be caused by overheating electrical wires, kitchen fires, gas leaks • Houses vaporize (flame over) at 1000°C so firefighters need to get out Firefighter Safety • Firefighters are most likely to burn their ears, chin, and neck • Protective gear is made of three layers – Kevlar: prevent injection (glass, needles) – Fire resistant: prevent heat transfer – Micro-fiber: waterproof prevents absorption • Visor melts at 700°C to signal it is time to get out Firefighter Equipment • Boots, pants, coat, helmet, gloves, mask Cool Facts • Firefighter equipment is both expensive and heavy Pop Can House Controlling Heat Transfer • How do pizza deliveries keep your pizza warm? Windows and Doors Leak Heat • How do we keep the heat in? • Older houses have storm windows or storm doors. Two doors help keep heat in. • Today we use an extra glazing on glass windows • Weather stripping Why do builders put more insulation in attics than in walls? Asbestos • Asbestos fibres are strong, durable and noncombustible • Used widely in the ‘50s - ‘70s • People in construction, maintenance, and renovation must be careful Asbestos • Good for reinforcing, insulating, fire-proofing • No risk if fibres are enclosed or tightly bound in a product, (asbestos siding or floor tiles) • Asbestos poses health risks only when fibres are present in the air that people breathe Asbestos • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GjMsV4V sJew • Until 3:45 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BIHpsyuy V4I Thermal sensors How do police use infrared heat to find grow ops? • Officers are trained to look for infrared hot spots on walls and windows, unusually warm foundations, and exhaust emissions Vacuum Bottle: Thermos • Insulated to keep your food or beverage warm • Insulation slows heat transfer • How does it work? How does a vacuum bottle reduce convection, conduction, radiation? • Double glass jar (similar to double pane window) • Partial vacuum from removing some air between glass jars • Reflective coating • Rubber/plastic outer case • Insulated cap 6.3 Keeping Cool • People in deserts wear more clothes to minimize heat transfer • You protect your hands from the oven’s heat using oven mitts 6.3 Keeping Warm • Multiple layers keep you warm in the winter Polar bears have hollow guard hairs Air is an insulator Chapter 6 Review • Key Term Definitions or Reviewing Key Terms • #2, 4, 7, 10, 12, 13