* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Warm-up
Inclusive fitness in humans wikipedia , lookup
Origins of society wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary psychology wikipedia , lookup
Before the Dawn (book) wikipedia , lookup
Human evolutionary genetics wikipedia , lookup
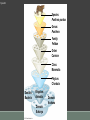
Chapter 26: Phylogeny and the Tree of Life CONT ’D MONDAY, 9/22/2014 Warm-up Which came first, the chicken or the egg? Explain how you would use phylogenetics to solve this puzzle. Warm-up Which came first, the chicken or the egg? Explain how you would use phylogenetics to solve this puzzle. Hanken. 1998. Eggs first. Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 4: 58. Homework 1. MasteringBiology Questions on Chapter 26: Due Wednesday, 10:45 AM 2. Short Essay: Read this short article and summarize. Instructions posted on wiki. Due Friday, 9/26 http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/news/080301_elephantshre w 3. Bring your textbooks, or access to your online textbooks, tomorrow!!!!!!! Interactive activity with phylogenetics (useful as review): http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/creating-phylogenetic-trees-dna-sequences Homework http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/creating-phylogenetic-trees-dna-sequences http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/news/080301_elephantshrew Phylogenetics Phylogenetics is the study of evolutionary relatedness among various groups of organisms, which is discovered through molecular sequencing and morphological data. Tucuxi Cladogram Diagram that shows relationships among organisms Analogous vs. homologous structures *Convergent evolution produces analogous structures ◦ Convergent evolution: evolution of similar features in independent evolutionary lineages ◦ Homoplases (analgous features) are when different lineages have the same solutions to ecological problems *Homologous structures are a result of common ancestry We can also use morphological differences to deconstruct evolutionary relationships Derived Ancestral Ancestral vs. derived features Ancestral characters: a character that originated in the ancestor of the taxon Derived characters: character that is an evolutionary novelty to a particular clade ◦synapomorphies: derived characters shared with taxon (ex. Hair is a synapomorphy of mammals) Molecular clock Method for estimating time required for a given amount of evolutionary change, based on the observation that some regions of genomes (genetic material of an organism/virus) evolve at constant rates The cytochrome c gene reflects a pattern of differences in DNA sequences due to mutations. The changes accumulate at a constant rate, and can be used as a molecular clock to help date evolutionary divergences. Figure 26.3 Species: Panthera pardus Genus: Panthera Family: Felidae Order: Carnivora Class: Mammalia Phylum: Chordata Domain: Bacteria Kingdom: Animalia Domain: Eukarya Domain: Archaea