* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heating Curves
Dynamic insulation wikipedia , lookup
Thermal comfort wikipedia , lookup
Space Shuttle thermal protection system wikipedia , lookup
Thermoregulation wikipedia , lookup
Passive solar building design wikipedia , lookup
Underfloor heating wikipedia , lookup
Intercooler wikipedia , lookup
Building insulation materials wikipedia , lookup
Thermal conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Heat exchanger wikipedia , lookup
Solar water heating wikipedia , lookup
Solar air conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Heat equation wikipedia , lookup
Copper in heat exchangers wikipedia , lookup
Cogeneration wikipedia , lookup
R-value (insulation) wikipedia , lookup
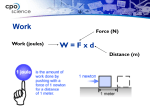
Heating Curves Phase Changes • A heating curve graphically represents the phase transitions that a substance undergoes as heat is added to it. • The plateaus on the curve mark the phase changes. • The temperature remains constant during these phase transitions. Thermal Energy = PE + KE PE or KE? • When the phase (liquid, solid or gas) does not change, the heat being absorbed is accounted for as KE and T changes • When the phase changes, the heat is accounted for as PE and T does not change Specific Heat Capacity • Different materials respond differently to energy (heat) inputs. • Specific Heat Capacity is a way to measure mathematically how materials respond to heat. Formula for Specific Heat • Q=cm∆T – Q=heat added (Joules) – C =specific heat capacity (Joules/kg*°C) – M=mass of object (kg) – ∆T = change in temperature (°C) <<<<<OR>>>>> Joules = Joules x (kg) x (°C) (kg)(°C) An Example • Find the change in thermal energy of a 10 kg container of water that warms from 10°C to 30°C . The specific heat capacity of water is 4184 J/kg°C. LESS L = List • • • • Q=? C = 4184 J/kg°C M = 10 kg ∆T = 30°C -10°C = 20°C LESS E = Equation • Q=cm∆T LESS S = Substitution • Q=cm∆T Q = (4184)(10)(20) LESS S = Solve Q = (4184)(10)(20) Q = 836,800 Joules You try… Find the change in thermal energy of 20 kg wooden chair that warms from 5°C to 28°C if the specific heat capacity of wood is 1,700 J/(kg°C). You try… Find the specific heat capacity of an unknown object if the thermal energy added is 350,000 J and the mass of the object is 10 kg and the temperature change is 8.37°C. Beyond the bend… • The earth’s surface is 70% water. Why is our discussion of specific heat capacity important as it relates to climate change?