* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download capillaries
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
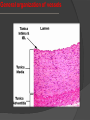
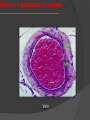
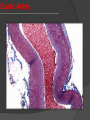
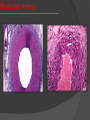
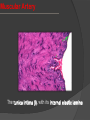
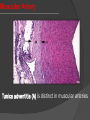
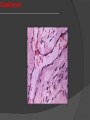
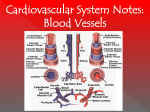
Khaleel Alyahya [email protected] Saturday November 14, 2009 Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Blood Circulation The left side of the heart pumps blood out the aorta (which is a large elastic artery) to a system of muscular arteries, arterioles then to capillaries. Blood from the arterioles enters the capillary bed where exchange of substances occurs. Blood Circulation The blood enters venules, on to small veins, medium veins, and finally the large veins that empty the venous blood back into the right side of the heart. Note: At the capillary beds, excess fluid and protein is picked up by lymphatic vessels, filtered through lymph nodes, and returned to the large veins. General organization of vessels Vessel walls are divided into 3 layers, called tunicae. 1) Tunica intima: includes the endothelium (SSE) and the underlying loose C.T. 2) Tunica media: the middle layer which contains smooth muscle and or elastic membranes. 3) Tunica adventitia: the outermost connective tissue layer composed mainly of dense irregular connective tissue. The tunica adventitia is broad and contain numerous vasa vasorum. General organization of vessels General organization of vessels The tunica intima of veins is similar to that of arteries, but the internal elastic lamina is thin or absent The tunica media is much thinner than the accompanying artery. Tunica adventitia is much thicker than tunica media. General organization of vessels Vein Arteries Elastic Arteries These are the largest arteries in the body, and include the aorta, pulmonary trunk and their major branches. This elasticity permits elastic arteries to resist the force of pressure of the heart beat. Elastic Artery Arteries Muscular (distributing) Arteries Muscular (Distributing) Arteries have the same basic structure as elastic arteries BUT the elastic tissue is reduced. The tunica media is composed of concentric layers of smooth muscle. They show a well-defined Internal elastic lamina (IEL). They may show External (outer) elastic lamina (EEL). Muscular Artery Muscular Artery Muscular Artery The tunica intima (I), with its internal elastic lamina Muscular Artery Tunica adventitia (A) is distinct in muscular arteries Capillaries Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels, and contain only a single layer of flattened endothelial cells and their basal laminae. Muscular and adventitial layers are absent. Pericytes may be present at the periphery of capillaries. Capillaries are designed to permit exchange of gas, nutrient and waste in the tissue. Connect the two sides. Capillaries Questions?