* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5, Section 2
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Coherence (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Shear wave splitting wikipedia , lookup
Stokes wave wikipedia , lookup
Wave packet wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
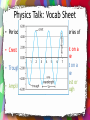
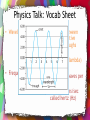
Chapter 5, Section 2 Making Waves February 10, 2014 HW: PTG #1, 2, 5-8, pg. 505-506, Due Next Wednesday/Thursday • Learning Objective: – Describe how waves carry energy – Describe how wavelength, frequency and speed of a wave are related • Success Criteria: – Observe the motion of a pulse – Calculate the speed of a wave pulse – Observe standing waves – Investigate the relationship among wave speed, wavelength, and frequency – Make a model of wave motion – Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves • Do Now: –Write LO and SC on a new left-side page –WDYS/WDYT pg. 492 WDYS? WDYT? • T-chart February 10, 2014 HW: PTG #1, 2, 5-8, pg. 505-506, Due Next Wednesday/Thursday • Learning Objective: – Describe how waves carry energy – Describe how wavelength, frequency and speed of a wave are related • Success Criteria: Observe the motion of a pulse Calculate the speed of a wave pulse Observe standing waves Investigate the relationship among wave speed, wavelength, and frequency – Make a model of wave motion – Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves – – – – • Do Now: – Grab physics books (pg. 492) – Take out your notebooks and quietly review the WDYS? WDYT? That was completed last class. Investigate: Part A • Stadium Wave • Standing Wave • Investigation 5.2 Making Waves handout Part A Big Idea Summary Answer the following on a half sheet of paper by writing down the entire sentence frame and answering in complete sentences • 1. The wave moves _____________, but people move _________ and __________. • 2. Waves are produced by neighboring ___________ moving up and down, causing the wave to move ___________. • 3. Which learning objective do your answers directly relate with? Investigate: Part B • Transverse Waves • Demo #1-2 (answer questions) demo 3-4 answer question • #6-7-in groups • #7-choose amplitude as a class – Prediction: How do you think amplitude will affect the speed of the wave? – Groups 1-2, 3-4, 5-6 different amplitudes Exit ticket • Turn in Investigation 5.2 Making Waves handout February 13, 2014 HW: PTG #1, 2, 5-8, pg. 505-506, Due Fri • Learning Objective: – Describe how waves carry energy – Describe how wavelength, frequency and speed of a wave are related • Success Criteria: – Observe the motion of a pulse – Calculate the speed of a wave pulse – Observe standing waves – Investigate the relationship among wave speed, wavelength, and frequency – Make a model of wave motion – Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves • Do Now: – How would you know if you were observing a transverse wave? February 12/13, 2014 HW: PTG #1, 2, 5-8, pg. 505-506, Due Fri • Learning Objective: – Describe how waves carry energy – Describe how wavelength, frequency and speed of a wave are related • Success Criteria: – Observe the motion of a pulse – Calculate the speed of a wave pulse – Observe standing waves – Investigate the relationship among wave speed, wavelength, and frequency – Make a model of wave motion – Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves • Do Now: – Once bell rings it needs to be quiet and people seated in their assigned seats with a text book – Read procedures #1013, pgs 495-6, SILENTLY!! – You will be getting a work habits grade today based off of following directions and remaining on task • #10-13 Demo then in groups • #14-Demo, discuss energy • #15-groups, discuss a. A transverse pulse is one in which the motion of the wave is perpendicular (90 degrees) to the motion of the particles of the medium b. As the amplitude of a transverse pulse on a spring increases, its speed remains the same c. As the frequency of a standing wave increases, the wavelength decreases and the wave velocity remains the same. January 11, 2011 HW: PTG #1, 2, 5-8, pg. 505-506, Due Wed, Bring Tissues • Learning Objective: – Describe how waves carry energy – Describe how wavelength, frequency and speed of a wave are related • Success Criteria: – Observe the motion of a pulse – Calculate the speed of a wave pulse – Observe standing waves – Investigate the relationship among wave speed, wavelength, and frequency – Make a model of wave motion – Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves • Do Now: – LO and SC reflection • Go through what we have covered so far and write page #s next to each item • How do you know you have met this success criteria or learning objective? On left side page Part B Big Ideas • Transverse Wave: • Standing Wave: • Speed of a wave=distance/time • Speed=frequency x wavelength • Frequency=#times the wave moves up and down each second • Energy travels in waves Investigate: Part C • Longitudinal Waves • Complete all sections, OK with teacher Part C Big Ideas • Compressional/Longitudinal Waves Investigate: Part D • Skip February 14, 2011 HW: PTG #1, 2, 5-8, pg. 505-506, Due Tues • Learning Objective: – Describe how waves carry energy – Describe how wavelength, frequency and speed of a wave are related • Success Criteria: – Observe the motion of a pulse – Calculate the speed of a wave pulse – Observe standing waves – Investigate the relationship among wave speed, wavelength, and frequency – Make a model of wave motion – Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves • Do Now: – Describe how wavelength, frequency, and speed of a wave are related. – Suppose you shake a long, coiled spring back and forth. Then you shake it rapidly. • Describe how the waves change as you shake the coiled spring more rapidly. • What wave characteristics (amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed) change? • What wave characteristics did not change? Physics Talk: Vocab Sheet • Waves Transfer Energy • A wave transfers energy with no transfer of mass • Example • When you throw a ball the mass and kinetic energy move from one place to another • A wave transfers only energy, no mass is moving. Physics Talk: 2 column notes • How is energy transferred? • Chemical energy in musclesmechanical energy in armkinetic energy in spring • Energy transferred from one form to another, but TOTAL energy remains the same…Conservation of Energy! Physics Talk: 2 Column notes • How do waves “add”? • They continue to travel as though the other wave never existed. • http://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=Xqo6sEt1c UE • · A B • What will this look like when the pulses meet? • After that meet? Physics Talk: Vocab Sheet • Periodic Wave • Crest • Trough • Amplitude • Repetitive series of pulses • Highest point on a periodic wave • Lowest point on a periodic wave • Height of crest or depth of trough Physics Talk: 2 Column Notes • How does amplitude relate to sound? • Large amplitudeLoud sound! • Small amplitudesoft sound • How does amplitude relate to energy? • Large amplitudeLarge amount of energy • Small amplitudesmall amount of energy Physics Talk: Vocab Sheet • Wavelength (λ) • Frequency (f) • Distance between two consecutive crests or troughs • Symbol is λ (pronounce lambda) • Number of waves per unit time • Usually waves/sec called hertz (Hz) Wavelength Practice • In the diagram below, what is the wavelength of this standing wave? • 12m Physics Talk: Vocab Sheet • Period (T) • Time required to complete one complete wave (crest-trough-crest) • Period and frequency are inversely proportionate • T=1/f • f=1/T Period Practice • What is the period if 8 waves are produced each second? • What is the period if 5 waves are produced in 10 seconds? Physics Talk: Vocab Sheet • Transverse Waves • Compressional (Longitudinal) Wave • The medium moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave • The medium moves parallel to the direction of the wave • http://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=MoVz2ENJ b8M Physics Talk: Vocab Sheet • Standing Wave • Wave pattern that remains in a constant position. • Does not go right/left, but does go up/down. • http://www.youtube. com/watch?v=03cUrk jqdE0 Physics Talk: 2 Column notes • What type of wave is sound? • Compression Wave • Air molecules get compressed and move through the air Physics Talk: 2 column notes • How can you calculate the speed of a wave? • Speed=Distance/Time • Wave speed=wave frequency x wavelength v=fλ Sample problems on pg. 502 January 12, 2011 HW: Finish Vocab Boxes • Learning Objective: – Describe how waves carry energy – Describe how wavelength, frequency and speed of a wave are related • Success Criteria: – Observe the motion of a pulse – Calculate the speed of a wave pulse – Observe standing waves – Investigate the relationship among wave speed, wavelength, and frequency – Make a model of wave motion – Distinguish between transverse and longitudinal waves • Do Now: – Finish LO and SC reflection • Go through what we have covered so far and write page #s next to each item • How do you know you have met this success criteria or learning objective? On left side page – Essential Questions Pg. 504 • What does it mean? • How do you know? • Why should you care? Essential Questions • Pg. 504 – What does it mean? – How do you know? – Why should you care? Vocabulary Activity Book Definition: Definition in YOUR words Example Picture or Equation HW: PTG #1, 2, 5-8, pg. 505-506