* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Is Insomnia?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
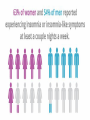
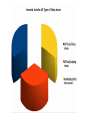
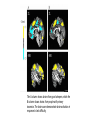
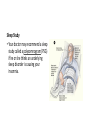
• A Sleep Disorder: Insomnia • Research Team: DESERT EAGLES • Fatih Türk, Ali Cem Uçar, Özgür Biçer • 05 May, 2017 This presentation is submitted in partial • fulfillment of the requirements for • GPC 126 • Physiological Psychology • METU-NCC • Spring 2017 The Objectives of the Presentation To show: 1. Definition of Insomnia 2. Symptoms of Insomnia 3. Who is at risk? 4. Graphs and Statistics 5. Types of Insomnia 6. Causes of Insomnia 7. Diagnosing Insomnia 8. Treatment 9. Drugs 10. Conclusion What is Insomnia? Insomnia is a sleep disorder that is characterized by difficulty falling and/or staying asleep. People with insomnia have one or more of the following symptoms: (WebMD, 2017) • Difficulty falling asleep • Waking up often during the night and having trouble going back to sleep • Waking up too early in the morning • Feeling tired upon waking • Insomnia can cause daytime sleepiness and a lack of energy. • It also can make you feel anxious, depressed, or irritable. • You may have trouble focusing on tasks, paying attention, learning, and remembering. • These problems can prevent you from doing your best at work or school. Who Is at Risk for Insomnia? Insomnia is a common disorder. It affects women more often than men. The disorder can occur at any age. However, older adults are more likely to have insomnia than younger people. People that are at risk: • Have a lot of stress. • Are depressed or have other emotional distress, such as divorce or death of a spouse. • Have lower incomes. • Work at night or have frequent major shifts in their work hours. • Travel long distances with time changes. • Have certain medical conditions or sleep disorders that can disrupt sleep. • Have an inactive lifestyle. TYPES OF INSOMNIA Primary insomnia Not directly associated with any other health condition or problem. Secondary insomnia Because of something else, such as a health condition, pain, medication they are taking or substance they are using. Acute vs. Chronic Insomnia Insomnia also varies in how long it lasts and how often it occurs. Causes of Insomnia • Significant life stress (job loss or change, death of a loved one, divorce, moving) • Illness • Emotional or physical discomfort • Environmental factors like noise, light, or extreme temperatures (hot or cold) that interfere with sleep • Some medications (for example those used to treat colds, allergies, depression, high blood pressure, and asthma) may interfere with sleep • Interferences in normal sleep schedule (jet lag or switching from a day to night shift, for example) • Severe long-term effects of insomnia could be associated with diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. Extented lack of sleep also causes earlyaging. (Joseph, 2017) Sleep is the time when the body renews and revitalizes itself; it is a time of rebalancing, detoxification, and the rebooting of the immune system. • “Based on these results, it is not surprising that someone with insomnia would feel like they are working harder to do the same job as a healthy sleeper,” (Drummond, 2013) The A column shows brains from good sleepers, while the B column shows brains from people with primary insomnia. The brain scans demonstrate brain activation in response to task difficulty. Surprising causes of insomnia Chronic Pain • Any condition that leaves you in discomfort can understandably disrupt your sleep. Certain Medications • Drugs for conditions ranging from the common cold and high blood pressure to depression and asthma can cause insomnia. Clinical Anxiety Or Depression • Our daily ups and downs can certainly keep us awake now and then, but an underlying anxiety disorder or clinical depression could be to blame if worries and concerns are consistently upsetting your sleep. (Klein, 2017) Your Eating And Drinking Habits • Despite your best intentions, you may be consistently sabotaging your own sleep with what you eat and drink close to bedtime. Neurological Diseases • People with brain conditions like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and stroke often have problems sleeping as well. Allergies • Itchy eyes and stuffed-up noses can certainly steal shut-eye on a consistent basis. In fact, about 59 percent of people with nasal allergies reported trouble sleeping due to their symptoms in a 2013 Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America survey. (Klein, 2017) How Is Insomnia Diagnosed? Medical History • To find out what's causing your insomnia, your doctor may ask whether you: • Have any new or ongoing health problems • Have painful injuries or health conditions, such as arthritis • Take any medicines, either over-the-counter or prescription • Have symptoms or a history of depression, anxiety, or psychosis Sleep History • To get a better sense of your sleep problem, your doctor will ask you for details about your sleep habits. Before your visit, think about how to describe your problems Physical Exam • Your doctor will do a physical exam to rule out other medical problems that might cause insomnia. You also may need blood tests to check for thyroid problems or other conditions that can cause sleep problems. Sleep Study • Your doctor may recommend a sleep study called a polysomnogram (PSG) if he or she thinks an underlying sleep disorder is causing your insomnia. TREATING INSOMNIA Highlights 1. Good sleep habits and a healthy diet can remedy many cases of insomnia. 2. Some sleep experts recommend light exposure for people who tend to fall asleep too early at night or wake up too early in the morning. 3. It’s important to determine whether or not an underlying issue or medical condition is causing your insomnia. Healthy lifestyle changes Often, making lifestyle changes can cure insomnia. You might want to try some of these suggestions: Go to bed when you feel tired. Use your bedroom only for sleep and sex. Activities that stimulate the brain, such as watching TV, reading, or eating, should take place outside the bedroom. Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day. Reduce the stresses in your life that are disrupting your sleep. Dont smoke • If you smoke, quit. Nicotine is a stimulant that triggers insomnia. Watch what you drink • Avoid drinking excessive amounts of alcohol. Alcohol is a sedative that may induce sleep initially, but it can disrupt deeper stages of sleep that allow your body to rest fully. Long-term heavy drinking can also trigger high blood pressure, heart failure, and stroke. Exercise • Exercising 20 to 30 minutes every day can encourage a good night’s sleep. Maintain a healthy diet • Avoid foods that are high in saturated fat, which may cause heartburn and indigestion. These foods can be hard to digest, particularly when you eat them late at night. This can make it difficult to sleep. Insomnia drugs Some of the more popular prescription sleep medications include: eszopiclone (Lunesta), which is a nonbenzodiazepine sedative ramelteon (Rozerem), which is a melatonin receptor agonist trazodone (Desyrel), which is an antidepressant of the serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor class zaleplon (Sonata), which is a nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic zolpidem (Ambien), which is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic Talk to your doctor • Try the varied treatments available for insomnia to help restore your normal sleep. Talk to your doctor and discuss which of the lifestyle changes, behavioral therapies, or medication options are right for you. What It's Like To Have Insomnia https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wwkKcqdrfGo Summary of the Presentation We have talked about • Definition of Insomnia and its symptoms • Types, causes and treatments of Insomnia • Diagnosing Insomnia • Drugs of Insomnia QUESTIONS 2 true/false 2 multiple-choice INSOMNIA is… 1. Common in men 2. Common in the elderly INSOMNIA is… 1. Common in men 2. Common in the elderly • The nurse recognizes that a client is experiencing insomnia when the client reports … I. II. III. IV. Extended time to fall asleep Falling asleep at inappropriate times Difficulty staying asleep Feeling tired after a night’s sleep Which of the followings shows that client is experiencing insomnia? A) Only I B) I, II C) I, III, IV D) All of them • The nurse recognizes that a client is experiencing insomnia when the client reports … I. II. III. IV. Extended time to fall asleep Falling asleep at inappropriate times Difficulty staying asleep Feeling tired after a night’s sleep Which of the followings shows that client is experiencing insomnia? A) Only I B) I, II C) I, III, IV D) All of them A sleep disorder in which an awake person suffers from repeated, sudden, and irresistible REM sleep attacks is known as: A) B) C) D) Insomnia Narcolepsy Somnambulism Sleep Apnea A sleep disorder in which an awake person suffers from repeated, sudden, and irresistible REM sleep attacks is known as: A) B) C) D) Insomnia Narcolepsy Somnambulism Sleep Apnea Thank you for your attention. References WebMD. (2017). An Overview of Insomnia. Retrieved from: http://www.webmd.com/sleepdisorders/guide/insomnia-symptoms-and-causes#1. Nhlbi.nih.gov. (2017). What Is Insomnia? - NHLBI, NIH. Retrieved from: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/inso. J, Dr. (2017). Results Of Insomnia - A Lack Of Sleep Can Cause - Whole Person Health. [online] Whole Person Health. Retrieved from: http://www.wholepersonhealth.com/results-of-insomnia-a-lack-ofsleep-can-cause/. Klein, S. (2017). 7 Surprising Causes Of Insomnia. [online] The Huffington Post. Retrieved from: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2015/03/09/surprising-insomnia-causes_n_6817800.html. Insomnia., (2002). IMDb, Retrieved from: http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0119375/