* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning Objectives
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
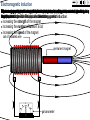
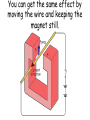
Generators • To explain how a generator works to produce electric current. • To explain the difference between alternating and direct current. Producing Electricity • Electricity is produced by generators. Key Terms You need to Understand! • Electricity is the flow of charged particles called electrons. • Current is the rate of flow of electrons. • Voltage is the push of electrons – it measures the amount of energy at a given point. How a generator works • You need three things for a generator to work: –A magnet –Coils of wire –Movement Producing electricity… • Moving a piece of wire in a magnetic field causes an electric current to flow through the wire. • This process is called electromagnetic induction. • Current produced this way is called an induced current. AUTO Electromagnetic Induction |< || >| Asthe This IfA The When galvanometer athe the stronger size can number magnet the athe magnet magnet magnetic be ofmagnet magnet the investigated magnet of moves induced moves is turns stops moves field an faster, instrument isin voltage into moving in ‘cuts’ using used, the out an acoil the though coil of the out the can there the is for size following ofof size increases, be measuring, wire, coil, is athe increased ofno conductor, ofthe the acoil, the induced pieces voltage induced polarity the induced aorby: size current of detecting, voltage aisequipment: voltage voltage induced of of voltage the the isand induced very induced isincreases, and increases, no induced, small current current voltage that voltage currents. resulting flows resulting periodically flows increases, reverses in in onea flow the and resulting larger direction. changes ofcurrent. electric current in a larger direction. current. flows This current. in the This is called opposite is called an alternating direction. electromagnetic current.induction. ● increasing the strength of the magnet ● increasing the number of turns in a coil ● increasing the speed of the magnet coil of insulated wire permanent magnet 0 galvanometer You can get the same effect by moving the wire and keeping the magnet still. How current can be increased… • Adding more turns on a coil of wire • Using stronger magnets • Moving the wire faster Direction of current • The direction of current can be changed by changing the direction… –Of the movement of wire –Of the magnetic field Dynamos A dynamo is a particular type of generator which is often used on bikes to power lights. Here the magnet is rotated instead of the coil. They dynamo is attached to a wheel so as you turn the wheels, your turning inside the dynamo. Dynamos • Current produced in a simple dynamo can flow in two ways, if it flows in the same direction and is called direct current (DC). • If it flows and keeps changing direction it is called alternating current(AC). Generators • In a generator wire goes up and down within the magnetic field. • This causes the induced current to change direction. • Current that changes direction like this is called alternating current (AC). Generators in Power Stations • Generators in power stations produce a lot of energy and need to induce a strong voltage. • To do this, electromagnets are used instead of permanent magnets, which are expensive. • Electromagnets are stronger magnets which can be switched on and off. Question 1. Put more turns of wire on the coil, spin the coil faster, use stronger magnets 2. They need to generate large currents, so they need powerful magnets and electromagnets are stronger than permanent magnets.