* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lab 14a directions
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
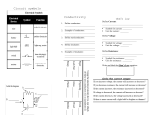
Lab 14A series vs. parallel and short circuits Set up your circuit board as shown above Record the voltage drops at the above points and answer the questions below: 1) What relationship is there among the four voltage drops you measured? 2) Is AD the same as the voltage across the batteries? What percent difference is there (if any)? 3) Compare the sum of AB, BC, and CD with AD. What percentage difference is there? Explain why there is a difference. Explain the difference in #2 if there was one. Measure the current for the three circuits above. Answer the following questions: 1. What happens to the current as more bulbs are added? Explain using Ohm’s Law 2. What happens to the other two bulbs when one bulb is unscrewed? Explain why. Add a short circuit (wire) that bypasses two bulbs and measure the current before and after. Answer the following questions: 1. Use Ohm’s Law and the concept of resistance to explain the change in current. 2. How does the current in a one-bulb circuit compare with the current through this short circuited circuit? 3. How does the resistance of a wire compare with the resistance of a bulb? 4. Directly measure the resistance of a wire (set multimeter to 200 Ω) 5. Why are short circuits dangerous? Build the following parallel circuit. Measure the following and answer the questions: 1. Compare brightness of 3 bulbs in series vs. 3 bulbs in parallel. 2. Unscrew one bulb. What happens to the others? Explain the difference between this result and the one you got in series. 3. Would you want a string of holiday lights wired in series or parallel? Why?