* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Reserve currency wikipedia , lookup
Foreign exchange market wikipedia , lookup
Purchasing power parity wikipedia , lookup
Currency War of 2009–11 wikipedia , lookup
Currency war wikipedia , lookup
Fixed exchange-rate system wikipedia , lookup
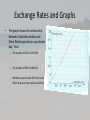
Chapter 2 Measurement 2C: TLW 1. Write numbers in scientific notation 2. Perform simple operations with numbers in scientific notation • Scientific Notation or Standard Form 𝑎 𝑥 10𝑘 , 1 ≤ 𝑎 < 10 and k is and integer a is between 1 and 10 Write in scientific notation. • 9 448 800 000 • 0.000 000 053 04 Write as a decimal number • 1.45 𝑥 10−5 • 3.016 𝑥 106 GDC and scientific notation • Use the EE button! • 870, 000 x 95, 000, 000 • 6.2 𝑥 103 8 𝑥 1012 • P. 43 #1 - 10 2D: TLW convert between International System (SI). • Base Units Quantity Name Symbol Distance Meter m Mass kilogram kg Time Second s Electric Current Ampere A Temperature kelvin K Intensity of Light Candela cd Amount of substance mole mol Derived Units– defined in terms of base units Quantity Name Area square meter 𝑚2 Volume cubic meter 𝑚3 Mass Gram Velocity meters/second Angle Symbol g Radian (𝑚 𝑠 ) 𝑚𝑠 −1 rad Some More Quantity Name Symbol Force newton N Pressure pascal Pa Energy joule J Power watt W Frequency hertz Hz Finally An Example • Density is defined as mass per unit volume. an SI unit to represent density. • A newton is defined as the force which accelerates a mass of 1 kg at the rate of 1 meter per second per second. Write as a SI unit. It wasn’t going to last long. Quantity Name Symbol SI equivalent Time minute hour min H 60 s 3600 s Mass tonne t 1000 kg Capacity liter L 0.001 𝑚3 Area hetare ha Angle degree ⁰ Temperature Celsius ⁰C 10,000 𝑚2 𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑 180 K – 273.15 Pressure millibar mb 100 Pa Distance at sea Nautical mile Nm 1.852 km Speed at sea Knot Kn 1.852 𝑘𝑚ℎ−1 Energy Kilowatt hour kWh 3.6 MJ Smaller or Larger Multiples milli m kilo k 𝟏 𝟏 𝟎𝟎𝟎 𝟎𝟎𝟎 𝟎𝟎𝟎 1 10−6 = 1 000 000 1 −3 10 = 1000 103 = 1000 mega M 106 = 1 000 000 giga G 109 = 1 000 000 000 nano N 𝟏𝟎−𝟗 = 𝜇 micro When writing the value of a measurement, the prefix used should give the value as a measure between 0.1 and 1000. Which is why one nautical mile is written as 1.852 km and not 1852 m. Conversion in Metric • K H D (l g m) d c m – King Henry drinks lime green milk dead cows make. Convert 3540 mm into ________________ meters Convert 7.14 kg into ___________ grams Non Meteric Units • Write conversion as a fraction with what you want to cancel in the denominator. • Convert 4 hours and 12 minutes into seconds • Convert 15 knots into kilometers per hour • Convert 16𝑚𝑠 −1 into 𝑘𝑚ℎ−1 • Convert 54 kWh into MJ What do you think? • Does the use of SI notation help us to think of mathematics as a “universal language”? Exercises • P. 47 #1-9, Hint for #9: Use Example 7 on page 46 2E Goal: TLW round numbers. • How is rounding numbers useful? – Population count • We use to approximate answers. • Symbol: ≈ 𝑜𝑟 = The Rules 1. Look right, if less than 5 round down 2. Look right, if greater than or equal to 5 round up • Round to the nearest 10: 48 583 5705 Stop and try these • 2E.1 p. 48 #1-4 Rounding Decimals • A traffic survey showed that 1852 cars carried 4376 people. Which is more appropriate to write people per car? • 2.362 850 972 or 2.4 • Why? Where to round? • You will be given a specific decimal place (d.p.) or significant figure (s.f.) • Round to 1 decimal place (1 dp) 3.27 Round to 2 dp: 6.3829 Calculate to 2 dp • Use your GDC • (2.8 + 3.7)(0.82 – 0.57) • 18.5 − 12.2−4.3 5.2 Try These • P. 49 – 50 # 1-3 Significant Figures (sf) • To round off to n significant figures look at (n+1)th digit 1. If (n + 1) digit is 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 don’t change the nth digit 2. If (n + 1) digit is 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 increase nth digit by 1 Delete all digits after nth digit, replacing with 0s if necessary. • Round to 2 s.f.: 7.182 • Round to 2 s.f.: 0.00132 • Round to 1 s.f.: 423 • Round to 3 s.f.: 4.057 • IB exams round to 3 s.f. unless otherwise stated. Exercises • P.51 #1-8 3H: Goal: TLW find error and percentage error. • Approximation is close but NOT equal to the true value. • Estimation is a value found by judgment/prediction instead of using accurate measurement. • How do we account for this difference? Error • Estimate the product: 38.7 x 5.1 • Find the true value: • What is the approximation? • Error is the difference between our measurement and the actual value. – Error = 𝑉𝐴 − 𝑉𝐸 Percentage Error • Usually error is represented as a percentage. – Look at the size of the error and ignore the sign. – Percentage Error: 𝐸 = 𝑉𝐴 −𝑉𝐸 𝑉𝐸 𝑥100% • You estimate a fence length to be 70 m whereas its true length is 78.3 m. Find to 1 d.p. – Error – Percentage Error • Alan wants to lay carpet on his 4.2 m x 5.1 m lounge room floor. He estimates the area of the lounge room by rounding to the nearest meter. • Estimate the area. • The carpet costs $39 per 𝑚2 . Find the cost using Alan’s estimate. • Find the actual area. • Find the percentage error. • Will Alan have enough carpet to cover his lounge? • How should he have rounded? Exercises • P. 22 #1-7 2J: TLW convert between different currencies. • Currency is the money of a country. • When you go to a different country with different currency you must exchange it. • Exchange Rate = how much your money is worth in a foreign currency. – Rates are published and change all the time. – Simple Currency Conversions : no commision and no fees to pay for exchanging currency. Exchange Rates • 1 British pound (GBP) = 1.65 Australian dollar (AUD) • Convert 40 GBP to AUD • Convert 500 AUD to GBP Exchange Rate Table Currency converting to Currency converting from Hong Kong (HKD) China (CNY) Japan (JPY) Hong Kong (HKD) 1 0.817 9.885 China (CNY) 1.225 1 12.106 Japan (JPY) 0.101 0.083 1 That means 1 CNY = 12.106 JPY • Convert 2000 CNY to JPY – Just like other conversions write as a fraction. Hong Kong (HKD) China (CNY) Japan (JPY) Hong Kong (HKD) 1 0.817 9.885 China (CNY) 1.225 1 12.106 Japan (JPY) 0.101 0.083 1 USD GBP CHF USD 1 0.640 0.91 GBP 1.56 1 1.43 CHF 1.10 0.70 1 Write down the exchange rate from CHF to USD. Exchange 3000 USD to GBP Write down the exchange rate from USD to CHF Exchange 10 000 francs to pounds Exchange Rates and Graphs • The graph shows the relationship between Australian dollars and Great Britain pounds on a particular day. Find – The number of AUD in 250 GBP – The number of GBP in 480 AUD – Whether a person with 360 AUD could afford to buy an item valued at 240 GBP. Exercises • P. 65-66 #1 - 5