* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 Compounds, Naming, Formula Writing
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Bose–Einstein condensate wikipedia , lookup
Ionic liquid wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
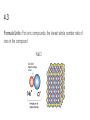
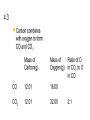
Unit 4 Compounds, Naming, Formula Writing Accelerated Chemistry 4.1 Molecule: Smallest unit of a covalently bonded compound. Molecular Compounds: Compounds composed of nonmetal atoms and formed by the sharing of valence electrons. 4.1 Characteristics of Molecular Compounds Representative Particle Molecule Type of Elements Nonmetals Physical State Solid (C12H22O11), Liquid (H2O), Gas (CO2) Melting Point Low (Usually Below 300°C) 4.1 4.2 Ions: atoms or groups of atoms that have a positive or negative charge. Cation: An ion with a positive charge, formed by the loss of electrons, usually metals. Ex. Na+ Anion: An ion with a negative charge, formed by the gain of electrons, usually nonmetals. Ex. ClIonic Compounds: Compounds composed of metals and nonmetals formed by the transfer of valence electrons. 4.2 Characteristics of Ionic Compounds Representative Particle Formula Unit Type of Elements Metals and Nonmetals Physical State Solid (ex. NaCl) Melting Point High (Usually Above 300°C) 4.3 Chemical Formula: Shows the kinds and numbers of atoms in a compound Diatomic Elements: 7 nonmetallic elements exist as diatomic molecules I Bring Clay For Our New House I2, Br2, Cl2, F2, O2, N2, H2 4.3 Molecular Formulas: shows the kinds and numbers of atoms present in a molecule of a compound H2O 4.3 Formula Units: For ionic compounds, the lowest whole number ratio of ions in the compound NaCl 4.3 The Law of Definite Proportions In samples of any chemical compound, the masses of the elements are always in the same proportions. 4.3 4.3 The Law of Multiple Proportions Whenever 2 elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. 4.3 4.4 Monatomic ions: ions consisting of only one atom. Ionic Charges of Representative Elements Group 1 Group 2 Group 13 Li+ Na+ K+ Rb+ Cs+ Be2+ Mg2+ Ca2+ Sr2+ Ba2+ Al3+ Ga3+ Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Group 17 N3P3As3- O2S2Se2- FClBrI- Group 18 4.4 Many of the transition metals have more than one charge. You must know the charges and include the charge with Roman numerals in the name. 4.4 4.4 Polyatomic Ions: ions composed of more than one atom. Know the names, formulas, and charges for 18 of these ions. 4.4