* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Light
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
A Brief History of Time wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
History of optics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
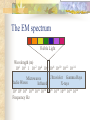
Light Chapter 27 and 28 What is light? The only thing you can see. Most objects you see reflect light from some other source. If you remove the light source, the object cannot be seen. However some objects can also produce their own light (fire, light bulbs). Light is an electromagnetic wave (EM wave or radiation) Electromagnetic waves need no medium to travel through, but if they have a medium it will effect the speed. All electromagnetic waves have an oscillating electric field and a magnetic field at right angles to each other. Frequency and wavelength of light Frequency of light corresponds to color. Visible light- what we can see, spectrum goes from red (lowest frequency) to violet (highest frequency) The colors follow the order: ROY G BIV Red orange yellow green blue (indigo) violet Other types of EM radiation There are more types of electromagnetic waves, however, if the frequency is outside of the visible range the waves are invisible to the human eye. The wave with a frequency just higher than violet is called ultraviolet, the frequency just below red is called infrared. What are infrared and ultraviolet used for? Ultraviolet lights are used as black lights, to sterilize things, and are used in tanning beds. Infrared are used as warmers (heat lamps) and for thermometers (infrared cameras). They are both invisible to the naked eye. Both lights also have visible light mixed in so you know it is on. The EM spectrum Visible Light Wavelength (m) 104 102 1 10-2 10-4 10-6 10-8 10-10 10-12 10-14 Ultraviolet Gamma Rays Microwaves Radio Waves Infrared X-rays 104 106 108 1010 1012 1014 1016 1018 1020 1022 1024 Frequency Hz The speed of light People used to think the speed of light was infinite when all conventional speed tests failed since the light was so fast. Michelson devised an experiment to test the speed of light in 1880. All electromagnetic waves travel at the fastest speed known to man. The symbol for the speed of light is c. c =3.00 x108 m/s How fast is that? Someone from Copley decided they had to be the first to hear a concert. They went to LA to see it, however, it was also being broadcast by HBO (TV waves are electromagnetic). Los Angeles is 3,800,000 m from Copley, but we will double that distance to 7,600,000 m since the signal has to go by way of satellites. If the student has good seats, 10. m from the speakers (the speed of sound is 345 m/s), and physics students in Copley watch the concert on HBO who hears it first? Answer Student in LA v = d/t 345 m/s = 10 m /t t = .029 s Students in Copley 3x108 m/s = 7,600,000 m / t t = .025 s These students hear it faster Yes, light is really that fast. If it were a straight path, light could go completely around the planet in 0.13 s For most practical purposes the speed of light is instantaneous on the planet Earth Homework Read section 27.1, 27.2 and 27.3 Pg 548 1-8; 24-25