* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain (Ch 11) keynotes 08--1st
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
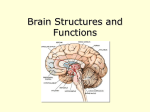
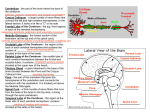
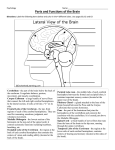
CNS & PNS Ch. 11 CNS = brain and spinal cord The brain is the largest and most complex part of the nervous system. It is composed of about 1011 neurons ( 100 billion ) Brain made up of -----> cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem and ! ! ! ! ! ! cerebellum The brain is protected by the bony skull and the spinal cord is protected by the vertebral column. Below these bony coverings of the CNS are membranes between the bone and the soft tissue to protect the CNS. These membranes are called meninges. Meninges have 3 layers : dura mater, arachnoid mater and the pia mater ( see fig 11.1 / 11.2 ) The dura mater is the outermost layer. Between the arachnoid and the pia mater is a space which contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF helps protect and nourish the CNS by maintaining a stable internal environment and absorbing forces to the brain or spinal cord. Itʼs this fluid that bacteria and/or viruses invade causing spinal meningitis, which is an inflammation of the meninges. A ”spinal tap” (Fig. 11A / 11B) is a method used to remove CSF and check for abnormalities in the fluid that may indicate an injury to the CNS. The brain is divided into 5 major divisions, each consisting of a variety of parts. The following Table lists these 5 divisions and some of the part associated with each. Brain Divisions //////////////////////////////////////// Text External Brain Brain Region Location Frontal lobe Area associated with the frontal bone of the skull Occipital lobe Area associated with the occipital bone of the skull Parietal lobe Area of the brain associated with the parietal bone. Its between the frontal and occipital lobes Temporal lobe Area associated with the temporal bone of the skull Limbic lobe Only lobe of the brain which is located on the inside of the brain External Brain Brain Region Location Longitudinal fissure Deep groove that goes the length of the brain. Separates the left & right hemisphere Lateral sulcus fissure Deep groove that divides the temporal lobe with the rest of the body. On lateral side of brain Sulcus Little grooves of the brain (sulci) Gyrus ( Convolutions ) Little ridges found on the brain (gyri) Cerebellum Located mainly inferior to the occipital lobe of the brain Pons First big bulge of the brainstem Medulla oblongata A smaller bulge, inferior to the pons Sagittal View of Brain Brain Structure Brief Description Cerebrum Major part of the brain. It consists of folds (gyri) and valleys (sulci) Corpus callosum Curved, elongated white matter connecting the 2 hemispheres together Lateral ventricle This is a cavity filled with fluid. It is located near the corpus callosum Choroid plexus A group of cells that are located near the corpus callosum. They produce cerebrospinal fluid Pituitary gland Small gland located inferior and connected to the hypothalamus Sagittal View of Brain Brain Structure Brief Description Limbic lobe Lobe which is an elongated gyrus located immediately superior to the corpus callosum Thalamus General area located inferior to the corpus callosum Hypothalamus General area located inferior and anterior to the thalamus Midbrain Located between the pons and thalamus Various Brain Structures & their Functions Frontal lobe Controls many of the fine motor movements (muscle movement) Important in higher level thinking Occipital lobe Involved in the interpretation of vision Parietal lobe Involved in the interpretation of all senses except hearing, smelling and vision (Important in touch, pressure, temperature and pain involving the skin) Temporal lobe Involved in the interpretating odors and hearing (Also help remember visual scenes & music) Limbic lobe Involved in long-term memory, emotional experiences and feelings Various Brain Structures & their Functions Cerebrum Important in higher level thinking Corpus callosum Group of nerves connecting the 2 hemispheres of brain together. It also provides communication between the 2 hemispheres. Instructions from the cerebrum tells the body to start walking. This info is sent to the cerebellum to carry out this task. The cerebellum coordinates skeletal muscle movement. Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Pons Controls the rhythmic pattern of the heart and breathing. Also important in causing one to sneeze/cough in order to expel irritants thereby protecting the lungs. Alters the rhythmic pattern of heart rate & breathing. Midbrain Controls muscle tone, also keeps us “alert” Thalamus Acts as a relay station, by taking external info and sending it to various parts of the cerebrum for storage. Consists of nerves that are involved in detection of thirst. Also involved w/ various behavior characteristics. Hypothalamus