* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Theory of Plate Tectonics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
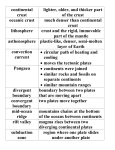
The Theory of Plate Tectonics (tectonicus-building) Earth’s lithosphere (the crust and the upper mantle) is broken into separate sections called plates. The plates fit closely together along cracks in the crust. They carry the continents, or parts of the ocean floor, or both. The geological theory of plate tectonics states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in constant, slow motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle. Remember, a scientific theory is a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations The theory of plate tectonics explains the formation, movement, and subduction of Earth’s plates. The fluid in the Earth’s mantle is actually molten (melted) rock. As the molten rock is heated it becomes less dense and therefore, begins to rise in a convection current, and push on the plates at the top of the Earth’s mantle. These lithospheric plates float on top of the asthenosphere (the soft layer of mantle) which allow them to move. A convection current is the transfer of heat within a fluid. As the plates move, they produce changes in Earth’s surface, including volcanoes, mountain ranges, and deep-ocean trenches. The edges of different pieces of the lithosphere meet at lines called plate boundaries. Faults—breaks in Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other—form along these boundaries. There are three types of plate boundaries: transform boundaries, divergent boundaries, and convergent boundaries. A transform boundary is a place where two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions. Earthquakes occur frequently along these boundaries. The place where two plates move apart, or diverge, is called a divergent boundary. Most divergent boundaries occur at the mid-ocean ridge. When a divergent boundary develops on land, two slabs of Earth’s crust slide apart. A deep valley called a rift valley forms along the divergent boundary. Magma from within the mantle rises and then cools off to form new sea floor in a process called sea floor spreading. The place where two plates come together, or converge, is a convergent boundary. When two plates converge, the result is called a collision. When two plates collide, if they are of different densities, one will sink under the under. This is the process of subduction. Oceanic crust is more dense than continental crust resulting in the oceanic crust subducting beneath the continental crust. The plate that is subducted is then crushed by the weight from the plate on top of it and it melts. Eventually, volcanic mountains can form on the shore line. When two plates carrying oceanic crust meet at a trench, the plate that is less dense dives under the other plate and returns to the mantle. The result can be the formation of a volcanic island arc. When two plates carrying continental crust collide, subduction does not take place because both plates are mostly low-density granite rock. Instead, the plates crash head-on. The collision squeezes the crust into mighty mountain ranges. The plates move at amazingly slow rates, from about 1 to 10 centimeters per year which can be observed using a GPS (global positioning satellite). The theory of continental drift says that they have been moving for tens of millions of years. The theory continues to say about 260 million years ago, the continents were joined together in the supercontinent Pangaea. Then about 225 million years ago, Pangaea began to break apart and that. since then, the continents have moved to their present locations. Name: ____________________________ The Theory of Plate Tectonics Date: _______ Class: ______ Seat #_____ 1. According to theory, the Earth’s crust is broken into sections called ____________________. 2. What is a scientific theory? ______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What are some of the things that can be on these plates? ______________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What does the theory of plate tectonics say? _________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. What does the word tectonics mean? _______________________________ 6. What causes the plates to move? _______________________________________________ 7. What is a plate boundary? _____________________________________________________ 8. What is a fault? ______________________________________________________________ 9. Name the three types of boundaries. ___________________________, __________________________, and __________________________ 10. What is the movement of the plates at a transform boundary? _______________________________________ 11. What occurs at transform boundaries? ________________________________________________ 12. Which direction are the plates moving at divergent boundaries? _____________________________________ 13. Which direction are the plates moving at convergent boundaries? ____________________________________ 14. Where are most divergent boundaries found? ____________________________________________________ 15. When two plates pull apart at a divergent boundary, it forms a valley called a ___________ valley. 16. The process where magma rises in between plates, cools, and forms new rock that makes up new sea floor is called _________________________________ 17. What is the result when two plates converge? ___________________________ . 18. At a convergent boundary the more dense plate will sink underneath the less dense plate in a process called _________________________. 19. Which is more dense oceanic or continental crust? _______________________________ 20. True or False? Two plates with continental crust will converge and one will sink under the other forming a trench. 21. What forms when two plates with continental crust converge (collide)? ________________________ 22. What forms when continental crust converges with oceanic crust? __________________ and ________________________________ 23. What forms when oceanic crust converges with oceanic crust?___________________ and ___________________________________ 24. Why would some oceanic crust be more dense than other oceanic crust? _________________________________ 25. At what rate are tectonic plates moving? _____________________________________________________ 26. What is used to get this information? ______________________________________________ Review; Fill in the boxes. Look at the arrows. Name the boundary and what forms there. Use these words; volcanic island arc trench mountains seafloor spreading mid ocean ridge earthquakes coastal volcanoes (arc) Where would you see collision? Where would you see subduction? Write it in the box? _______________ boundary ________________boundary _________________boundary __________________boundary