* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weathering and Erosion Activities
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Landslide mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary rock wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
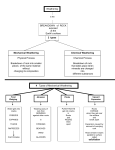
Name: _______________________________________________________ Period: ___________ Weathering and Erosion Activities Part 1 – Broken Rocks Weathering causes the disintegration of rock near the surface of the earth. Plant and animal life, atmosphere and water are the major causes of weathering. Weathering breaks down and loosens the surface minerals of rock so they can be transported away by agents of erosion such as water, wind and ice. There are two types of weathering: mechanical and chemical. Observe the sugar cube – describe its features below: ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 1. Take 1 sugar cube and put it into the container. 2. Shake vigorously for 30 seconds. Observe the sugar cube – What does the sugar cube look like now? What happened as a result of the shaking? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 1. What does the sugar cube represent? ______________________________________________________ 2. Which type of weathering was this an example of? ______________________________________________________ 3. What are ways that this type of weathering can occur? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Part 2 – Bubbling Rocks Certain rocks with carbonate compounds erode or dissolve when they come in contact with acidic chemicals. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere sometimes can produce rain that is slightly acidic. Over time, this acid rain erodes rocks. You can see it happen quickly if you use vinegar, which is a much stronger acid than acid rain. 1. Place a piece of chalk into the beaker. 2. Add 50 mL of vinegar. Observe the chalk in the beaker – describe its features below: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Observe the chalk outside of the beaker – describe its features below: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 1. What does the chalk represent? _______________________________________________________ 2. What does the vinegar represent? _______________________________________________________ 3. Which type of weathering was this an example of? ______________________________________________________ 4. What are ways that this type of weathering can occur? _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ Part 3 – Sediments on the Move Rocks can be broken down by either mechanical or chemical weathering. As a result sediments and tiny pieces of rock are created. So, where do all the tiny pieces of rock and sediment end up? 1. Spread out the sand on the bottom of the pan, leaving the bottom 3 inches uncovered.. 2. Elevate the pan on one end – use your binders to prop up the pan. 3. Slowly pour the water onto the sand from the elevated end. Observe what happens to the sand as the water moves over the surface. ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 1. What landform / feature is created as a result of the water? _______________________________________________________ 2. What was carried by the water to the bottom of the pan? _______________________________________________________ 3. What process is this an example of? _________________________ 4. What are other ways that sediments can be moved? _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________