* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bones anatomy day 1 skull
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
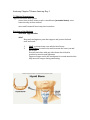
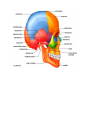
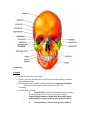
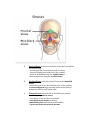
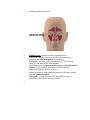
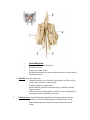
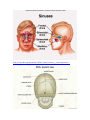
Anatomy Chapter 7 Bones Anatomy Day 1 7.5 Skeletal Organization approx 206 bones adult- varies suture lines in skull- some people- sutural bones (wormian bones) extra bones develop in these sutures. extra small sesamoid bones may dev in tendons. Divisions of the Skeleton Axial and Appendicular Axial Bony and cartilaginous parts that support and protect the head neck and trunk. 1. 2. Skull- cranium- brain case and the facial bones. Hyoid Bone- located in the neck between the lower jaw and the larynx. Does not articulate with any other bones but is fixed in position by muscles and ligaments. Supports tongue and is the attachment for certain muscles that help move the tongue during swallowing. 3. Vertebral Column- vertebrae- separated intervertebral discs. Central axis of skeleton. Sacrum- distal end, 4 vertebrae fused together, part of the pelvis. Coccyx-a small tailbone formed by the fusion of 4 bones attached to the end of the sacrum. 4. Thoracic cage-protects organs of thoracic and upper abdominal cavity. 12 pairs of ribs- articulate posteriorly with the thoracic vertebrae. Sternum-breastbone- ribs attached anteriorly. Appendicular Consists of bones of the upper and lower limbs and the bones that anchor the limbs to the axial skeleton. 1. 2. 3. 4. pectoral girdle- scapula, clavicle upper limb- humerus, radius and ulna, carpals, metacarpals phalanges. Pelvic girdle Lower limb- femur, tibia, fibula, patella, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges. Know Table of terms Used to Describe Skeletal Features 7-2 in your book. 7.6 Skull 22 bones that, except for the jaw are firmly interlocked along sutures. 8 of the interlocked bones make up the cranium. 14 form the facial skeleton. Mandible- lower jawbone- movable bone held to the cranium by ligaments. Orbit of eye- formed by cranial and facial bones. Cranium Encloses and protects the brain. Surface provides attachments for muscles that make chewing and head movements possible. Some cranial bones contain air filled cavities called paranasal sinuses. Reduce wt of skull and increase intensity of voice by resonance. 8 bones of the cranium • 1. Frontal bone- anterior portion above eyes, includes forehead roofs of nasal cavity, roofs of eye sockets. • Supraorbital foramen or notch-hole thru which blood vessels and nerves pass to the tissues of the forehead. • • 2 Frontal sinuses—above each eye near midline. 2. Parietal Bone- located on each side of the skull just behind the frontal bone. - each shaped like a curved plate with 4 corners. - form the bulging sides and roof of the cranium. - fused at the midline along the sagittal suture. -meet frontal bone along the coronal suture. 3. Occipital Bone- joins the parietal bones at the lambdoid suture. - forms the back of the skull and the base of the cranium. -Foramen Magnum-large opening at base where base of brainstem connects with spinal cord. 4. Temporal bone-on each side of the skull joins parietal bone along a squamous suture. - form parts of side and base of cranium. -external acoustic meatus- auditory. -mandibular fossa-articulates with mandible. -2 processes below the acoustic meatus- a) Mastoid process (rounded)-provides attachment for certain muscles of the neck. The mastoid may become infected. This tissue in this region of the temporal bone contains number of interconnected air cells lined w/ mucous membranes that communicate with the middle ear. Microorganisms from an infected middle ear (otitis media) can spread into air cells, causing infection and inflammation, called mastoiditis. The danger is that it may spread to nearby membranes that surround the brain. b) Styloid processes (Pointed)-anchors muscles assoc w/tongue and pharnyx -Zygomatic process-projects anteriorly from temporal bone-area of acoustic meatus. . joins temporal process of Zygomatic bone- cheekbone- Zygomatic arch. 5. Sphenoid Bone- helps to form base of cranium, sides of skull, floors and sides of orbits. - along midline w/in cranial cavity forms saddle shaped sella turcica - holds pituitary gland. • • • contains 2 sphenoid sinuses. • 6. • • • • • • • • Ethmoid Bone- located in front of sphenoid bone. Consists of 2 masses-one on each side of the nasal cavity. Joined by thin cribiform plates (horizontally) A perpendicular plate projects downward for the cribiform plates to form most of the nasal septum. Scroll shaped plates-superior nasal concha and middle nasal concha- project inward; these plates support mucous membranes that line the nasal cavity. Lateral portions of ethmoid bone contain air cells that together form the ethmoid sinuses. Crista galli- - triangular process of ethmoid bone where membranes that enclose the brain attach. • • • • • Facial Skeleton Consists of 13 immovable bones Movable jawbone Form basic shape of face Provide attachments for muscles that move the jaw and control facial expressions. • 1. Maxillae-form the upper jaw. o Compose anterior roof of mouth- hard palate, the floors of the orbits, sides and floor of nasal cavity. o Contain sockets for upper teeth. o Inside maxillae, lateral to the nasal cavity- maxillary sinuseslargest sinuses. o Anterior portion of hard palate- palatine process (cleft palate) incomplete fusion of palatine processes. o 2. Palatine bone- located behind the maxillae-horizontal portions form the posterior section of the hard palate and nasal floor cavity. Perpendicular portions form the lateral walls of the nasal cavity. 3. 4. Zygomatic bones- responsible for prominences in cheeks below to the sides of the eyes. o Help form lateral walls and floors of the orbits. o Each bone has a temporal process, which extends posteriorly to join the zygomatic process of the temporal bone. Lacrimal bone-thin scale like, located in medial wall of each orbit, tear ducts. 5 Nasal Bones-form Bridge of nose-attachments for cartilaginous tissues that form the shape of the nose. 6 Vomer Bone-located along midline with nasal cavity, posteriorly joins perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone and form the nasal septum. 7 Inferior nasal concha-notes in ethmoid bone section 8 Mandible-lower jawbone, horizontal, horseshoe shaped body. Only movable bone of skull. Know Table of Cranial Bones in textbook. Know table of Bones of the Facial Skeleton in textbook. http://www.bir.org.uk/media/76496/cranial_sutures___craniosynostosis__ka_eley__f_sheerin__d_johnson__final_.pdf