* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biosafety-Post-Exp-SOP-HCV - UCLA Office of Environment
Survey
Document related concepts
2015–16 Zika virus epidemic wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
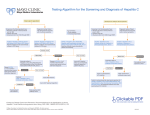
Hepatitis C Virus Post Exposure Plan SOP 501 Westwood Plaza, 4th Floor • Los Angeles, CA 90095 Phone: 310-825-5689 • Fax: 310-825-7076 • www.ehs.ucla.edu Date: PI Name: Name of Virus: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Known Mode of Transmission: Blood or sexual exposure Signs and Symptoms which might be anticipated if exposed to this virus Hepatitis C Virus Hepatitis (HCV) is a single stranded, small, positive sense RNA, enveloped virus. The primary routes of infection are parenteral or sexual exposures. Healthcare worker needlestick exposures to infected blood have been estimated to have 2 to10% chance of infection. About a quarter of infected persons clear the infection, and the rest develop chronic infection that is associated with a long term risk (over years or decades) for hepatic cirrhosis and cancer. After exposure, the incubation period before detectable infection ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months. Acute infection may be asymptomatic, or associated with mild and nonspecific symptoms including decreased appetite, fatigue, nausea, muscle/joint pains, and weight loss. Less commonly, acute infection may be associated with serious liver dysfunction and jaundice. However, with monitoring and early treatment if infection develops, the prognosis for clearing the infection is good. Risk Assessment Identify genotype of HCV in the exposure if known. a. What is the effect of the genotype on the virulence of the HCV? Identify source of HCV exposure (human body fluid or laboratory culture) If exposed to a laboratory culture, describe cell type (e.g. primary human hepatocyte cultures, Huh-7) a. 1. 2. 3. 4. Any other risks associated with the cells (e.g. HIV status of primary human cell cultures, other potential bloodborne pathogens, modifications of cell line)? Definition of Exposure Direct skin, eye or mucosal membrane exposure to the virus, Parenteral inoculation by a syringe needle or other contaminated sharps (needlestick), Ingestion of liquid suspension of an infected material or by contaminated hand to mouth exposure, Inhalation of infectious aerosols. EH&S Biosafety Program: SOP for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (rev 08/12) Page 1 of 4 NOTICE TO LAB STAFF 1. Remove exposed PPE taking care to avoid contact of unexposed areas to infectious agents on the PPE. 2. Inform others in one area about any biohazardous materials out of containment to prevent further exposure. If possible, contain with absorbent materials and decontaminate with bleach, and seal off the site. ALL exposed individuals should leave the area. 3. Immediately wash/clean the area of exposure/cut/puncture with soap thoroughly for 5 minutes. For mucous membrane exposure, flush the exposed membrane with the eye wash continuously for 5 minutes. 4. After wash, immediately proceed to receive medical treatment. Take this entire copy of the SOP with you! For Graduate students and staff, report to: Occupational Health Office: 310-825-6771 (See maps on page 4) Open 7:30 am- 4:30 pm Mon – Fri Located in 67-120 CHS (6th floor 7th corridor room 120) For undergraduate students, report to : Arthur Ashe Center: 310-825-4073 (See maps on page 4) Open 8:00 am- 5:00 pm Mon – Thurs: 9:00 am – 4:00pm Fri Located in next to the John Wooden Center After hours, weekends and holidays, report to: UCLA emergency Med: 310-825-2111 (See maps on page 4) Always open Located in the UCLA Ronald Reagan Medical Center 5. Post exposure prophylaxis must be initiated within 2 hour of exposure since other bloodborne pathogens may be involved 6. Give health care provider (HCP) information about the exposure and inform them that baseline Hepatitis C Virus serology and Hepatitis C Virus plasma quantitative RNA should be sent as per the UCLA IBC. 7. If the exposure was to primary human materials, then other human pathogens (HIV, Hepatitis B Virus, etc) should be considered. 8. Inform HCP of any medical conditions or drug treatment that they currently have or take. The HCP must have this information to evaluate and form proper post treatment evaluation. 9. After medical care, ensure that the incident is immediately reported to Biosafety ([email protected] or x63929) EH&S Biosafety Program: SOP for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (rev 08/12) Page 2 of 4 Guidance and Recommendation to HCP for Hepatitis C Virus from the UCLA Institutional Biosafety Committee Urgent care is required The Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) used in this research protocol is _______________ derived and _______________ genotype. The HCV used in this research protocol has been genetically modified with the following insert DNAs: __________________________ ___________________________ The anticipated biological effects of the HCV genotype used in this research protocol include: __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ The exposure to HCV resulted from exposure to the following materials (i.e. human blood, human cell culture [please specify cell type], animals infected with HCV, etc.): __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ Refer to the attached recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for post exposure evaluation and follow-up testing. “Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational Exposures to HBV, HCV, and HIV and Recommendations for Postexposure Prophylaxis.” MMWR Weekly Report. June 2001 (50), 1-52. (http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/PDF/rr/rr5011.pdf) Management of Exposures to HCV (pages 21-23, 45-46) Approved by ____________________________ EH&S Biosafety Program: SOP for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (rev 08/12) Page 3 of 4 Maps of Treatment Centers Arthur Ashe Center Occupational Health Ronald Reagan ER EH&S Biosafety Program: SOP for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (rev 08/12) Page 4 of 4