* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infection Prevention and Control Speaker
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Hookworm infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
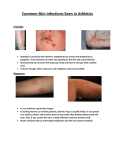
INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL In-service Training Guide INFECTION CONTROL What is an infection? DEFINITION • Infection - is the invasion of a host organism's bodily tissues by disease-causing organisms, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce. - Infections are caused by microorganisms such as viruses, prions, bacteria, and viroids, and larger organisms like macroparasites and fungi. HOW DO WE STOP IT? THE SIX LINK CHAIN OF INFECTION How a pathogen is transmitted from one person to another LINK 1 Causative agent – pathogen or infectious microorganism • Bacteria • Viruses • Mold • Fungi LINK 2 Reservoir – Place where pathogen lives • Lungs • Blood • Digestive Tract • ETC LINK 3 Portal of Exit – Any body opening on infected person • Nose • Mouth • Eyes • Cut in Skin • Urethra/Anus LINK 4 Mode of Transmission – How the Pathogen travels from one person to the next • Air • Hands • Other Surfaces LINK 5 Portal of Entry – Any body opening on uninfected person • Nose • Mouth • Eyes • Cut in Skin • Urethra/Anus LINK 6 Susceptible Host – an uninfected person STOP THE BUGS • Cleansing • Disinfecting • Sterilizing No Sharing Bag Hazardous Waste Linen Handling LINEN HANDLING • Bag at the point of use • Minimum agitation • Do not sort or prerinse in resident care areas • Use PPE when sorting No damp linen left overnight Hot water above 160°for 25 minutes HAND HYGIENE: When to Wash • When coming on duty • Before and after direct resident contact • Before and after performing any invasive procedure • Before and after entering isolation precaution settings • Before and after assisting with personal care • Before and after handling peripheral vascular catheters and other invasive devices • Before and after inserting indwelling catheters Before and after changing a dressing Upon and after coming in contact with a resident’s intact skin After blowing or wiping nose After handling soiled linen After handling soiled equipment or utensils After removing gloves or aprons After completing duty HAND HYGIENE: Use Soap and Water • • • • • • When hands are visibly soiled Before and after eating or handling food Before and after assisting a resident with meals After personal use of the toilet After contact with a resident with infectious diarrhea After performing your personal hygiene HAND HYGIENE: How to wash • Wet hands first with clean, running warm water • Apply the amount of product recommended by the manufacturer to hands • Rub hands together vigorously for a t least 15 seconds covering all surfaces of the hands and fingers • Rinse hands with water • Dry with disposable paper towel • Turn off the faucet with disposable paper towel. STANDARD PRECAUTIONS Use with everybody Wear gloves Handle used equipment with care Dispose of needles properly Wear face mask & eye protection when necessary TRANSMISSION BASED PRECAUTIONS • Airborne • Contact • Droplet Infectious Disease Prevention Strategies Routinely using barriers (such as gloves and/or goggles) when anticipating contact with blood or body fluids. Immediately washing hands and other skin surfaces after contact with blood or body fluids. Carefully handling and disposing of sharp instruments during and after use. Source: CDC: Occupational HIV Transmission and Prevention Among Health Care Workers REMEMBER…. IF IT’S WET AND NOT YOURS DON’T TOUCH IT!! WASH YOUR HANDS!! WASH RESIDENTS’ HANDS!! BAG IT!! CLEAN IT!! F441 INFECTION CONTROL F441 ESTABLISH A PROGRAM IN WHICH THE FACILITY – • Investigates, controls, and prevents infections in the facility • Decides what procedures, such as isolation, should be applied to an individual resident; and • Maintains a record of incidents and corrective actions related to infections. INFECTION CONTROL F441 PREVENTING SPREAD OF INFECTION – • When the Infection Control Program determines that a resident needs isolation to prevent the spread of infection, the facility must isolate the resident. • The facility must prohibit employees with a communicable disease or infected skin lesions from direct contact with residents or their food, if direct contact will transmit the disease. • The facility must require staff to wash their hands after each direct resident contact for which hand washing is indicated by accepted professional practice. INFECTION CONTROL F441 LINENS • Personnel must handle, store, process and transport linens as to prevent the spread of infection. MORE TO KNOW Remember: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention…… “Clean Hands – Save Lives” YOUR TURN….. Questions? Comments? Concerns? Thank you! For all that you do to prevent the spread of infections in our home. Arkansas Innovative Performance Program (AIPP) 1020 W 4th Street, Suite 430 • Little Rock, AR 72201 877-375-5700 • (Fax) 501-375-5926 [email protected] • aipp.afmc.org arkansasculturechange.com nhqualitycampaign.org THIS MATERIAL WAS PREPARED BY THE ARKANSAS FOUNDATION FOR MEDICAL CARE INC. (AFMC) UNDER CONTRACT WITH THE ARKANSAS DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN SERVICES, DIVISION OF MEDICAL SERVICES. THE CONTENTS PRESENTED DO NOT NECESSARILY REFLECT ARKANSAS DHS POLICY. THE ARKANSAS DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN SERVICES IS IN COMPLIANCE WITH TITLES VI AND VII OF THE CIVIL RIGHTS ACT.