* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Problems Name Monohybrid/Dihybrid Crosses Date Period
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
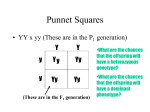
Practice Problems Monohybrid/Dihybrid Crosses Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Period _______ Read each question carefully. Answer the questions on a separate sheet of paper. Show all work and put a box around your answer. If you take the time to follow the directions below, you will be able to solve most genetics problems. Determine the genotypes of the parents or whatever is given in problem. Set up your Punnett square as follows: *# sq. based on possible gametes that can be formed. Fill in the squares. This represents the possible combinations that could occur during fertilization. Write out the possible genotypic ratio of the offspring. Using the genotypic ratio determine the phenotypic ratio for the offspring. Monohybrid Crosses 1. In humans, brown eye color (B), is dominant over blue eye color (b). What are the phenotypes of the following genotypes? In other words, what color eyes will they have a. BB ________________________ b. Bb ________________________ c. bb ________________________ 2. In dogs, wire hair (S) is dominant to smooth (s). In a cross of a homozygous wire-haired dog with a smooth-haired dog, what will be the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the F1 generation? 3. Woodrats are medium sized rodents with lots of interesting behaviors. You may know of them as packrats. Let's assume that the trait of bringing home shiny objects (H) is controlled by a single locus gene and is dominant to the trait of carrying home only dull objects (h). Suppose two heterozygous individuals are crossed. What are the genotypic and phenotypic ratios? http://www.hastingsreserve.org/Mammals/Woodrats/Woodr atPics/RatDrawng.jpeg 4. Saguaro cacti are very tall cylindrical plants that usually have two Lshaped arms, one on each side. Suppose you lived in southern Arizona where the Saguaro cactus is common and you happen to have one growing in your yard. Your Saguaro has two arms but one is longer than the other. Now, assume that arm length in these cacti is controlled by a single gene with arms of the same length (A) being dominant to arms of different lengths. What is the genotype of your cactus? http://www.garden-services.com/gallery/4 5. The ability to curl your tongue up on the sides (T, tongue rolling) is dominant to not being able to roll your tongue. A woman who can roll her tongue marries a man who cannot. Their first child has his father's phenotype. What are the genotypes of the mother, father, and child? Use the information given to work backward to the initial genotypes. Use a Punnett Square to support your conclusion. Dihybrid Crosses 6. In pea plants, the round seed allele is dominant over the wrinkled seed allele, and the yellow seed allele is dominant over the green seed allele. (R = round, r = wrinkled, Y= yellow, y = green) The genes for seed texture and those for seed color are on different chromosomes. A plant heterozygous for seed texture and seed color is crossed with a plant that is wrinkled and heterozygous for seed color. What is the phenotypic ratio of the offspring produced by this cross? 7. In cats B= brown hair color, b=white hair color, S= short hair and s=long hair. Make a Punnett square for the following crosses and determine the phenotypic ratios of the offspring produced. a. BbSs x bbSs b. BbSs x BbSs 8. A couple has three children, all of whom have brown eyes and blond hair. Both parents are homozygous for brown eyes (BB), but one is blond (rr) and the other is a redhead (Rr). What is the probability that the next child will be a brown-eyed redhead? 9. In watermelons, the alleles for green color (G) and short shape (S) are dominant over the alleles for striped color (g) and long shape (s). A plant with long, striped fruits is crossed with a plant that is heterozygous for both characteristics. What genotypes and phenotypes will be found among the offspring, and in what proportions? 10. In hounds, drooping ears is dominant to erect ears. Also barking while trailing rabbits is dominant to silent trailers. What kind of pups (phenotypic ratio) can be expected from a cross between a heterozygous droop-eared barker mated to an erect eared silent trailer? http://fineartamerica.com/images-medium/basset-hound-dognan-wright.jpg