* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download New Genetics Problems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
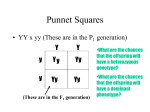
Genetics Practice Problems Single Trait and Monohybrid Crosses 1. Cross two pea plants. Both are heterozygous for seed type; round (R) is dominant to wrinkled (r). 2. For bears, black fur (B) is dominant to white fur (b). Determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring resulting from the following parents: a) homozygous black and homozygous white; b) two heterozygous blacks; c) heterozygous black and white 3. Imagine that you encounter creatures in outer space whose traits are inherited according to Mendel's laws. In these creatures, purple eyes (P) are dominant to yellow eyes (p). Two purple-eyed creatures mate and produce six offspring (four purple-eyed and two yellow-eyed). What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the parents? What are the genotypes of the offspring? 4. In fruit flies, long wings (L) are dominant to short wings (l). Two long-winged flies produced 49 short-winged and 148 long-winged offspring. What were the probable genotypes of the parents? About how many of the longwinged offspring should be heterozygous? 5. In humans, brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue eyes (b). A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman. They have eight children (all are brown-eyed). What are the possible genotypes of both parents and their offspring? 6. In humans, gender is determined by the 23 rd pair of chromosomes. XX results in females, whereas XY results in males. a) What fraction of a female's ova would be expected to bear an X chromosome? b) What fraction of a male's sperm would be expected to bear an X chromosome? A Y chromosome? c) What is the genotypic and phenotypic ratios expected for the sex of human offspring? Two-Trait and Dihybrid Cross 7. Do a dihybrid cross of two peas plants. Seed type, round (R) is dominant to wrinkled (r); and height, tall (T) is dominant to dwarf (t). 8. Determine the results of a cross between two tomato plants. One is homozygous dominant for both fruit color and leaf type. The other is heterozygous for both traits. Red (R) is dominant to yellow (r) fruit color and curled (C) is dominant to potato (c) leaf type. 9. Determine the results of a cross between two tomato plants. One is homozygous dominant for fruit color and heterozygous for height and the other is heterozygous for both traits. Red (R) is dominant to yellow (r) fruit color and tall height (T) is dominant over the dwarf variety (t). List all genotypes and phenotypes for the F1 generation. 10. Cross two dihybrid individuals for hair color pigment: dark (D) and light (d); and the ability to taste PTC (Phenylthiocarbamide): taster (T) and non-taster (t). List all genotypes and phenotypes of the first generation of offspring. 11. In moose, brown coat color (B) is dominant to albino (no pigment) (b) and rough coat (R) is dominant to smooth coat (r). Two moose are selected for breeding and their genotypes are BBRR (female) and bbrr (male). Determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the: a) F1 generation; b) F2 generation; c) cross between an F1 moose and a moose with the genotype BBRr. 12. In Drosophila (fruit flies), cut wing (C) is dominant to scalloped wing (c) and vermillion eye (V) is dominant to bar eye(v). Cross two flies: The female is heterozygous for both traits with a scalloped wing, bar eyed male. Show the punnett square and give the offspring ratios. 13. In tulips, red flowers (R) are dominant to yellow flowers (r) and broad leaves (L) are dominant to slender leaves (l). A gardener crosses a RrLl plant with a rrll plant. Seeds from this cross produce 52 red, broad-leaf tulips and 48 yellow, slender-leaf plants. Explain these results (hint: think Mendel's three laws). 14. In cocker spaniels, black color is due to dominant (B), red color is recessive (b). Solid is due to a dominant gene (S), while spotted depends on the recessive allele (s). A red male was mated to a black, spotted female. Of the five puppies, one was black and white (black with spots), two red and whites (red with spots), one black, and one red. What were the genotypes of the parents? 15. A black, smooth guinea pig was mated with an albino, rough guinea pig. Their offspring were black, rough and black, smooth. These were the only offspring types produced over a period of several years after multiple matings. Black color and rough fur are the dominant traits for guinea pigs. What was the probably genotype of each parent? 16. Two black crested chickens are mated. They produce 13 offspring; 7 black crested, 3 red crested, 2 black plain, and 1 red plain. What were the genotypes of the parents? What type of inheritance is this? Incomplete Dominance, Codominance, and Sex-Linked Crosses 17. In Andalusia fowl, B is the gene for black plumage (head feathers) and B' (pronounced "B prime") is the gene for white plumage. These genes, however, show incomplete dominance. The heterozygous (BB') condition results in blue plumage. List the genotypic and phenotypic ratios expected from the following crosses: a) black x blue b) blue x blue c) blue x white 18. One parent has type A blood (IAIA or IAIO) and the other has type B blood (IBIB or IBIO). What are the parents genotypes if they produce a large number of children whose blood types (phenotypes) are: a) all AB b) 50% AB and 50% B c) 50% AB and 50% A d) 25% AB, 25% A, 25% B, 25% O? (hint: remember to write the alleles I-I-) 19. What is the probable genotypic ratio among children born to a mother having the genotype I AIO and a father with the blood type AB? 20. In snapdragons, petal color is determined by a single gene locus with two alleles making the "red" allele (R) incompletely dominant to the "white" allele (W). Heterozygotes have petals, which are neither red nor white, but pink. a) If a true-breeding red flower is pollinated with pollen from a white flower: What fraction of the seeds (F1 generation) would be expected to produce red-flowered plants? What fraction of the gametes produced by the F1 plants would be expected to bear the R allele? b) If two pink flowered plants are crossed, what genotypic and phenotypic ratios are expected among the offspring (F1 generation)? 21. In Drosophila (fruit flies), the gene for eye color is sex-linked, red eyes (XR) is dominant to the gene for white eyes (Xr). Determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios expected from a cross between the following parents: (a) a heterozygous female and a red-eyed male; (b) a heterozygous female and a white-eyed male; (c) a white eyed female and a red eyed male. (hint: remember to write the alleles X -X- and X-Y) 22. In humans, the gene for blood clotting is a sex-linked trait; normal blood clotting (X H) is dominant to the gene for hemophilia (Xh). Determine the following crosses: a) a female carrier and a normal male; b) a normal male and a hemophiliac female; c) a female carrier and a diseased male. Show the punnett squares. Pedigrees 23. Diagram the pedigree of a family for the trait of colorblindness in which the mother is a carrier, the father is colorblind, and they have six children: two girls with normal color vision, one colorblind girl and three boys all with normal color vision. The allele for colorblindness (Xc) is recessive to normal color vision (XC). Shade in appropriately. If someone is a carrier, color in half. Could this couple have produced these offspring? Show work. 24. In humans, the gene for blood clotting is a sex-linked trait; normal blood clotting (XH) is dominant to the gene for hemophilia (Xh). A woman and a man, both with the ability to clot blood normally, have have a normal son, a hemophiliac son, and two normal daughters. What is the probable genotype of each family member? Miscellaneous Two-Trait Crosses 25. If brown-eyed fruit flies with long wings are mated to red-eyed flies with long wings, and the following results are observed: 51 red, long-winged; 53 brown, long-winged; 18 red, short-winged; 16 brown, short-winged. What are the genotypes of the parents? What are dominance relationships between the alleles at each of the loci? 26. A plant is wanted which has the genotype Aabb. Given parental strains AABB and aabb, outline the method you would use to obtain such a plant. How would you test the genotype of the plant once you think you have obtained it? 27. In humans eye color is not sex-linked, but colorblindness is, Brown (B) eye color is dominant to Blue (b) eye color, and normal color vision (XC) is dominant to colorblindness (Xc). Cross a colorblind blue-eyed male with a heterozygous brown-eyed colorblindness-carrier female. Give the genotypic and phenotypic ratios