* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry - Science with Mr. Enns
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
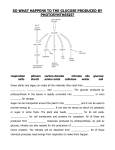
Biochemistry Part 1: Macromolecules Macromolecules Macro means “large”. Macromolecules are huge molecules made from long chains of smaller units. There are four major types of macromolecules in the human body: carbohydrates fats (lipids) proteins nucleic acids Macromolecules While each type of macromolecule is different, they have one major thing in common: Macromolecules are made of long chains called polymers (poly = “many”) Polymers are made up of smaller subunits called monomers (mono = “one”) Let’s look at an example… Monomer vs. Polymer Take a pearl necklace, for example: Polymer Monomer Made up of many pearls in a chain Each pearl is a separate unit G G G G G G G G glucose carbohydrates amino acids proteins glycerol + fatty acids lipids phosphate + ribose nucleic acids G Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are made from glucose. Glucose can be combined in different ways to make 3 types of carbohydrates: starch glycogen cellulose Starch is a branched chain of glucose used in plants G G For storing energy G G G G G G G Glycogen is a branched chain used in animals G G G For storing energy G G G G G G Cellulose is a long chain of glucose used in plants G G For building G G G G G G G G G G G G G G G Carbohydrates Clusters Starch of glycogen (black dots) in a liver cell. Cellulose granules fibres inside in plant paper cells. Lipids Fats are only one type of lipid. Lipids are made up of fatty acid molecules bonded to a glycerol molecule. There are 4 main types of lipids in living things: fats / oils phospholipids cholesterol hormones Fats vs. Oils Fats and oils are very similar. Fats are usually solid at room temperature. Fats have fatty acid chains closely packed. saturated fat Fats vs. Oils Fats and oils are very similar. Oils are usually liquid at room temperature. Oils have fatty acid chains loosely packed. unsaturated fat (oil) Phosholipids Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Phospholipids combine together to make a twin layer (bilayer) that is waterproof. The Cell Membrane Proteins Proteins are made from smaller amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, which can combine in a huge number of ways. Proteins have a huge number of uses: structure defense digestion energy Protein Structure Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids make up our DNA. Nucleic acids are made of ribose (a sugar), a phosphate group and a nucleotide. There are 4 different nucleotides in DNA: adenine guanine cytosine thymine Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids make up our DNA. Nucleic acids are made of ribose (a sugar), a phosphate group and a nucleotide. There are 4 different nucleotides in DNA: adenine guanine cytosine thymine A C G T Nucleotide Pairing The nucleotides pair up in a certain way. Adenine always pairs with Thymine A T Cytosine always pairs with Guanine G C Nucleotide Pairing The nucleotides pair up in a certain way. Adenine always pairs with Thymine A T All Tigers Can Growl Cytosine always pairs with Guanine G C Nucleic Acids A Review carbohydrates proteins Made from glucose e.g. starch, glycogen, and cellulose Made of amino acids e.g. keratin, muscle, collagen, enzymes energy, structures wide range of uses lipids nucleic acids Made of glycerol + fatty acids e.g. fats, oils, steroids Make up of ribose + 4 nucleotides e.g. adenine, guanine energy, structures storing information Any Questions? Biochemistry Part 2: Photosynthesis Glucose Leaves make food for the plant. The food that a plant uses is a macromolecule called glucose. Glucose is a hexagon-shaped molecule made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Glucose stores chemical energy in its chemical bonds. Photosynthesis Leaves make glucose from sunlight. Plants produce glucose through a chemical reaction called photosynthesis. PHOTO SYNTHESIS “with light” “making” Photosynthesis occurs mainly in the leaves of plants. Photosynthesis Leaves make glucose from sunlight. Plants produce glucose through a chemical reaction called photosynthesis. PHOTOSYNTHESIS “making with light” Photosynthesis occurs mainly in the leaves of plants. Chloroplasts Photosynthesis take place in cells with chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are organelles that capture light energy and use it to make glucose. Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy to create glucose. Chloroplasts Raw Materials Energy from sun O2 to air CO2 Chlorophyll from air chloroplasts H 2O from soil C6H12O6 to plant The Reaction The word and chemical equation for photosynthesis: Sunlight Carbon Dioxide + Water > Glucose + Oxygen CO2 + H 2O > C6H12O6 + O2 Chlorophyll Chemical Equation The chemical equation for photosynthesis is: 6CO2 + 6H2O Light Energy Chlorophyll C6H12O6 + 6O2 Using Glucose Glucose has several uses in the plant. 1. Glucose is burned in mitochondria for energy e e G G 2. Glucose is stored as larger starch molecules G G G G G G G G G 3. Glucose is turned into cellulose to build things G G G G G G G G G G G G G G G G G 4. Glucose is turned into proteins to build things G G 5. Glucose is turned to fats and stored in seeds G G G Leaf Anatomy Leaves are adapted to perform photosynthesis. green coloring broad and flat shape chlorophyll traps sunlight To collect sunlight easily waxy covering veins and stem Waterproofs the leaf on top To carry water from the roots Leaf Anatomy Leaves are adapted to perform photosynthesis. cuticle upper epidermis spongy cells palisade cells air spaces vein stomata lower epidermis Leaf Anatomy cuticle upper epidermis spongy cells palisade cells air spaces stomata lower epidermis Stomata Leaves have tiny pores on the bottom. These holes are called stomata (pl). Singular: one stoma Stomata allow gases to enter and exit the leaf CO2 enters O2 exits H2O vapor exits Stomata Stomata can be opened or closed. Stomata are surrounded by sausage-shaped guard cells that control its opening/closing . When guard cells swell up with water, the stomata opens. When guard cells lose water, the stomata closes. Stomata Stomata Limiting Factors Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction. Since it is a chemical reaction, it can be sped up or slowed down. The rate of the reaction depends on 3 factors: Light Levels CO2 Levels Temperature They are called limiting factors because if any ONE of them is in short supply, it will limit the rate of P/S. Light Levels P/S ↑ as light levels ↑ …but it will then be limited by CO2 or temperature CO2 Levels P/S ↑ as CO2 levels ↑ …but it will then be limited by light or temperature Temperature P/S ↑ as temperature ↑ …but soon the enzymes in P/S are destroyed by heat IMPORTANT! Plants go through respiration, just like humans do! 1. Glucose is burned in mitochondria for energy The difference between plants and us is that G plants make their own food through P/S e! e G During the day, plants take in CO2 and H2O to produce C6H12O6 and release O2 as waste. But at night, plants take in O2 and burn C6H12O6 to produce CO2 and H2O as waste. Any Questions? Biochemistry Part 3: Cellular Respiration Like A Fire? In order for a fire to burn, it needs TWO things: Fuel Oxygen A fire combines these 2 things in a chemical reaction that releases energy Our bodies are NO different! Energy For Life All cells require energy to survive. Glucose is the main source of energy. Cells release energy in three different ways: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Fermentation Aerobic Respiration Aerobic means “with oxygen”. In aerobic respiration, cells use oxygen to release the energy stored in glucose. Aerobic respiration takes place in organelles called mitochondria. The mitochondria absorb glucose and oxygen from the blood and produce energy for the cell. Aerobic Respiration The word equation for aerobic respiration is: Brought to cells by the blood Inhaled by lungs Carried by blood Carried by blood Carried by blood Exhaled by lungs Lost as sweat, etc. Used for all body actions Aerobic Respiration The word equation for aerobic respiration is: The chemical equation is: Aerobic Respiration Facts: It is used for non-strenuous activities. It supplies daily energy for the body in slow and steady amounts. It is a very efficient reaction. One glucose molecule makes 20x more energy than anaerobic respiration. It is a relatively safe reaction. It produces no negative side effects. Anaerobic Respiration Sometimes, energy is needed much quicker! Anaerobic respiration releases small amounts of energy without oxygen. This reaction is also called fermentation. There are two types of fermentation: Anaerobic Respiration In muscle cells Alcoholic Fermentation In yeast cells Anaerobic Respiration The word equation for anaerobic respiration is: Brought to cells by the blood Builds up in muscles Makes them fatigue & ache Energy released very quickly Anaerobic Respiration The word equation for lactic acid fermentation is: The chemical equation is: Why Use Fermentation? Anaerobic respiration is a harmful process. It releases lactic acid as a waste, causing muscles to fatigue and cramp. It is only used when the muscles work very hard. When this happens, the heart cannot deliver oxygen and glucose fast enough for aerobic respiration. Anaerobic Respiration Facts It produces energy almost instantly. It is only used for high intensity activities for a short time (sprinting, climbing). It is an inefficient reaction. One glucose molecule makes 1/20th the amount of energy as aerobic respiration. It can only last for a short time. Lactic acid build up will damage muscles. Alcoholic Fermentation Other organisms create energy differently. Alcoholic fermentation breaks down glucose into alcohol & carbon dioxide. Remember, it occurs without oxygen! Yeast cells can use alcoholic fermentation to produce energy if they are deprived of oxygen. Yeast Cells Alcoholic Fermentation The word equation for alcoholic fermentation is: Fed to the yeast cells Used to make alcoholic beverages Used to make dough rise Used by the yeast cells Fermented Food Alcoholic fermentation produces useful products: Alcohol can be used to make: Carbon dioxide can be used to make: Fermented Food Some bacteria use anaerobic respiration to make energy, the lactic acid can be used in food. Lactic acid hardens milk to produce: A Summary Aerobic Respiration – with oxygen C6H12O6 + 6O2 à 6CO2 + 6H2O + 32 ATP Anaerobic Respiration – without oxygen C6H12O6 à 2 C3H6O3 + 2 ATP Alcoholic Fermentation – without oxygen C6H12O6 à Alcohol + CO2 + Some Energy Any Questions?

































































![fermentation[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008290469_1-3a25eae6a4ca657233c4e21cf2e1a1bb-150x150.png)