* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advanced Placement World History
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
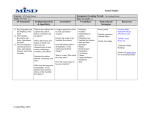
Advanced Placement World History Course Texts Stearns, Peter N., Michael Adas, Stuart B. Schwartz, and Marc Jason Gilbert. World Civilizations: The Global Experience , 6th edition. Pearson. Course Description: AP World History is an academic yearlong course that is meant to be the equivalent of a freshman college course and can earn students college credit. This course covers the history of the world from approximately 10,000 B.C.E. to the present. The course examines the history of human experience from a global perspective. It stresses the linkage between people and states formed through trade, the migration of people and ideas, the mobilization of mass society, revolutions, and the impact of technology upon humankind. The students in this course are expected to do a considerable amount of reading in both the major text and supplementary sources. This course is designed to continue the development of historical research and writing skills. The student is required to complete all summer assignments, which will be collected on the first day of AP class in August. Important: This is a collegecredit course and, as such, is more laborintensive than normal World History. The students will be responsible for their own work, both in class and as homework. Summer Assignment: Make sure to check out your textbook before you leave for the summer. Your summer assignment has been designed to help support your learning for the coming school year. It is imperative that you complete this work before returning to school in August, this will be collected the first day of class, the teacher reserves the right to ask you to drop the class if this work is not completed by the first day of school. If you plan and space out your assignment you should not be overwhelmed. You will have 5 chapters to read from your textbook (Stearns, Peter N., Michael Adas, Stuart B. Schwartz, and Marc Jason Gilbert. World Civilizations: The Global Experience , 6th edition. Pearson.) Chapter 1: From Human Prehistory to the Early Civilizations (page 829) Chapter 2: Classical Civilization: China (page 4057) Chapter 3: Classical Civilization: India (page 6076) Chapter 4: Classical Civilizations in the Mediterranean and Middle East (page 80100) Chapter 5: The Classical Period: Directions, Diversities, and Declines by 500 C.E. (page 104125) Taking notes on these chapters can only help you in the long run, however, they will not be required. What will be required will be the worksheets below. There are three worksheets. The first one will cover Chapter 1, then the next two will be covered by Chapters 25. Please read through these chapters, hopefully some of what you read is review from Grade 9 History. Name: The Neolithic Revolution Use Chapter 1 from the textbook to answer the following questions . 1. According to the text, the Neolithic Revolution was “probably triggered by two results of the ice age’s end.” What were these two results that caused the Neolithic Revolution? __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____ 2. Why was agriculture able to spread so extensively? List 3 reasons. __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____ 3. Huntergatherer bands and pastoral nomadic communities persisted despite the agriculturalists’ “takeover” of most parts of the world. What places were these huntergatherer communities located in? What is the main reason why they did not embrace and practice agriculture? __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____ 4. The Neolithic Revolution sparked technological innovation that led to improvements in agricultural production, trade, and transportation. For the following items, explain what each is used for. ∙ Pottery: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ∙ Plows: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ∙ Woven textiles: _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ∙ Metallurgy (see “metalworking”): _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ∙ Wheels/wheeled vehicles: ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ In addition to the technological innovations, the following terms are effects or results of the Neolithic Revolution. For each term: define it, give an example of it OR why it’s significant, Definition Domestication : Example or Significance Agriculture: Stratification: Pastoralism: Irrigation: Patriarchy: Formulate a thesis statement for the following question . 5. How did the domestication of plants and animals result in demographic and technological transformations? __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______ The Classical Era (Unit 2) Part I (Chapters 25) AP World History Part I: Identifications Definition Significance (why is it important, what does it lead to, etc) 1. Achaemenid Empire 2. Teotihuacan 3. Hellenistic 4. Diplomacy 5. Xiongnu Confederacy 6. Chang’an 9. Judaism & the Jewish 7. Shamanism 8. Filial piety diaspora 10. Hinduism Part II: Short Answer Directions: Answer the following questions directly below the question. Each answer should be at least a paragraph in length and should contain specific historical examples from the reading. Be sure to include the page number(s) where you got your information. 1. Which states and empires throughout the world become important during this time period? Describe the administrative institutions they create in order to organize their subjects and how they project their military power over large areas. 2. Explain how cities are used by these large empires. How does the social structure of these empires maintain the status quo and ensure food production? 3. Analyze the collapse, caused by both internal, and external forces, of the Roman, Han, Persian, Mauryan, and Gupta empires. Be sure to include examples for EACH empire. 4. Compare the rise of Buddhism with that of Confucianism, Daoism, and Christianity. How did each of these religions affect the development of culture and gender roles? The Classical Era (Unit 2) Part II AP World History Part I: Identifications Definition Significance (make connections, why is it important, what does it lead to, etc) 1. Meroe 2. Axum 3. Bantu 4. Lateen Sail 5. Gandhara Buddhas Part II: Short Answer Directions: Answer the following questions directly below the question. Each answer should be at least a paragraph in length and should contain specific historical examples from the reading. Be sure to include the page number(s) where you got your information. 1. Distinctive artistic expressions emerged during this time period that influenced developments in neighboring regions and later time periods. Compare Indian epics and Greek plays. Describe the distinctive architecture of either India, Greece, Rome, or Mesoamerica and how it reflects its culture. 2. New trade routes became the basis for exchange in the Eastern Hemisphere. Describe how the climates and locations of the trade routes, the typical trade goods, and the ethnicity of the people involved shaped the Silk Roads, TransSaharan caravan routes, Indian Ocean Sea lanes, and Mediterranean Sea lanes. Be sure to include examples from each. 3. What new land and sea technologies facilitated long distance communication and exchange? 4. Alongside trade in goods, the exchange of people, technology, religious and cultural beliefs, food crops, domesticated animals, and disease pathogens developed across the Eastern Hemisphere. Provide and describe an example for each!














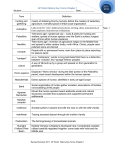






![Topics: 1. Paleolithic Age [Old Stone Age] 2. Neolithic Age [New](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001124397_1-b9324b59722d081f0d18939d5f1294cc-150x150.png)