* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Developmental Biology 8/e
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
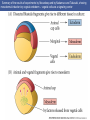
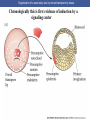
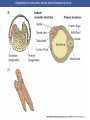
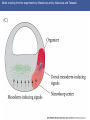
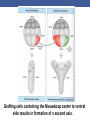
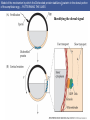
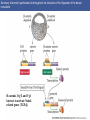
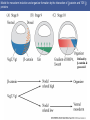
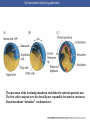
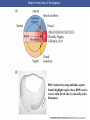
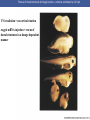
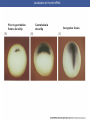
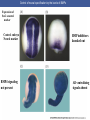
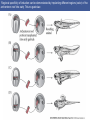
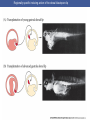
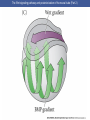
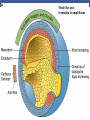
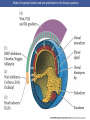
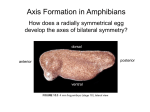
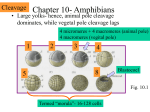
Cortical Rotation Cleavage of a frog egg Frog egg cleavage Fate maps of the blastula of the frog Xenopus laevis Cell movements during frog gastrulation Cell movements during frog gastrulation Surface view of an early dorsal blastopore lip of Xenopus Epiboly of the ectoderm Importance of localized cytoplasmic determinants Spemann’s first classical experiment There are determinants in the cytoplasm of the fertilized egg At the vegetal half – maternal m-RNAs Vg-1 – TGF-β signal – mesoderm induction Xwnt-11 – dorso-ventral axis specification VegT – transcription factor-mesoderm induction Summary of the results of experiments by Nieuwkoop and by Nakamura and Takasaki, showing mesodermal induction by vegetal endoderm – vegetal cells are a signaling center Organization of a secondary axis by dorsal blastopore lip tissue Chronologically this is first evidence of induction by a signaling center Organization of a secondary axis by dorsal blastopore lip tissue Now we have two levels of induction: 1. The vegetal cells 2. The dorsal lip of the blastopore Dorsal lip of the blastopore patterns a new D/V axis and a new A/P axis. How does the dorsal lip of the blastopore become a signaling center? Model resulting from the experiments by Nieuwkoop and by Nakamura and Takasaki Grafting cells containing the Nieuwkoop center to ventral side results in formation of a second axis. Model of the mechanism by which the Disheveled protein stabilizes -catenin in the dorsal portion of the amphibian egg – PATTERNING THE AXES Identifying the dorsal signal Model of the mechanism by which the Disheveled protein stabilizes -catenin in the dorsal portion of the amphibian egg (Part 2) Signaling center established in the dorsal vegetal side Nieuwkoop center Summary of events hypothesized to bring about the induction of the Organizer in the dorsal mesoderm Β-catenin, VegT, and Vg1 interact to activate Nodalrelated genes (TGF-β) Model for mesoderm induction and organizer formation by the interaction of -catenin and TGFproteins Defined by β-catenin & goosecoid Steps to the establishment of a dorsal side in a Xenopus embryo: 1. cortical rotation 2a. induction of mesoderm by vegetal cells maternal factors 2b. establishment of Nieuwkoop center - dorsalization 3. establishment of the Organizer 4. gastrulation – dorsal lip of blastopore Cell movements during frog gastrulation The movement of the involuting mesoderm establishes the anterior-posterior axis. The first cells to migrate over the dorsal lip are responsible for anterior structures. Dorsal mesoderm “dorsalizes” ectoderm above. Model for the action of the organizer BMP visualized by using antibodies against Smad1 (highlights region where BMP is active. Arrows show dorsal side ( by dorsal lip of the blastopore) Rescue of dorsal structures by Noggin protein – embryos ventralized by UV light UV irradiation = no cortical rotation noggin mRNA injection = rescue of dorsal structures in a dosage dependent manner Localization of noggin mRNA in the organizer tissue, shown by in situ hybridization Dorsal marginal Zone at gastrulation Precursors of notochord, prechordal plate, pharyngeal endoderm during convergent extension Dorsal blastopore lip after involution Beneath ectoderm Localization of chordin mRNA Prior to gastrulation Future dorsal lip Gastrulation in dorsal lip In organizer tissues Control of neural specification by the levels of BMPs Expression of Sox2 a neural marker Control embryo Neural marker BMP4 signaling not present BMP inhibitors knocked out All ventralizing signals absent Regional specificity of induction can be demonstrated by implanting different regions (color) of the archenteron roof into early Triturus gastrulae Regionally specific inducing action of the dorsal blastopore lip Paracrine factor antagonists from the organizer are able to block specific paracrine factors to distinguish head from tail Cerberus mRNA injected into a single D4 blastomere of a 32-cell Xenopus embryo induces head structures as well as a duplicated heart and liver The Wnt signaling pathway and posteriorization of the neural tube (Part 2) Model for axes formation in amphibians Model of organizer function and axis specification in the Xenopus gastrula