* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homologous and Analogous Structures
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
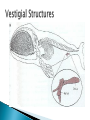
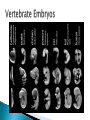
A hypothetical trace of evolution ◦ One original common ancestor Scientists use both morphology and genetics to produce phylogenic trees ◦ Morphology- share similar physical characteristics ◦ Analysis of genetic similarity the study of the body structures in different organisms ◦ anatomical similarities gives evidence of a common ancestor Human Dog Seal Structures that are similar but has different functions ◦ Shows common ancestry Acquiring the same biological trait independently Example: Flight Humming bird and moth - last common ancestor did not have wings They acquired these traits separately ◦ Only very few designs for a wing would allow for hovering Similar functions but differ in structure ◦ Ex: wings of a hummingbird and humming moth – both can hover to feed Two or more related populations or species become more and more dissimilar. Divergence is nearly always a response to differing habitats and can result in new species ◦ Many related species evolve from a single ancestral species ex: Galapagos finches Features that were useful to an ancestor, but they are not useful to the modern organism that has th. ◦ tailbone in humans ◦ Appendix ◦ Some snakes have tiny pelvic bones and limb bones Closely related organisms often have similar stages in their embryonic development ◦ All vertebrate embryos are similar ◦ Vertebrates share a common ancestor lemur pig human All organisms share related biochemical processes: ◦ All cells use DNA as genetic blueprint ◦ All use RNA, ribosomes, and approximately the same genetic code for translation ◦ All use roughly the same set of 20 amino acids to build proteins ◦ All use ATP to transfer energy the DNA nucleotide sequence of the human and mouse cytochrome c gene is very similar, suggesting shared ancestry 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8