* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NUR101ModB
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
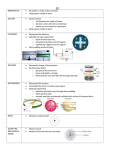
NUR 101: Body Structure and Function Module B – Chemistry of Life Chemistry of Life BIOCHEMISTRY is devoted to studying the chemical aspects of life. The basic principles of anatomy and physiology are ultimately based on principles of chemistry. Levels of Chemical Organization MATTER is any thing that occupies space and has mass. MOLECULES are particles of matter that are composed of one or more smaller units called atoms. ATOMS are composed of several kinds of subatomic particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons. Atom Organization Atom nucleus is the center core of the atom and contains protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged particles within the nucleus of an atom. Neutrons are electrically neutral particles within the nucleus of an atom. Electrons are negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus of an atom. Levels of Chemical Organization ELEMENTS are pure substances, composed of only one kind of atom MOLECULES are particles of matter that are composed of one or more smaller units called atoms COMPOUNDS are composed of molecules having more than one kind of atom. CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDING occurs when one atom donates an electron to another atom and the resulting ions attract each other. COVALENT BONDING occurs when atoms share electrons ORGANIC VERSUS INORGANIC Organic compounds are composed of molecules that contain Carbon-Carbon (C-C) covalent bonds or CarbonHydrogen (C-H) bonds. Few inorganic compounds contain carbon atoms and none contain Carbon-Carbon or CarbonHydrogen bonds. Organic molecules are generally larger and more complex . Solvent and Solute SOLVENT is a substance in which other substances are dissolved; for example, In saltwater the water is the solvent SOLUTE is substance that dissolves into another substance; for example In saltwater the salt is the solute dissolved in water. TYPES OF INORGANIC MOLECULES Water Acids Bases Salts Concepts related to PH level PH is a unit expressing relative H+ (hydrogen) concentration Formula used to calculate PH units gives a value of 7 to pure water therefore 7 is a neutral value neither acidic or basic PH values higher than 7 is basic PH values lower than 7 is acidic Normal body function can be maintained only within a narrow range of PH. Normal range 7.35-7.45 Acid – Base Concepts Acid is any substance that when dissolved in water, contributes to an excess of H+ (hydrogen) ions. A lower PH value indicates a higher H+ concentration –acidic Normal range 7.35 to 7.45 Base is any substance that when dissolved in water, contributes to an excess of OH- (hydroxide) ion. TYPES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES Carbohydrates Lipids Triglycerides Phospholipids Cholesterol Proteins Nucleic Acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) Carbohydrate Structure and Function Monosaccharide (glucose, galactose, fructose ) single monosaccharide unit. Utilized as a primary source of energy and to build other carbohydrates Disaccharide (sucrose, lactose, maltose ) two monosaccharide units. Broken into a monosaccharide for energy Polysaccharide (glycogen, starch) many monosaccharide units. Used to store monosaccharides (thus to store energy) Lipid Structure and Function Triglycerides are formed by one glycerol unit and three fatty acids. Utilized to store energy in cells Phospholipids are formed by two fatty acids and a phosphorus containing unit. Utilized to form a stable foundation for the cell membrane Cholesterol has four carbon rings at core. Assists in stabilizing the cell membrane and is the basis of steroid hormones Protein Structure and Function Structural proteins (fibers) are amino acids that form essential structures of the body Functional proteins (enzymes, and hormones) are amino acids that facilitate chemical reactions; send signals ; compose some of the hormones cell membrane channels and receptors and enzymes Nucleic Acid Structure and Function Nucleic acids are made from nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate unit, a sugar unit and a nitrogen base. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) nucleotide base includes adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. Contains information (genetic code) for making proteins Ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide base includes adenine, uracil, guanine, and cytosine Serves as a copy of a portion of the genetic code