* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hello!!! - Elida Local Schools
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
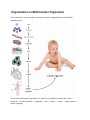
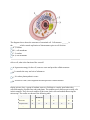
Hello!!! Hope this assignment finds you warm and cozy on this snow day!! To complete this first lesson you will need to read the nonfiction text on cells and levels of organization. Hopefully this will jog your memory to review what we learned in the earlier part of the school year! After you have read the text, you will need to complete the questions that go along with the text. If you do not have printer access please write the answers on a sheet of notebook paper. You have 2 weeks from the day this lesson is assigned to return it to me. If you have any questions make sure to ask for clarification on a day when class is in session or by email ([email protected], or [email protected]) . Work hard, have fun, and STAY WARM!!! ;) See you soon! Mrs. Adcock and Mrs. Hawk PS- Click here for a musical review of cell information! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-zafJKbMPA8 Organization in Multicellular Organisms From simplest to most complex, the proper levels of organization in multicellular organisms are: The levels of biological organization in order from smallest to largest are: atom → molecule → macromolecule → organelle → cell → tissue → organ → organ system → whole organism. Organelles are specialized subunits in the cell, which each have their own specific function. They are usually enclosed in their own lipid membrane. There are many types of organelles, such as ribosomes, nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. Cells are the structural and functional units of all living organisms. Some organisms, such as bacteria, are each made up of only one cell. Other organisms, such as animals, are each made up of many cells. Cells in many-celled organisms specialize depending upon their location and function in the body. All cells come from other cells, and they divide by mitosis or meiosis. Cells contain organelles and the genetic information of an organism. Tissues are composed of many cells that work together to perform a specific function. Tissue covers most parts of an organism. There are several types of tissues, such as connective tissue, muscle tissue, nervous tissue, and epithelial tissue. Organs are composed of several tissues and perform one or more functions in the body. In most organs there is a unique 'main' type of tissue (such as the myocardium of the heart) and several other tissues that are found in many organs (such as connective tissue). The body is made up of many organs, including the heart, lungs, liver, eyes, and brain. Organ systems are groups of related organs that work together to perform a function or set of functions. The functions of the various organ systems usually overlap and are influenced by each other. There are eleven major organ systems in the human, including the respiratory, reproductive, digestive, skeletal, muscular, nervous, circulatory, endocrine, urinary, integumentary, and lymphatic systems. There are two main organ systems in vascular plants: the root system and the shoot system. The whole organism is composed of all of the various organ systems. Its functions are carried out by cooperation of all of the systems. Cells Are Specialized The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform specific functions. The cellular processes carried out within these specialized cells are essential for the survival of the organism. **All information obtained from Study Island Study Island Copyright © 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 01/30/2014 Generated By: Trisha Adcock 1. Which of the following life processes requires specialized cells in multicellular organisms? A. respiration B. circulation C. digestion D. all of these 2. Which of the following statements is true? A. Only some organs contain cells. B. Tissues are made up of organs and cells. C. All cells contain at least one tissue. D. Organs are made up of cells and tissues. 3. The diagram above shows the structures of an animal cell. Cell structure _______ is the _______, which controls replication of chromosomes prior to cell division. A. 3; nucleus B. 1; cell membrane C. 2; nucleus D. 4; cell membrane 4. In a cell, what is the function of the vacuole? A. B. C. D. It generates energy for the cell, removes waste and provides cellular structure. It controls the entry and exit of substances. It is where photosynthesis occurs. It removes waste, stores ingested food and provides cellular structure. During science class, a group of students went on a field trip to a nearby pond where they collected samples of pond water and pond plants. The students used a microscope to study cells in their samples. They also took samples of their own cheek cells and studied them using the microscope. The results are shown in the following table. Sample Nucleus Cell Cell Wall Cytoplasm Chloroplast Vacuole Membrane cheek cells X X X X pond plant cells X X X X X X pond organism #1 X X X X X X pond organism #2 X X X X 5. Looking at the chart provided, the students need to develop a classification scheme to distinguish plant and animal cells. The presence of which of the following structures/organelles would be most useful for this purpose? A. cell wall B. nucleus C. vacuole D. plasma membrane 6. The cell membrane A. converts glucose to other energy molecules. B. alters and packages proteins and lipids. C. is the site of most cellular chemical reactions. D. controls which substances enter and exit the cell. 7. Living systems are organized in levels according to their structures and functions. Which word is missing from the organizational chart above? A. water B. bacteria C. cells D. protons 8. All living organisms are composed of A. at least 100 cells. B. only one cell. C. at least three cells. D. one or more cells. 9. Which of the following is a main difference in cell structure between an onion cell and a human cheek cell? A. B. C. D. An onion cell contains one nucleus, whereas a human cheek cell contains two nuclei. There is no difference between an onion cell and a human cheek cell. A human cheek cell contains chloroplasts. An onion cell has a cell wall. 10. The diagram below shows two organelles—a chloroplast and a mitochondrion. How are these organelles similar? A. They both have an inner membrane and an outer membrane. B. They are both designed to create food for the cell. C. They are both found in animal cells. D. all of these 11. Cells perform many functions in living organisms. Which of the following processes occur in cells? A. nutrient acquisition B. excretion of wastes C. energy extraction D. all of these