* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Liturgy (ancient Greece) wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Persian Wars wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
List of oracular statements from Delphi wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek philosophy wikipedia , lookup
First Persian invasion of Greece wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
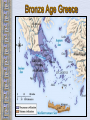
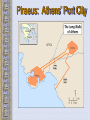
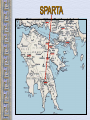
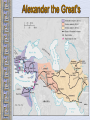
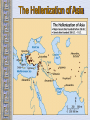
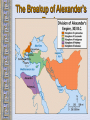
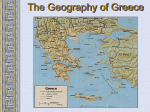
The Geography of Greece Bronze Age Greece Crete: Minoan Civilization (Palace at Knossos) Knossos: Minoan Civilization Minoan Civilization The Mycenaean Civilization Homer: The “Heroic Age” Paris v Menelaus http://youtu.be/eS9kqq6PNnQ Hector v Ajax http://youtu.be/7GyDoL7ij3A Death of Patroclus http://youtu.be/0Cz7u8RPYKo Achilles v. Hector http://youtu.be/80SsC_ZNbyI The Mask of Agamemnon ATHENS: 700’sbce300’sbce Piraeus: Athens’ Port City Early Athenian Lawgivers $ Draco First written code created around 621 “draconian” Solon(archon in 594 B.C.) Outlawed selling people into slavery to pay their debt Divided citizens into 4 groups based on wealth: wealthiest 2 could hold office $ Cleisthenes Athenian Society • 3 class groups – Citizens: extended to all those born in Athens, only the men had political rights – Metics: born outside Athens, free and had to pay taxes but had no political rights and could not own land – Slaves: captured in war, together with metics made up more than half of Athenian society Persian Wars: 499 BCE – 480 BCE Persian Wars: Famous Battles $ Marathon (490 BCE) 26 miles from Athens $ Thermopylae (480 BCE) 300 Spartans at the Mountain pass $ Salamis (480 BCE) Athenian navy victorious Golden “Age of Pericles”: 460 BCE – 429 BCE The Delian League Thasos Lesbos Delos Naxos Melos The Age of Pericles • Not only did Pericles bring great changes to the government of Greece, he also brought great changes to the nature of art and progress of his time. • The great structures of Greece, The New Temple of Athena and the Parthenon among others, were built during his time. Not only did Pericles use these structures to change the face of Greek art and the cultural pulse of the nation but he also used them for political reasons as well. $ Great Athenian Socrates Philosophers Know thyself! question everything only the pursuit of goodness brings happiness. Plato The Academy The world of the FORMS The Republic philosopher-king Great Athenian Philosophers $ Aristotle The Lyceum “Golden Mean” [everything in moderation]. Logic. Scientific method. Athens: The Arts & Sciences $ DRAMA (tragedians): Aeschylus Sophocles Euripides THE SCIENCES: Pythagoras Democritus all matter made up of small atoms. Hippocrates “Father of Medicine” Phidias’ Acropolis The Acropolis Today The Parthenon The Agora The Classical Greek “Ideal” Olympia The Ancient Olympics: Athletes & Trainers Olympia: Temple to Hera The 2004 Olympics SPARTA SPARTA Helots Messenians enslaved by the Spartans. Spartan society • 3 social groups – Equals: descended from the invaders, controlled Sparta – Half-citizens: free, paid taxes and served in the army but had no political power, some farmed but others worked in the city as traders or artisans – Helots: slaves, greatly outnumbered the other groups so Spartans used force to control them, in large part this is why Sparta became a military city-state Spartan Government • Two kings led Sparta – 1 king handled military – 1 king took care of domestic matters • A council of Elders – Made up of 28 male citizens over the age of 60 – Proposed laws and served as a criminal court • An assembly – Included all male citizens over 30 – Elected 5 ephors • Made sure the kings stayed within the law Peloponnesian Wars Macedonia Under Philip II Alexander the Great Alexander the Great’s Empire Alexander the Great in Persia The Hellenization of Asia Pergamum: A Hellenistic City The Economy of the Hellenistic World Hellenistic Philosophers $ $ Cynics Diogenes ignore social conventions & avoid luxuries. citizens of the world. live a humble, simple life. Epicurians Epicurus avoid pain & seek pleasure. all excess leads to pain! politics should be avoided. Hellenistic Philosophers $ Stoics Zeno nature is the expansion of divine will. concept of natural law. get involved in politics, not for personal gain, but to perform virtuous acts for the good of all. true happiness is found in great achievements. Hellenism: The Arts & Sciences $ $ Scientists / Mathematicians: Aristarchus heliocentric theory. Euclid geometry Archimedes pulley Hellenistic Art: More realistic; less ideal than Hellenic art. Showed individual emotions, wrinkles, and age! The Breakup of Alexander’s Empire