* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answers Pretest Module 16 Unit 1
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
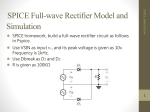
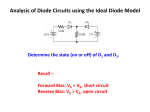
Pretest Module 16 Unit 1 1. How does rectified DC power differ from DC power from a pure DC source? It pulsates in value 2. What is half-wave DC power? (Draw Diagram) Only half of the input AC power is converted to unidirectional DC leaving gaps and allowing only half the power value of Full Wave 3. What is full-wave DC power? (Draw Diagram) Both alternations of the AC input are converted to DC and there are no gaps resulting in double the power of a half wave rectifier 4. What is the minimum PIV rating for a diode that is to be used on a 120V system? 170 V 5. What is the minimum PIV rating for a diode that is to be used on a 240V system? 340 V 6. What is the minimum PIV rating for a diode that is to be used on a 30V system? 42.4 V 7. What are the two types of full-wave rectifier circuits? Biphase and bridge 8. How is a full-wave bridge rectifier constructed? Four diodes connected in a bridge pattern so that with each half cycle, there are two diodes forward-biased diodes in series with the load 9. What is the result of one diode being reversed in a full-wave biphase rectifier? Short circuit 10. What voltage value must the diodes be rated for in a full-wave biphase rectifier? Peak line to line 11. How many diodes are required for a full-wave bridge rectifier? Four 12. What ohmmeter reading on the supply (connected either polarity) indicates a correctly connected full-wave bridge rectifier? Infinity 13. What is “ripple frequency”? Number of output pulses above or below the average value 14. What is the ripple frequency for a full-wave bridge rectifier connected to a 60 cycle source? 120 Task 2 1. What is the purpose of filter circuits for rectified DC power? Smooth out the DC pulses 2. What are the two main types of filters for rectified DC power circuits? Capacitors and inductors 3. What two factors determine the average output voltage when filters are used on a rectified DC circuit? Load resistance and size of capacitance 4. How are electrolytic capacitors connected in a rectified DC circuit? Positive lead to positive of the load and negative to negative 5. What is the maximum PIV rating of the diode when maximum filtering is used on a rectified DC power circuit? More than twice the peak of the AC input 6. What precaution should be taken before working on a filtering circuit for DC rectified power? Discharge through a bleeder resistor 7. What is a “choke” filter? Inductance filter 8. What is an “LC” filter? Inductor and capacitor filter 9. What is a “PI” filter? Combination of two types of LC filters 10. What are the five filter design considerations? 1. Allowable ripple 2. Allowable regulation 3. Output voltage 4. Rectifier peak current limits 5. Load current Task 3 1. What value of AC voltage is used to calculate power in a circuit? Effective 2. What value of AC voltage is used to calculate PIV value in rectifier circuits? Peak 3. What value of AC voltage is used to calculate what a DC meter would indicate? Average 4. What is the formula for calculating Eav when you know Emax? Eav = Emax x .637 5. What is the formula for calculating Erms when you know Emax? Erms = Emax x .707 6. What is Eav if Erms = 120V? (2 steps) Eav = 120/.707 x .637 = 108 V 7. What is Erms if Eav = 120V? (2 steps) Erms = 120/.637 x .707 = 133 V 8. What is Emax if Erms = 120V? 170 V 9. What is Emax if Eav = 120V? 188 V 10. How does Eav for a half-wave circuit compare to full-wave rectified DC? 50% 11. What is the formula for power in a full-wave rectifier circuit? P = EMax x IMax/2 12. What is the formula for power in a half-wave rectifier circuit? EMax x IMax/4 13. Calculate the power in a full-wave rectified circuit when an ammeter at the load reads 8 amps and a voltmeter reads 6 volts. (2 steps) 47.46 W 14. Calculate the power in a full-wave rectified circuit when an ammeter at the load reads 3 amps and a voltmeter reads 10 volts. (2 steps) 30 W 15. Calculate the power in a half-wave rectified circuit when an ammeter at the load reads 2 amps and a voltmeter reads 12 volts. 12 W 16. Calculate the power in a half-wave rectified circuit when an ammeter at the load reads 7 amps and a voltmeter reads 16 volts. 56 W