* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 16 Class 10th
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
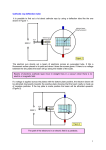
CHP#16 INTRODUCTORY ELECTRONICS Q.1 What is electronics? Describe its branches. (Ans) Electronics The branch of physics that deals with the devolpement of electron emmiting devices and their utilization. There are two main branches of electronics. i. Analogue electronics ii. Digital electronics Analogue electronics The branch of electronics that consists of electronic circuits which works on analogue quantities is known as analogue electronics. Analogue quantities Those quantities whose value vary continuously or remain constant are known as analogue quantities. For example Temperature of air changes continuosely during day and night. Digital electronics The branch of electronics that consists of electronic circuits which works on digital data is known as digital electronics. Digital data A digital data processed on two digits ie zero (0) and one (1). This data can be easily processed, because the whole data is provided in binary system. Uses Digital electronics technology is used in computers, telephone, radar, medical equipments, etc. Q.2 What is meant by thermionic emission? (Ans) Thermionic emission The emission of electrons from a metallic surface due to the gain of heat energy is called thermionic emission. Explanation Metals have free electrons that form a sea over the surface of their material. When we give heat to a metallic substance, these electrons gain energy and become excited. Some of the electrons may gain enough energy to escape from the surface of the metal. Q.3 Write a note on electron gun. (Ans) Electron gun The device use to investigate the properties of the electron beams is known as electron gun. Costruction It consists of a glass tube at a very low pressure. The electrons are produced by thermionic emission from a tungsten filament heated by a 6V supply. A high positive potential (several thousands volts) is connected to a cylindrical anode (+). The electrons will be accelerated to high speed and they shoot straight through the hole of the anode in a fine beam of electrons. This electron beam is also called as cathode rays (-). The path of these free electrons can be affected by electric and magnetic field. Deflection by electric field An electric field can be set up by appling a potential difference across two parallel metal plates placed horizontally some distance apart. When an electron beam passes between the two plates, it can be observed that the electrons are deflected towards the positive plate. The reason being that electrons are attracted by the positive plate and repelled by the negative plate. Delection by magnetic field A magnetic field is applied at right angle to the beam of electrons by placing two poles of the magnet. It can be observed that the electron beam is deflected by the magnetic field. We concluded that cathode rays are actually negatively charged electrons. Q.4 Explain construction, working, principle and uses of C.R.O? (Ans) Cathode ray oscilloscope An electronic device that becomes a part of everyday life. Construction It consists of the following components: i. The electron gun ii. The deflecting plates iii. A fluorescent screen (i) The electron gun It consists of a grid, which is connected to a negative potential. The more negative the potential, more electrons will be repelled from the grid and fewer electrons will reach the anode and the screen. The number of electrons reaching the screen determines the brightness of the light. The other feature in the electron gun is the use of the anode. Anode accelerates the electrons towards the screen. (ii) The deflecting system Two pairs of plates are fitted in cathode ray oscilloscope. Voltage can be applied to these plates to deflect the electron beam. The Y-plate deflects the electron beam vertically while the X-plate deflect electron beam in horizontal direction. (iii) The fluorescent screen The screen is coated with a fluorescent salt, for example, zinc sulphide. When the electrons hit the screen, it will cause the salt to produce a flash of light and hence a bright spot on the screen. Principle A cathode ray oscilloscope works on the principle, when the electron beam falls on the fluorescent screen forms a wave on the screen. As a result, we can know understand the strength of the wave from the brightness of the wave. Uses A cathode ray oscilloscope is used in the screen of televisions and computer monitors. It is also used to study the waveform of a repetitive electronic signal. Q.5 What are electronic logic gates? Describe different types of logic gates. (Ans) electronic logic gates To keep the precious things, cash or important documents in safe custody safes are used. The doors of such safes are opened and closed by a set of switches to be used in proper order. This synthetic order system is called electronic logic gates. If the buttons of the safe are pressed in proper order, then the safe will opened. Otherwise, the door will start alarming. Types of logic gates The different types of logic gates are as under. i) NOT-GATE The NOT gate is also known as inverter, because it changes “ON” to “OFF” and “OFF” to “ON”, that is if input is zero “0” then the output will be one “1”. As shown in the truth table below. Truth table Input Output A A 0 1 1 0 Symbol of “NOT” gate A ii) OR-GATE In case of “OR” gate the output will be “ON” if both the input or any one input is “ON” and bulb will be on. The output will be “OFF” if both inputs are “OFF” as shown in truth table below. Truth table Input Input Output A B A+B 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 Symbol of “OR” gate A+B iii) AND-GATE in case of “AND” gate the output will be “ON” if both the input are “ON” and the bulb will on and output will be “OFF” if any one of them is “OFF” as shown in truth table below. Truth table Input Input Output A B A.B 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 Symbol of “AND” gate A AB B iv) NAND-GATE In case of “NAND” gate the output of “AND” gate is inverted, which can be explained in truth table below. Truth table Input Input Output A B A.B 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 Symbol of “NAND” gate A AB B v) NOR-GATE In case of “NOR” gate the output of “OR” gate is inverted, which can be explained in truth table below. Truth table Input Input Output A B A B 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 Symbol of “NOR” gate A B A B USES OF LOGIC GATES Wireless door and window alarm To prevent that your child do not walked outside the front door without telling you, a special type wirless door alarms can prevent such a risk and keep your child safely inside. When the door is opened the alarm emits a continous 120 db sound (until the door is shut) to tell you that your child is at risk of leaving. Other uses of logic gates Logic gates are used in computers, mobiles, calculators, digital watches, etc. Short questions 1. What are the logic values of P, Q and R in the following logic circuit? See fig in book. A. The value of P is 1 (NOT-GATE), the value of Q is 1 (AND-GATE), while the value of R is 1 (OR-GATE). 2. Identify the logic gates below and write out their respective truth table? See fig in book. See Q.5 Name five digital devices that are commonly used in everyday life. Name of five digital devices that are commonly used in daily life is; 1. Computer 2. Telephone 3. Fax machine 4. Calculator 5. Digital watch A. 3. A. 4. A. What do you mean by analogue? See Q.1