* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - SOCIAL SCIENCE
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
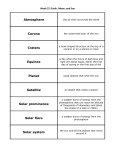
U. 1 THE UNIVERSE TEACHERS: Noelia Fernández y Sara Pascual 1 AROUND THE SOLAR SYSTEM - Celestial bodies: the objects we can see in the sky are called celestial bodies. They are luminous and nonluminous. - Planetary system: it has at least one star, different planets and celestial bodies that orbit around it. STARS They give off their own light and heat. THE SUN - It’s the centre of the solar system. - It give us light and heat, that are vital on our planet. LUMINOUS CELESTIAL BODIES PLANETS - They are shapped almost like spheres. - They orbit around a star. EARTH - It orbits around the Sun and splits around itself. - Most of its surface is taken up by water. NON-LUMINOUS CELESTIAL BODIES PLANETARY SYSTEMS 3 EARTH Is called the ‘blue planet’ 5 JUPITER Is the biggest planet 7 URANUS Is the coldest planet 1 MERCURY Is the closest to the Sun 8 NEPTUNE Is the furthest planet 2 VENUS Is the hottest planet 4 MARS Is called the ‘red planet’ 6 SATURN Has giant rings around it 2 EARTH SPINS - Eatrh’s rotation - Day and night EARTH’S ROTATION Earth’s axis in an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole. Earth spins on its axis. This movement is called rotation. DAY and NIGHT It is DAY where the Sun’s rays reach the planet. It is NIGHT where the Sun’s rays don’t reach the planet. Earth takes 24 hours to completely spins around its axis. 3 EARTH ORBITS - Eatrh’s revolution - The seasons EARTH’S REVOLUTION Revolution is Earth’s movement around the Sun. It takes 365 days to orbit all the way around the Sun. In other words, one year. SPRING It is warmer and the days get longer. WINTER In winter it is colder and the days are cold. SUMMER It is very hot because the Sun’s rays reach you directly. AUTUMN The days are shorter and it starts to get colder. THE SEASONS Because of Earth’s titled axis, our inclination towards the Sun changes as Earth orbits the Sun. This produces the seasons. 4 THE MOON - The Moon orbits - The phases of the Moon - The Moon and Earth’s tides THE MOON ORBITS The moon is Earth’s satellite. A satellite is a spherical celestial body that orbits around a planet. It takes the moon 28 days to orbit around Earth. THE PHASES OF THE MOON Satellites are nonluminuous celestial bodies. The moon only looks bright because the Sun is shining on it. Depending on the moon’s position in relation to Earth and the Sun, we can see different parts of it. They are called PHASES OF THE MOON. FULL MOON WANING MOON NEW MOON WAXING MOON THE MOON AND EARTH’S TIDES HIGH TIDE When the moon is right above you, it attracts Earth’s water and there is a high tide. LOW TIDE When the moon is not right above you, there is a low tide. 5 WE ARE PART OF THE UNIVERSE - How scientists study the universe OUR GALAXY: THE MILKY WAY A galaxy is a group of stars and planetary systems. Our solar system is part of a galaxy with other suns, stars, planets and satellites. The universe is made up of all celestial bodies that exist: - Planets - Satellites - Asteroids - Stars - Planetary systems - Galaxies… HOW SCIENTISTS STUDY THE UNIVERSE SPACE TELESCOPES go far out into space and send information and photographs back to Earth. To see celestial bodies in more detail, astronomers use telescopes on Earth or on outer space. LAND TELESCOPE QUESTIONS Answer TRUE or FALSE. a) The Sun is a planet that gives us heat and light. b) The Sun orbits around a star called Earth. c) Jupiter is the smallest planet in the solar system. d) Mercury is the closest planet in the solar system. Answer the questions about the picture. a) Which of Earth’s movement is this? b) Why is it day in one part of Earth and night in the other? a) Earth takes a day to completely spin around its axis. b) Earth’s axis is not inclined. c) Earth’s axis runs from the North Pole to the South Pole. Find out the wrong fact if exists. Match the words above with the definitions below. SOLAR SYSTEM The star of the solar system. THE SUN The third planet in the solar system. SOLAR SYSTEM The galaxy we are in. EARTH A planetary system where Earth is. Match the seasons with their definitions. SPRING The days are short and it is colder. SUMMER The days get longer and it is warmer. AUTUMN The days are shorter and it starts to get colder. WINTER The days are long and it is very hot. Read the questions and answer. a) In which Moon phase does the Moon get none of the Sun’s rays? b) In which Moon phase does the Moon get all of the Sun’s rays? c) In which phase does the Moon look like it is getting bigger? d) In which phase does the Moon look like it is getting smaller? solar Sun planet galaxy system a) Earth is our ………………… and it orbits around the ……………… Earth is in the solar …………………… a) The ………………….. system is in a ……………………. called the Milky Way. Use the words given to complete the sentences. Say TRUE or FALSE. a) Telescopes let scientists see things that are too small to see. b) The scientists that use telescopes are called astronauts. c) Telescopes can be on land or in space. END