* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6.2 - The Blood System
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
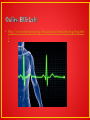
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
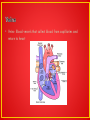
Nicole Boylan, Ava Gulino & Jack McBride • Arteries are blood vessels that take blood away from heart that hasn’t reached capillary • Arteries used by autonomic nervous system; used to maintain blood pressure • Arteriole- smallest of arteries • Capillary bed- network of capillaries that drain into single venule • Arteries convey blood @ high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body • Arteries have muscle cells and elastic fibers in their walls • The muscle & elastic fibers assist in maintaining blood pressure between pump cycles • Blood flows through tissues in capillaries. Capillaries have permeable walls that allow exchange of materials between cells in the tissue of the capillary • Veins collect blood @ low pressure from the tissues of the body & return it to the atria of the heart • Valves in veins & the heart ensure circulation of blood by preventing backflow • There is a separate circulation for the lungs • The heart beat is initiated by a group of specialized muscle cells in the right atrium called the sinoatrial node • This node acts as a pacemaker • This node sends out an electrical signal that stimulates contraction as it is propagated through the walls of the atria & then the walls of the ventricles • The heart rate can be increased or decreased by impulses brought to the heart through 2 nerves from the medulla of the brain • Epinephrine increases the heart rate to prepare for vigorous physical activity • Veins- Blood vessels that collect blood from capillaries and return to heart • Human heart is a pair of side-by-side pumps; form 2 major routes for blood to flow • Right side of heart- pulmonary circulation (lungs) • Left side of heart- systematic circulation (organs) • Majority of tissue that makes up heart is muscle • Sinoatrical node (SA Node)- acts as pacemaker for heart by sending “electrical signal” to contract • Heart activity/blood pressure increases during activity • Fatty/unhealthy foods can cause plaque buildup in arteries and cause heart attacks • The First artificial heart pacemaker was plugged into a wall socket! • The Blue whale has the largest heart weighing over 1,500 pounds! • Your heart beats around 100,000 time a day! • Each minute your heart punmps through about one and a half gallons of blood! • http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/ecg/ecg.htm l • Jack: Oh my goodness! I am having discomfort in my chest and in my upper body! I am also short of breath and nauseous… • Ava: What do you think is wrong with him? • Nicole: These might be signs of a heart attack! • Ava: Wow really? What can we do to help him? • Nicole: Let’s call 9-1-1 • A link showing what your heart does during a heart attack: http://watchlearnlive.heart.org/CVML_Player.php?moduleSelec t=hrtatk • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ruM4Xxhx32U Cute video on the heart and its functions. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EA2DY0tjpFI Slightly less cute video explaining with more detail the heart and its functions. • http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/cardiology-virtual-lab Fun virtual lab! • Enjoy!