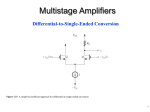
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Attachment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Learning through play wikipedia , lookup
Attachment theory wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Attachment in adults wikipedia , lookup
Maternal deprivation wikipedia , lookup
Attachment measures wikipedia , lookup
CHAPTER 3 Infancy and Childhood PHYSICAL, PERCEPTUAL, AND LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT Developmental Psychologists study main issues: 1. Continuity versus stages of development 2. Stability versus change 3. *Nature versus nurture *Behavior develops as a result of the interactions of both heredity and environment NEWBORNS Before birth some: hiccup, suck thumb Capacities: See, hear, smell, and respond at birth Most have: grasping reflex and rooting reflex Smile, show signs of surprise or fright Average: 7.3 pounds at birth (20 -25 by first year) and 18 – 22 inches Space of 2 years: will be able to walk, talk, and feed themselves MATURATION Infants grow/develop according to a built in plan: 3 mos. – lift head 4 mos. – true smiling 5-6 mos. – grasp objects 8-10 mos. – crawling and pulling self up Approx 12 mos. – will begin walking *Unless underfed, restricted movement or deprivation of human contact or things to look at, will develop more or less to this schedule* MATURATION Maturation plan is unique to each child May vary on time frames (Ex: walking: happen 9 – 18 mos; not walk by about age 2, tests to determine if something is wrong) Infants also have own temperament: Active vs quiet, cuddly vs aloof, criers vs hardly whimpering Infants may not mature according to the same timetable, but progress through same sequential steps PERCEPTUAL DEVELOPMENT Prefer looking at human faces and patterned material Benefit greatly from human (parental) touch Depth perception: Very young, little to no depth perception 6 mos and older – gain depth perception (crawling/movement LANGUAGE DEVELOPMENT Reinforced vs Inborn behavior Ist year: cooing and babble (includes every sound humans can make Imitate speech of parents and brothers and sisters First real words usual refers to things they can see and touch By early 2nd year beginning to speak more clearly 500 – 1500 words – telegraphic speech From 18 mos. To 5 years, add approx. 5 to 10 words a day COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Piaget – intelligence or ability to understand develops gradually Object permanence = about 7 – 12 mos. Representational thought = approx. 14 mos. Conservation = between the ages of 5 and 7 EMOTIONAL DEVELOPMENT Begins by attaching to specific people After attachment bond; most infants will experience: Stranger anxiety Separation anxiety 4 PATTERNS OF ATTACHMENT Secure attachment – need to explore, welcomes mother back when returns Avoidant attachment – avoid/ignore mother when leaves and returns Resistant attachment – not upset when mother leaves, acts angrily when she returns Disorganized attachment – behave inconsistently PARENTING STYLES AND SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT Parenting Styles: 1.) Authoritarian – parents boss, children have no say 2.) Democratic (authoritative) - children participate in decision; but parents have right to veto plans 3.) Permissive (laissez-faire) - children have final say; parents give up their child-rearing responsibilities (no rules) ignoring the young people SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT Learning the rules of behavior of the culture in which you were born and grow up. Acceptable vs Unacceptable behavior What is meaningful and valuable Learning to live with other people and yourself THEORIES OF DEVELOPMENT Freud’s Psychosexual Development - (child want immediate gratification and parent restricts it in some way) Erikson’s Psychosocial Development – individual goal is to satisfy desires with social needs Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development – stages of importance of being able to see other people’s point of view – deciding what is right and wrong