* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWI Power Point
Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
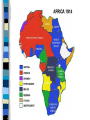
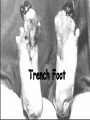
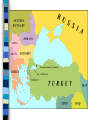
World War I The Great War 1914 - 1918 Fundamental Causes Militarism Alliances Imperialism Nationalism – 2 kinds Militarism Conscription (draft), training, build-up – each sought military superiority German military tradition (Prussia) Armament manufacturers increased supply; Krupp German naval build-up to compete with GB Alliances Triple Alliance – Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy – Central Powers – added Turkey and Bulgaria Triple Entente – France, Russia, Britain – France desired Alsace Lorraine back (Franco Prussian War) – England threatened by German naval build-up – Became “Allies” Creates tension, mistrust, fear Imperialism - Examples Russia and Austria-Hungary – rivals in the Balkans; France and Germany clashed over Morocco England and Germany (highly industrialized) competed for colonies in Africa and Middle East Nationalism Intense patriotism fueled war France wanted – Lost in Franco-Prussian War Serbia wanted Austria-Hungarian territory inhabited by Yugoslav peoples Russian kinship w/Slavic people in Balkans Subject nationalities - Czechs, Slovaks, Serbs, Yugoslavs, Slovaks, Poles, desired independence Balkans – “powder keg of Europe” Immediate Cause Assassination of Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand June 28, 1914 in Sarajevo Gavrilo Princip – Serbian nationalist The Black Hand The First World War: Long term - Why? 1. Alliance system 2. Imperialist Competition 3. Stockpiling of Weapons Franz Ferdinand, Archduke of Austria and his Wife Sophie, Duchess of Hohenberg one hour before their deaths, June 28, 1914 Short term Assassination of Franz Ferdinand of the AustroHungarian Empire Assassination and War Austria declares war on Serbia Russia mobilizes to help Serbia Germany declares war on Russia & France Invades France through neutral Belgium (“atrocities”) England declares war on Germany Assassination and War Alliance all fall into place Unstoppable chain of events Nations fueled by militarism, alliances, imperialism, nationalism honored their alliances War to end all wars Other Nations Join Central Powers – Germany – AustriaHungary – Turkey – Bulgaria Allied Powers – GB, France and Russia – Serbia – Belgium – Italy (changed sides) – Japan – U.S. - 1917 Countries Joining Allies Australia Brazil Canada China Costa Rica Cuba Greece Guatemala Haiti Honduras Japan Liberia Montenegro New Zealand Nicaragua Panama Portugal Romania San Marino Siam (Thailand) Side note on Japan 1905 – Russo Japanese War Japan attacked Russian bases Defeated Russia easily; fueled nationalism in Asia and Africa Emergence of the FIRST non-European power on the world stage Rapidly industrializing and militarizing Teddy Roosevelt brokered the peace treaty – won Nobel Peace Prize Von Schlieffen Plan - German Quick, decisive attack through neutral Belgium Goal: Destroy France quickly; one front Fails, First Battle of the Marne; taxis sent to the front 600 mile Western Front is established Stalemate Western Front Trenches – unaccustomed to this Mud, filth, lice, rats, trench foot, disease “No man’s land” – between trenches “Over the top” – suicidal charges into machine guns, barbed wire Deadly battles for small pieces of land War of attrition – wear the enemy down by constant killing Video Clips Trench Warfare: http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-i/world-war-ihistory/videos/trench-warfare WWI Firsts: http://www.history.com/topics/worldwar-i/world-war-i-history/videos/wwi-firsts Soldiers Learn to pack: http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-i/world-war-ihistory/videos/world-war-i-soldiers-learn-to-pack New Weapons of War Machine guns Tanks Flame Throwers Airplanes Zeppelins Poison Gas Barbed Wire Grenades Torpedoes Submarines Trench Warfare Giant Artillery Photo Gallery http://www.history.com/topics/worldwar-i/world-war-i-history/pictures/worldwar-i-trench-warfare/german-front-linetrenches http://www.history.com/topics/worldwar-i/world-war-i-history/pictures/worldwar-i-technology/postcard-of-a-us-armyballoon-and-hangar War in the East – 2 front war More mobile, no trenches or stalement Russia unprepared, not industrialized, unemployment, dissension Russians defeated at Tannenburg and Galicia; almost out of the war Italy changes sides – 1915 (Allies) Germany turned attention back to the West Battles War of attrition – wear enemy down Verdun – 1916 – 700,000 died over a few miles of land Ypres – first use of poison gas Gallipoli – Dardanelles (Bulgaria and Ottoman Empire w/Central Powers) Disastrous defeat of British and Australian troops on the beaches (ordered by Churchill) Battles cont. Somme – Allied forces helped by US stopped Germans (first battle to use tanks) Chateau-Thierry, St. Mihiel, Ypres – aided by US under John J. Pershing American Expeditionary Force – AEF– key allied victories Enter in April, 1917 “Doughboys” head “over there” Reasons for U.S. Entry Pres. Woodrow Wilson – neutrality “Unrestricted submarine warfare” – U- Boats – Lusitania – British, 128 Americans died – http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-i/world-war-ihistory/videos/u-boats-sink-the-lusitania-in-1915 Hostility toward Germany – Invasion through neutral Belgium – Zimmerman note – Germans promised Mexico U.S. territory if they attacked U.S. U.S. Entry cont. Idealism – “the world must be made safe for democracy” (Wilson) Kinship/history with democratic allies Security – feared autocratic and militaristic Germany in Europe Significance: – Turned tide of battle towards Allies – Broke U.S. policy of isolation – America emerges as a world leader Home Front – Impact Total War – involving complete mobilization of resources and people 1. Increased government power 2. Economic controls 3. Manipulation of public opinion (propaganda) to keep war effort going Home Front cont. Gov’t. increases power during war – conscription – Selective Service Act Free market capitalism temporarily put aside – price, wage, rent controls, rationing of food and supplies, regulation of imports, control of transportation – planned economies WIB – War Industries Board – Bernard Baruch CPI – Committee of Public Information – George Creel All citizens were made part of the war – Victory gardens, Liberty bonds Home Front cont. Enthusiasm weakens as war drags on Censorship of press, civil liberties suspended Espionage Act – silence criticism of war Eugene V. Debs – Socialist leader imprisoned Schenk v. U.S. – “clear and present danger” Conscientious objectors – moral or religious opposition to war Intense propaganda (started w/Belgium – “Germans cut off hands of Belgian children!”) U.S. propaganda strong also (see PP) Home Front cont. Many wanted to support Central Powers (Irish, German – why?) Women took jobs men left behind Lower wages, no job security Most lost jobs as men returned Overall, gave boost to women’s movement and status Great Migration – many African Americans move north for opportunities Home Front Lots of German words changed: – Sauerkraut – Liberty cabbage – German measles – Liberty measles – Hamburger – Liberty sandwich – Dachshund – Liberty pups – Gesundheit – frowned upon and illegal in certain places