* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
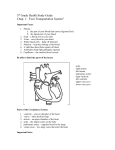
Cardiovascular System CHAPTER 7 Overview: what we will cover Combining forms of terms Anatomy & physiology of the heart Anatomy & physiology of the vascular system Coronary Artery Disease Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Medications Electrical Conduction of the heart Types of Aneurysms Additional terms to know Combining Forms for the Cardiovascular System angi/o vas/o vascul/o vessel angiogram vasospasm vascular aort/o aorta aortic Combining Forms for the Cardiovascular System arteri/o artery arteriosclerosis ather/o fatty (lipid) paste atheroma atri/o atrium atrioventricular ventricul/o ventricle (belly or pouch) ventricular Combining Forms for the Cardiovascular System cardi/o heart cardiology coron/o circle/crown coronary my/o muscle myocardial Combining Forms for the Cardiovascular System pector/o steth/o chest pectoral stethoscope sphygm/o pulse sphygmomanometer thromb/o clot thrombocyte Combining Forms for the Cardiovascular System ven/o phleb/o vein venous phlebitis varic/o swollen/ twisted vein varicosis Cardiovascular System Overview Consists of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood throughout the body Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Structure of the Heart Four Chambers Right atrium (upper chamber) Left atrium (upper chamber) Right ventricle (lower chamber) Left ventricle (lower chamber) Structure of the Heart (continued) Valves — Open and close with the heartbeat to maintain one-way flow of blood through the heart tricuspid valve — located between right atrium and right ventricle mitral (bicuspid) valve — located between left atrium and left ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve — opening from right ventricle to pulmonary artery aortic valve — located between left ventricle and aorta Layers of the Heart endocardium myocardium Thick, muscular layer epicardium membrane that lines the interior cavities of the heart Outer membrane Pericardium is the loose, protective sac that surrounds and encloses the heart Structures of the Heart Blood Vessels “oxygenated” Aorta Small vessels receive blood from arteries Cappillaries Tiniest of vessels that join the arteries & veins Venules Vessels that carry blood from the heart to… Arterioles Large artery branching from the ventricle Arteries “un-oxygenated” Small vessels that gather blood from the capillaries into the veins Veins Carry blood from the veins to the heart. Exception to the rule The pulmonary artery carries “un-oxygenated” blood to the lungs from the right ventricle Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins into the left atrium Coronary Artery Disease Coronary Arteries & Angiogram /c stent https://youtu.be/-BuazAhs7uA https://youtu.be/I45kJJoCa6s Blood Pressure & The Heart *The heart is a pump Force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of the arteries, veins and heart chambers Determined by the volume (think of hemorrhagic pt or dissecting aneurysm) of blood, the space within the arteries and arterioles, and the force of the heart contractions Blood Pressure Terms Systole (aka systolic) Diastole (aka diastolic) period in the cardiac cycle when the heart is in contraction and blood is ejected through the aorta and pulmonary artery period in the cardiac cycle when blood enters the relaxed ventricles from the atria normotension normal blood pressure (110/70) Blood Pressure Medications ACE inhibitors Beta Blockers End in …pril End in ...olol Calcium Channel Blockers End in …ipine Except diltiazem & verapamil Diuretics End in …ide Except spironolactone, aldactone, & chlorthalidone Electrical Conduction of the Heart SA (sinoatrial node) Pacemaker of the heart AV (atrioventricular node) Bundle of His Purkinje fibers Types of Aneurysms Additional Terms to Know… Hypo /hypertension Infarct Arteriosclerosis Angina pectoris Atherosclerosis Claudication Thrombus vs embolus Vegitation Stenosis, constriction, occlusion, ischemia Palpitation Not to be confused with palpate Additional Terms to Know… Arrhythmia or dysrhythmia Fibrillation Heart block Cardiomyopathy Congenital anomaly of the heart ASD (atrial septal defect) CHF CAD HTN MI DVT Myocarditis, pericarditis, & phlebitis Additional Terms to Know… Auscultation ECG or EKG ICD Cardioversion Pacemaker