* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Barbiturates
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Effects of long-term benzodiazepine use wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
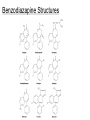
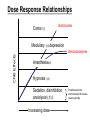
Sedatives And Anxiolytic Drugs 镇静和抗焦虑药 The Scream (Edvard Munch, 1893) Anxiety (Edvard Munch, 1894) Anxiety • • • • • • • • feeling of helplessness difficulty in concentrating irritability易怒& insomnia失眠[ GI disturbances muscle tension excessive perspiration大汗 palpitations心悸 dry mouth dread恐怖 Clinical Disorders disorder 急性焦虑症 Obsessive-compulsive disorder 强迫性(精神) 障碍 Social phobia 社会恐怖 Social anxiety disorder 社交焦虑障碍 Generalized anxiety disorder 一般焦虑症 Specific phobias 特异(单-)恐怖 Panic Drug Choices Older: • Barbiturates (drugs ending in “barbital”) • Alcohols / Choral Hydrate Newer: • Benzodiazepines (drugs ending in “lam” or “pam” such as Diazepam)** • Benzodiazepine “Like” (zolpidem & zaleplon) • 5-HT1A partial agonist (buspirone丁螺环酮) ** The most commonly used anxiolytics Benzodiazapine Structures Barbiturates. Benzodiazepine Mechanism of Action • GABAA receptor composition varies in different regions • BNZs bind to receptors with alpha & gamma subunits. • BNZ binding “enhances” the effect of GABA on the Clcurrent •BNZs increase the frequency channel openings in presence of GABA • BNZs exert no effect in the absence of GABA of Cl- Benzodiazepine Mechanism of Action •The effects & binding of BNZ was blocked by flumazenil氟马西尼(BNZ antagonist) • Not all BNZs are identical (may be due to differences in effects on different GABAA R isoforms) • BNZs - high doses commonly produce anterograde顺 行的,前进的amnesia遗忘. •Retrograde amnesia (逆行性遗忘) Barbiturates Multiple mechanisms Bind to GABAA receptors at different site • Don’t compete for BNZ binding & are not blocked by flumazenil • Increase the duration of Cl- channel openings GABA Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Barbiturate 1. Increase GABA effect (increased duration of openings) 2. Directly activate GABAA channels at high concentrations 3. Block effects of glutamate NT* 4. Block Na channels * Glutamate is an excitatory NT Dose Response Relationships Coma昏迷 Barbiturates Medullary 延髓 depression CNS Effects Benzodiazepines Anesthesia麻醉 Hypnosis 催眠 Sedation, disinhibition, anxiolysis抗焦虑 Increasing dose Possible selective anticonvulsant & musclerelaxing activity Buspirone (BuSpar ®)丁螺环酮 • • • • • Anxiolytic but not sedating 5-HT1A partial agonist No drug dependence Slow onset of action (week or more) Indication: - chronic anxiety disorders (generalized anxiety disorder) - anxiety disorders in patients with history of drug dependence or abuse Zolpidem (Ambien ®) & Zaleplon (Sonata ®) • Benzodiazepine “like” drugs – Bind to a subset of GABAA receptors w/ 1 subunits – Effects are blocked by flumazenil (BNZ antagonist) • Produce pure sedation (without anxiolytic, anticonvulsant or muscle relaxing effects) • Minimal effect on REM sleep • Indications: – Insomnia • Advantages: less daytime impairment vs. BNZs Chloral hydrate • • • • An older sedative-hypnotic Institutional惯例的,公共团体的,use (cheap) Converted to trichlorothanol Slow clearance Pharmacodynamic Effects BNZs & Barbiturates: • Medullary Depression - A cause for respiratory arrest • Tolerance & Dependence - Physiological tolerance - Physiological dependence (w/ withdrawal) - Withdrawal: anxiety, tremors, seizures - Cross tolerance - Buspirone - no dependence - Zolpidem & zaleplon - very low dependence liability Clinical Uses Anxiety Disorders – Alprazolam & Clonazepam - esp. useful in panic & phobic disorders (greater efficacy) – Buspirone - chronic forms of anxiety • Little sedative effect, slow onset • No drug dependence (Rx. Pts w/ history of drug abuse) Clinical Uses Insomnia – BNZs (estazolam,flurazepam, trizolam) • Day time sedation side effect • REM sleep reduced; rebound – Zolpidem & Zaleplon • Less daytime sedation* • No effect on REM sleep – Other Drugs: • Antihistamines (Excedrin PM ®) * w/o anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant side effects) Clinical Uses Alcohol Withdrawal戒酒 – Benzodiazepines are useful because: • Exhibit cross tolerance w/ alcohol • Have anticonvulsant effects • Little respiratory depression BNZ Metabolism • Chemical structures of barbiturates and other sedative-hypnotics. • hepatic metabolism, active metabolites • elimination half life duration of action • most have half lives >10 hrs. Enzyme Induction • Barbiturates (cyt P450) Toxicity • Cognitive impairment, daytime sedation • Elderly require lower doses • Anterograde amnesia • Additive CNS depression •Respiratory & CV depression