* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civil War Cavalry
Battle of Appomattox Station wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Cavalry in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
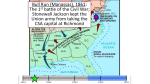
Pageant 20-22 Review Northern Advantages • • • • Strong Navy Transportation System Population Advantage- 22 to 9 million Immigrants to fill ranks Southern Advantages • Fighting a defensive war • Initially higher morale • More talented officers James Longstreet Stonewall Jackson Jefferson Davis • Former cabinet member under Buchanan • Defied rather than led public opinion • Hampered by CSA government emphasizing states rights Confederacy • CSA hoped that demand for cotton would lead to European intervention Great Britain • Influenced by• Need for US grain • Realization that they may use blockades in the future US/Great Britain Relations • Trent Affair almost resulted in war • CSA diplomats were removed from a British ship by federal authorities CSA Alabama • Effective in damaging Union shipping Abe Lincoln • Had the advantage of a long established government • Used dubious legal means to keep the border states • Was willing to preserve the Union with or without slavery Lincoln’s Methods • Declared blockade without congress • Increased size of Federal Army • Suspended habeas corpus to arrest antiunionists • “Supervised” voting in border states • Suspended certain newspapers and arrested editors Border Sates • Large Population • Supply of horses and mules • Manufacturing capacity • Navigable rivers Fort Sumter • In Charleston Harbor • Lincoln sent supplies, but viewed as reinforcements by the South • Northerners viewed the bombardment as an attack on the Union Call to Arms • Northern Army was only 16K strong • Lincoln call for 75K additional – Easily met Conscription • South turns to draft 1862 • North- 1863 Northern Soldiers • Eventually became known for discipline and determination • Benefitted from a larger population • Many from the working classes • Mainly a volunteer army First Bull Run • Showed that war would not be quick Shiloh • Showed that war would be bloody Peninsula Campaign • The Union was stopped short of Richmond • Union strategy turned to “total war” France, Great Britain, and Germany • Favored a Civil war in the US- hoping it would weaken the American presence in the hemisphere Civil War Congress • Legislated to aid Northern InterestsTax on Tobacco and alcohol increased Income tax levied for 1st time Morrill Tariff Act Issued Greenbacks National Banking System 1864 Election • Lincoln (Rep.) defeated McClellan (Dem.) Antietam • One of two major battles fought on Union soil • Probably prevented aid to the South from GB and France Vicksburg • CSA forces surrender on July 4, 1863 • Leads to union control of the Mississippi River Gettysburg • July 1-3, 1863 • 30% of Lee’s forces destroyed • Resulted in CSA inability to launch offensive war Gettysburg • Lee invaded the North, hoping to strengthen the Northern peace movement • The Union had strong defensive lines • Union victory doomed the Southern cause • Meade slowly pursued Lee • One of two major battles fought on Union soil Ulysses S. Grant • Started fighting in the West • Believed in assailing the enemy forces directly and simultaneously Civil War Cavalry • Considered the eyes of the army. • Also used for foraging and harassing actions. Monitor and Merrimack • Basically fought to a draw • Monitor was later lost in storm • Merrimack was destroyed by Southern soldiers to avoid capture by the North William T. Sherman • Began fighting in the West • Felt that a total war of destruction would end the war as quickly as possible Appomattox Court House • War ended with the South short of supplies • Lee felt it was futile to continue John Wilkes Booth • Assassinated Lincoln as a desperate measure to rescue the Confederacy • A calamity for the South George Armstrong Custer • Decorated Union cavalry officer. • Actions in the spring of ’65 helped end the war. Results of the War • Expanded federal powers of taxation • End of nullification and secession • Creation of the first federal social welfare system • End of slavery Post war North • Economy was stronger than before Postwar South • Completely destroyed- physically and economically Postwar South • Radical Reconstruction State Governments- passed needed legislation and reforms • Defeated CSA leaders were pardoned in 1868 • Viewed as conquered provinces by the Radical Republicans Andrew Johnson • Democrat from Tennessee- viewed as a champion of poor whites • Named Lincoln’s running mate in ’64attempt to attract War Democrats and pro-Union Southerners Andrew Johnson • As Pres- against the Freedman’s Bureau • Reconstruction based on restoration of Southern states after a few, basic conditions were met • Impeached for improperly dismissing Sec. of War Stanton Freed Blacks • • • • Searched for lost family Got married Formed own churches Gained educations Freedmen's Bureau • Headed by O.O. Howard • Intended to provide relief supplies, labor referral, arbitration services and a local court system Freedman’s Bureau • Most successful with education Thaddeus Stevens • Believed that economic gains were a priority to aid freed blacks Charles Sumner • Believed that political gains were a priority to aid freed blacks Tenure of Office Act • Officeholder appointed by Johnson and approved by Senate was to serve until Senate approved a successor • Limited Johnson’s ability to remove officials • ScalawagsSoutherners who assisted Federal reconstruction efforts • CarpetbaggersNortherners who went South during reconstruction Alaska • Purchased in 1867 from Russia • Russians felt they would lose it to GB • Felt selling it to the US, they would at least get money 1868 Election Ku Klux Klan • Intimidated blacks and undermined them politically Amendments 13th- Abolishes slavery 14th- Citizenship and civil rights to freed slaves 15th- Prohibits states from denying right to vote based on race, color or previous condition of servitude Reconstruction • Fell short of goals • Southern hierarchy was similar to pre Civil War • Ended with Federal troops leaving the South in 1877 Women in the Workforce • Women filled industrial jobs opened by men serving in the war. • Also served as clerks in Washington D.C. • Several hundred served in the military and some were spies. Black Codes • Attempt to ensure a stable and subservient labor supply 1872 Election Gilded Age • Term coined by Mark Twain • Showed how the prosperity of society was not penetrating to all Americans