* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Prediction of B cell epitopes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
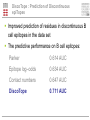
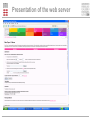
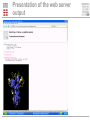
Prediction of B cell epitopes Pernille Haste Andersen Immunological Bioinformatics CBS, DTU [email protected] B cells and antibodies Antibodies are produced by B lymphocytes (B cells) Antibodies circulate in the blood They are referred to as “the first line of defense” against infection Antibodies play a central role in immunity by attaching to pathogens and recruiting effector systems that kill the invader What is a B cell epitope? B cell epitopes Accessible and recognizable structural feature of a pathogen molecule (antigen) Antibodies are developed to bind the epitope with high affinity by using the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) Antibody Fab fragment B cell epitope Motivations for prediction of B cell epitopes Prediction of B cell epitopes can potentially guide experimental epitope mapping Predictions of antigenicity in proteins can be used for selecting subunits in rational vaccine design Predictions of B cell epitopes may also be valuable for interpretation of results from experiments based on antibody affinity binding such as ELISA, RIA and western blotting Computational Rational Vaccine Design >PATHOGEN PROTEIN KVFGRCELAAAMKRHGLDNYR GYSLGNWVCAAKFESNF Rational Vaccine Design B cell epitopes, linear or discontinuous? Classified into linear (~10%) and discontinuous epitopes (~90%) Databases: AntiJen, IEDB, BciPep, Los Alamos HIV database, Protein Data Bank Large amount of data available for linear epitopes Few data available for discontinuous epitopes In general, B cell epitope prediction methods have relatively low performances Discontinuous B cell epitopes An example: The epitope of the outer surface protein A from Borrelia Burgdorferi (1OSP) SLDEKNSVSVDLPGEMKVLV SKEKNKDGKYDLIATVDKLEL KGTSDKNNGSGVLEGVKADK CKVKLTISDDLGQTTLEVFKE DGKTLVSKKVTSKDKSSTEE KFNEKGEVSEKIITRADGTRLE YTGIKSDGSGKAKEVLKG • ..\Discotope\1OSP_epitope\1OSP_epitope.psw A data set of 3D discontinuous epitopes A data set of 75 discontinuous epitopes was compiled from structures of antibodies/protein antigen complexes in the PDB The data set has been used for developing a method for predictions of discontinuous B cell epitopes Since about 30 of the PDB entries represented Lysozyme, I have used homology grouping (25 groups of non-homologous antigens) and 5 fold cross-validation for training of the method Performance was measured using ROC curves on a per antigen basis, and by weighted averaging of AUC values Epitope log-odds ratios Table 1. The Parker hydrophilicity scale and epitope log-odds ratiosa Frequencies of amino acids in epitopes Amino acid Parker Log-odds Ratios D 2.460 0.691 compared to frequencies of non-epitopes E 1.860 0.346 N 1.640 1.242 S 1.500 -0.145 Q 1.370 1.082 G 1.280 0.189 K 1.260 1.136 T 1.150 -0.233 R 0.870 1.180 P 0.300 1.164 H 0.300 1.098 C 0.110 -3.519 A 0.030 -1.522 Y -0.780 0.030 V -1.270 -1.474 M -1.410 0.273 I -2.450 -0.713 F -2.780 -1.147 L -2.870 -1.836 W -3.000 -0.064 Several discrepancies compared to the Parker hydrophilicity scale which is often used for epitope prediction Both methods are used for predictions using a sequential average of scores Predictive performance of B cell epitopes: Parker 0.614 AUC Epitope log–odds 0.634 AUC a Amino acids are listed with descending hydrophilicity using the values of the Parker scale. 3D information: Contact numbers Surface exposure and structural protrusion can be measured by residue contact numbers The predictive performance: Parker Epitope log–odds Contact numbers 0.614 AUC 0.634 AUC 0.647 AUC DiscoTope : Prediction of Discontinuous epiTopes using 3D structures A combination of: – Sequentially averaged epitope logodds values of residues in spatial proximity – Contact numbers .LIST..FVDEKRPGSDIVED……ALILKDENKTTVI. -0.145 +0.691+0.346+1.136+1.180+1.164 +0.346 Contact number : K 10 +1.136 Sum of log-odds values DiscoTope prediction value DiscoTope : Prediction of Discontinuous epiTopes Improved prediction of residues in discontinuous B cell epitopes in the data set The predictive performance on B cell epitopes: Parker 0.614 AUC Epitope log–odds 0.634 AUC Contact numbers 0.647 AUC DiscoTope 0.711 AUC Evaluation example AMA1 • Apical membrane antigen 1 from Plasmodium falciparum (not used for training/testing) • Two epitopes were identified using phage-display, point-mutation (black side chains) and sequence variance analysis (side chains of polyvalent residues in yellow) • Most residues identified as epitopes were successfully predicted by DiscoTope (green backbone) ..\Discotope\1Z40_epitope\1Z40_movie.mov DiscoTope is available as web server: http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/DiscoTope/ Future improvements Add epitope predictions for protein-protein complexes Visualization of epitopes integrated in web server Testing a score for sequence variability fx based on entropy of positions in the antigens Combination with glycosylation site predictions Combination with predictions of trans-membrane regions Assembling predicted residues into whole epitopes Presentation of the web server Presentation of the web server output Acknowledgements DiscoTope Ole Lund Ideas, supervision and support Morten Nielsen Ideas, development of method and web server Nicholas Gauthier Improving the method, improving the web server