* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AAA 15) Constructivism in International Relations
State (polity) wikipedia , lookup
Hegemonic stability theory wikipedia , lookup
Offensive realism wikipedia , lookup
Green theory wikipedia , lookup
Polarity (international relations) wikipedia , lookup
Postdevelopment theory wikipedia , lookup
Lateral pressure theory wikipedia , lookup
War of ideas wikipedia , lookup
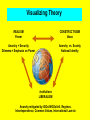
Constructivism in I.R. I. Actors and Systems II. The Role of Ideas III. Visualizing Theory I. Actors and Systems Realism and Liberalism: States and Anarchy as given problem of I.R. Constructivists are called Constructivists because they focus on how reality is ‘socially constructed’ Agent-Structure Debate – Agents = Actors (State and Non-State) – Structure = Structure of International System Q: Does the structure of the system shape actors behavior, or do actors shape the structure of the system? Theories and Agent-Structure (Neo-)Realism: Nature of the international system shapes states’ behavior Liberalism: Behavior of actors shapes the nature of the international system Constructivism: Actors and system mutually constituted II. The Role of Ideas Ideas important in their own right Consequences v. Appropriateness International Norms: shared expectations about appropriate behavior held by the international Community Changes in norms lead to changes in state behaviors Examples: Sovereignty, Colonialism, Land Mine Treaty “Anarchy is what states make of it ”(Wendt) The Role of Ideas II • One of the main assumptions of a constructivist approach is that identities, norms, and culture play important roles in world politics. Identities and interests of states are not simply structurally determined, but are rather produced by interactions, institutions, norms, cultures. It is process, not structure, which determines the manner in which states interact. • See Alexander Wendt, 'Anarchy is What States Make of It', International Organisation, 46/2, 1992. Norms and State Behavior State Behavior and International Norms “Mutually Constituted” ACTORS (States) •Behavior •Interests •Identities CONTEXT (System) •Ideas •Meanings •Rules Constructivism: Summary States and intl. system mutually constituted in IR (systemic dialectic ??) Ideas (separate from power) are important in shaping international relations Whether IR take place in an anarchical system of states or a legally ordered society of states is a function of divergent or convergent national identities Visualizing Theory REALISM Power CONSTRUCTIVISM Ideas Anarchy = Security Dilemma = Emphasis on Power Anarchy vs. Society National Identity Institutions LIBERALISM Anarchy mitigated by IGOs/INGOs/Intl. Regimes, Interdependence, Common Values, International Law etc Literaturtip • http://carbon.cudenver.edu/~mryder/itc _data/constructivism.html • Seminar CD Folder International Relations Theory Sub-folder F. FOURTH DEBATE Subfolder A. CONSTRUCTIVISM VS. POSITIVISM • Seminar CD Folder International Relations Theory Sub-folder Christmas Bonus Book Collection PDF Maja Zehfuss: Constructivism in International Relations That‘s it – folks…