Morgenthau`s Unrealistic Realism - Yale Journal of International Affairs
... judgment and looking at all states, including our own, “as political entities pursuing their respective interests defined in terms of power.” In this way, we are more likely to pursue “policies that respect the interests of other nations, while protecting and promoting those of our own.”9 Morgenthau ...
... judgment and looking at all states, including our own, “as political entities pursuing their respective interests defined in terms of power.” In this way, we are more likely to pursue “policies that respect the interests of other nations, while protecting and promoting those of our own.”9 Morgenthau ...
The Rational Design of Relations Between Intergovernmental
... 3 A small number of IGO representatives are double-hatted in that they also carry out diplomatic functions as a state representative. This excludes IGOs which do not have formal relations, such as NATO. ...
... 3 A small number of IGO representatives are double-hatted in that they also carry out diplomatic functions as a state representative. This excludes IGOs which do not have formal relations, such as NATO. ...
Theories of US Foreign Policy: An Overview
... Internal theories refer to the theories which take the domestic or internal factors into consideration and do not place an emphasis on systematic or external factors in their explanations of US foreign policy behaviour. Such domestic factors as socio-political and economic situations, public opinion ...
... Internal theories refer to the theories which take the domestic or internal factors into consideration and do not place an emphasis on systematic or external factors in their explanations of US foreign policy behaviour. Such domestic factors as socio-political and economic situations, public opinion ...
1 International Relations on State Sovereignty
... While making an attempt to bridge the gap between theory and research in international relations, but without a clear working definition of sovereignty, Thomson (a realist) presupposes liberal sovereignty to be defined in terms of “the state’s ability to control actors and activities within and acro ...
... While making an attempt to bridge the gap between theory and research in international relations, but without a clear working definition of sovereignty, Thomson (a realist) presupposes liberal sovereignty to be defined in terms of “the state’s ability to control actors and activities within and acro ...
The Agent-Structure Debate Most social sciences, political science
... George W. Bush to make conclusions about the Global War on Terrorism in the 2000s. It may evaluate different parts of the Cold War by studying Stalin, Kennedy, or Gorbachev and the bureaucratic circles that affected their decision-making processes. This level of analysis also includes cognitive theo ...
... George W. Bush to make conclusions about the Global War on Terrorism in the 2000s. It may evaluate different parts of the Cold War by studying Stalin, Kennedy, or Gorbachev and the bureaucratic circles that affected their decision-making processes. This level of analysis also includes cognitive theo ...
2015-2016 Camp Humphreys Schedule
... Schedule is subject to change. Please check the Troy University Global Campus website for changes: http://trojan.troy.edu/globalcampus. All courses are three semester hours. Weekday classes meet twice weekly for eight weeks (1800 — 2100). Weekend classes meet three weekends (0900-1700). Web-Enhanced ...
... Schedule is subject to change. Please check the Troy University Global Campus website for changes: http://trojan.troy.edu/globalcampus. All courses are three semester hours. Weekday classes meet twice weekly for eight weeks (1800 — 2100). Weekend classes meet three weekends (0900-1700). Web-Enhanced ...
Andrew Moravcsik, "Liberal Theories of International
... “preferences” in world politics at any point in time: the “tastes,” “ends,” “basic interests,” or “fundamental social purposes” that underlie foreign policy. Political institutions constitute a critical “transmission belt” by which these interests of individuals and groups in civil society enter the ...
... “preferences” in world politics at any point in time: the “tastes,” “ends,” “basic interests,” or “fundamental social purposes” that underlie foreign policy. Political institutions constitute a critical “transmission belt” by which these interests of individuals and groups in civil society enter the ...
Liberal Theories of International Relations: A Primer
... realism, institutionalism, or non-rational approaches, it is a name given to a family of related theories of international relations. Here it will not be used, as many use it in international relations, to designate theories that stress the importance of international institutions. Nor to designate ...
... realism, institutionalism, or non-rational approaches, it is a name given to a family of related theories of international relations. Here it will not be used, as many use it in international relations, to designate theories that stress the importance of international institutions. Nor to designate ...
No Slide Title
... • Alternative approaches at once differ considerably from one another, and at the same time overlap in some important ways. One thing that they do share is a rejection of the core assumptions of rationalist theories. ...
... • Alternative approaches at once differ considerably from one another, and at the same time overlap in some important ways. One thing that they do share is a rejection of the core assumptions of rationalist theories. ...
AAA7)Third Great Debate
... • The pluralists argue that the diversity of humankind - their differing political and religious views, ethnic and linguistic traditions, and so on - is best contained within a society that allows for the greatest possible independence for states, which can, in their forms of government, express tho ...
... • The pluralists argue that the diversity of humankind - their differing political and religious views, ethnic and linguistic traditions, and so on - is best contained within a society that allows for the greatest possible independence for states, which can, in their forms of government, express tho ...
International Communications
... This course describes the nature and characteristics of communication in international relations along with the role of mass media in shaping public opinion. This course discusses how to analyzes the media regarding to the propaganda, campaigns, and public relations and also analyzes how information ...
... This course describes the nature and characteristics of communication in international relations along with the role of mass media in shaping public opinion. This course discusses how to analyzes the media regarding to the propaganda, campaigns, and public relations and also analyzes how information ...
democratic peace theory
... In dyads of longstanding rivals, conflicts have only taken place when one of the two or more was non-democratic. ...
... In dyads of longstanding rivals, conflicts have only taken place when one of the two or more was non-democratic. ...
Hobbes vs. Kant: Theory, Evidence, and Policy Implications about
... the equation indicates, a combination of variables is required to reduce the likelihood of militarized conflict between states. In creating foreign policy, the United States must consider each variable of Russet and Oneal's equation to develop policy that utilizes elements of both realist and Kantia ...
... the equation indicates, a combination of variables is required to reduce the likelihood of militarized conflict between states. In creating foreign policy, the United States must consider each variable of Russet and Oneal's equation to develop policy that utilizes elements of both realist and Kantia ...
History of International Politics
... The course is a historical overview of the evolution of international politics from its early beginnings to the contemporary post-Cold War world. Its purpose is twofold. First and foremost to recall the major stages of this evolution with the view of enabling students to have an in-depth knowledge o ...
... The course is a historical overview of the evolution of international politics from its early beginnings to the contemporary post-Cold War world. Its purpose is twofold. First and foremost to recall the major stages of this evolution with the view of enabling students to have an in-depth knowledge o ...
Actors in IR
... There are many types of violent non-state actors. Their signature is the use of violence to further their financial or political goals. Terrorists use violence to intimidate, drug cartels use violence to assert their control over growers and to eliminate competitors, and traffickers use violence to ...
... There are many types of violent non-state actors. Their signature is the use of violence to further their financial or political goals. Terrorists use violence to intimidate, drug cartels use violence to assert their control over growers and to eliminate competitors, and traffickers use violence to ...
Federalism and Foreign Relations in the United States and the
... the paper firstly examines the constitutional landscape in the EU from an external vantage point, thereby creating a potential for critical assessment. Secondly, the paper explores whether lessons can be drawn from the experience of the United States in this area. The paper advances a twofold argume ...
... the paper firstly examines the constitutional landscape in the EU from an external vantage point, thereby creating a potential for critical assessment. Secondly, the paper explores whether lessons can be drawn from the experience of the United States in this area. The paper advances a twofold argume ...
The Institutionalist Paradigm
... The Institutionalist Paradigm (Liberal Institutionalism) The Institutional Foundation of International Politics ...
... The Institutionalist Paradigm (Liberal Institutionalism) The Institutional Foundation of International Politics ...
File - AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
... -land-based power (pivot area Europe) -Heartland was Eastern Europe and Central Asia Was resource rich and safe from sea power countries Spykman Rimland Theory: naval power; Britain and Japan ...
... -land-based power (pivot area Europe) -Heartland was Eastern Europe and Central Asia Was resource rich and safe from sea power countries Spykman Rimland Theory: naval power; Britain and Japan ...
Regions and power review
... Asserting that regional patterns of security are increasingly important in international politics, this study presents a detailed account of relations between global powers. It emphasizes their relationship with the regional security complexes which make up the contemporary international system. The ...
... Asserting that regional patterns of security are increasingly important in international politics, this study presents a detailed account of relations between global powers. It emphasizes their relationship with the regional security complexes which make up the contemporary international system. The ...
A Novel Approach to Politics
... • Globalization is a phenomena created, among other things, by advancing technology, increasing world-wide education, and the aggregate economic choices of billions of people around the world. • Is there anyone, any country, or any group of countries that could actually stop or reverse globalization ...
... • Globalization is a phenomena created, among other things, by advancing technology, increasing world-wide education, and the aggregate economic choices of billions of people around the world. • Is there anyone, any country, or any group of countries that could actually stop or reverse globalization ...
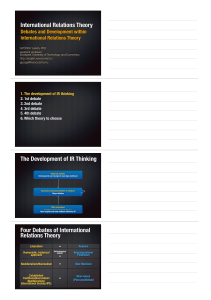
International Relations Theory The Development of IR Thinking Four
... "I am a most unhappy man. I have unwittingly ruined my country. A great industrial nation is controlled by its system of credit. Our system of credit is concentrated. The growth of the nation, therefore, and all our activities are in the hands of a few men. We have come to be one of the worst ruled, ...
... "I am a most unhappy man. I have unwittingly ruined my country. A great industrial nation is controlled by its system of credit. Our system of credit is concentrated. The growth of the nation, therefore, and all our activities are in the hands of a few men. We have come to be one of the worst ruled, ...
WWI Interpreted
... focus on sovereign nation states and the pursuit of power. It differs from Realism in that where areas Realism touts Balance of Power, Power Transition champions the exact opposite. Power Transition views the war as fundamentally unipolar in which one state is overwhelmingly more powerful the rest. ...
... focus on sovereign nation states and the pursuit of power. It differs from Realism in that where areas Realism touts Balance of Power, Power Transition champions the exact opposite. Power Transition views the war as fundamentally unipolar in which one state is overwhelmingly more powerful the rest. ...
Covenant University College of Development Studies School of
... will evolve naturally from the class discussions and debates. The students will be given three weeks to develop the term paper and consequently submit for assessment. Alignment with covenant university core values ...
... will evolve naturally from the class discussions and debates. The students will be given three weeks to develop the term paper and consequently submit for assessment. Alignment with covenant university core values ...
Political Science Classes in Subfields Political Philosophy
... The Rise of Asia Introduction to Latin American Studies Soviet and Post-Soviet Politics and Society: 1917 to the Present Social Movements in Comparative Perspective Comparative Electoral Politics Participation in Public Life Ethnic Conflict in World Politics Politics and Policy in Contemporary Japan ...
... The Rise of Asia Introduction to Latin American Studies Soviet and Post-Soviet Politics and Society: 1917 to the Present Social Movements in Comparative Perspective Comparative Electoral Politics Participation in Public Life Ethnic Conflict in World Politics Politics and Policy in Contemporary Japan ...
International relations theory

International relations theory is the study of international relations from a theoretical perspective; it attempts to provide a conceptual framework upon which international relations can be analyzed. Ole Holsti describes international relations theories as acting like pairs of coloured sunglasses that allow the wearer to see only salient events relevant to the theory; e.g. an adherent of realism may completely disregard an event that a constructivist might pounce upon as crucial, and vice versa. The three most popular theories are realism, liberalism and constructivism.International relations theories can be divided into ""positivist/rationalist"" theories which focus on a principally state-level analysis, and ""post-positivist/reflectivist"" ones which incorporate expanded meanings of security, ranging from class, to gender, to postcolonial security. Many often conflicting ways of thinking exist in IR theory, including constructivism, institutionalism, Marxism, neo-Gramscianism, and others. However, two positivist schools of thought are most prevalent: realism and liberalism; though increasingly, constructivism is becoming mainstream.