* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Benzodiazepines
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
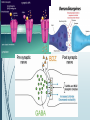
Benzodiazepines Rachel Anderson Introduction Benzodiazepines (BZD, BZs) "benzos” Psychoactive drugs Chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring Central nervous system depressants that are commonly known as tranquilizers, sedatives, or anxiolytics Due to the sedative effects they produce, they are often used as “date rape” drugs Approximately 2,000 benzodiazepines have been produced but only 15 are marketed in the U.S Schedule IV Twice as many women as men taking them CNS depressants • They are the most commonly prescribed medications in the U.S. and are mainly used to treat anxiety and insomnia • Second most frequently abused prescription • Combination with other CNS depressants can cause dangerous drug interactions, and contribute to death via overdose History As we learned in class: 1800’s looking for something other than alcohol to be used as CNSD Bromides 1800s helpful but toxic Barbiturates 1900s initially safe/effective; eventual problems with tolerance, safety and dependence Benzodiazepines 1950s safe for short periods of time; long term use cause dependence and withdrawal However, they are less toxic than their predecessors, (the barbiturates) and death rarely results when a benzodiazepine is the only drug taken. Benzodiazepines History 1955 – Synthesis of the first benzodiazepine, Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) 1960 – Librium (Chlordiazepoxide) made available 1963 – Valium (Diazepam) made available 1970s – Benzodiazepines had replaced barbiturates 1973 - 100 million prescriptions written 1977- Benzodiazepines were globally the most prescribed medications 1978 – 2.3 billion tablets of Valium sold 1980 – Researchers issued one of the earliest warnings against long term use Reason for Use • Benzodiazepines possess sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and amnesia actions, which are useful in a variety of indications: Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)/ Panic Attacks / Acute Anxiety, Insomnia Psychiatric Emergencies Muscle Spasms Epileptic seizures Alcohol Dependence Sedate patients Mechanism of Action Most are administered orally; however, they can also be given intravenously, or intramuscularly Mechanism of Action: Affect neurons that have receptors for neurotransmitter gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA) GABA is the most common inhibitory transmitter in brain regions Limbic System (alter mood) RAS (cause Drowsiness) Motor Cortex (relax muscles) Distinguished primarily by duration of action: (short acting) hypnotics, (long acting) sedatives Benzos are categorized as either short-, intermediate-, or long-acting: longer-acting benzodiazepines are recommended for the treatment of anxiety Short- and intermediate-acting benzodiazepines are preferred for the treatment of insomnia High doses of many shorter-acting benzodiazepines may also cause anterograde amnesia and dissociation Contraindications Respiratory depression - myasthenia gravis, sleep apnea, bronchitis, and COPD. Increase suicidal tendencies – major depression Life Threatening interactions – history or current drug comorbidity Not safe – Pregnancy Side Effects The most common side-effects of benzodiazepines are related to their sedating and muscle-relaxing action: Drowsiness Dizziness Decreased alertness Decreased concentration Lack of coordination Driving impairment Decreased libido Depression Less common side effects: Nausea Blurred vision Confusion Euphoria Nightmares ADDICTION/ DEPENDENCE /TOLERANCE AND WITHDRAWALS Main Sign of Physical Dependence Rebound Symptoms Withdrawal Symptoms Most Frequent Symptoms of Withdrawal Insomnia Gastric problems Tremors Agitation Anxiety Difficulty breathing Headaches Fear Muscle spasms Less Frequent Symptoms of Withdrawal Irritability Sweating Depersonalization Hypersensitivity Depression Suicidal behavior Psychosis Seizures Abrupt Withdrawal can be dangerous – gradual reduction regimen/ tapering is recommended Some Benzos to Know Of the 15 FDA-approved benzodiazepines in the U.S., the most commonly known include: Versed (midazolam) & Halcion (triazolam), which are ultra-short acting [These are often prescribed to help a person sleep or to calm a person down before surgery] Xanax (alprazolam), Klonopin (clonazepam), & Ativan (loraz epam), which are short-acting Librium (chlordiazepoxide) & Valium (diazepam), which are long-actin Prescribing rates per 100 persons (in quartiles), by state and drug type — IMS Health, United States, 2012 Wide variation exists from one state to another in prescribing rates for these drugs. High rates of prescribing these controlled substances are important determinants of rates of fatal overdose and drug abuse, especially when prescribed with opioids Alabama, Tennessee, and West Virginia were the three highest-prescribing states https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/m mwrhtml/mm6326a2.htm Charts/ Graphs National Overdose Deaths— Number of Deaths from Benzodiazepines. The figure is a bar chart showing the total number of U.S. overdose deaths involving benzodiazepines from 2002 to 2015. The chart is overlayed by a line graph showing the number of deaths of females and males. From 2002 to 2015 there was a 4.3-fold increase in the total number of deaths. https://www.drugabuse.gov /related-topics/trendsstatistics/overdose-deathrates Other/Interesting Toxicology screen - A toxicology screen refers to various tests that determine the type and approximate amount of legal and illegal drugs a person has taken. Benzodiazepines: up to 6 weeks with high level use 1966 hit “Mothers Little Helper” by Rolling Stones is a song written about Valium “What a drag it is getting old ‘kids are different today’ I hear every mother say. Mother needs something to calm her down. And though shes not really ill. Theres a little yellow pill. She goes running for the shelter of a mothers little helper Current Awareness https://www.madinamerica.com/2016/06/new-videofor-world-benzodiazepine-day/ in a new video for World Benzodiazepine Awareness Day (W-BAD) people from all over the world share about the iatrogenic harm they sustained from taking benzodiazepines as prescribed. Summary Benzodiazepines are psychoactive drugs They are classified as depressants and act on the Central Nervous System Benzodiazepines possess sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant, and amnesia actions They are the most commonly prescribed medications in the U.S. and are mainly used to treat anxiety and insomnia. Combination with other CNS depressants can cause dangerous drug interactions, and contribute to death via overdose Resources http://wickedsober.com/benzodiazepines/ https://vsearch.nlm.nih.gov/vivisimo/cgi-bin/querymeta?query=benzodiazepine&v%3Aproject=nlm-main-website http://www.pdr.net/drug-summary/Xanax-alprazolam-1873 http://www.pdr.net/search-results?q=clonazepam https://www.drugabuse.gov/related-topics/trends-statistics/overdosedeath-rates https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003578.htm http://genpsych.com/2015/08/11/quick-facts-aboutbendodiazepines/ https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/40352 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benzodiazepine http://www.narconon.org/drug-information/benzodiazepines.html