* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics and Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
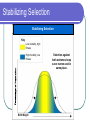
Genetics and Evolution Chapter 16-2 Standard 8c,d 8c: Students know the effects of genetic drift on the diversity of organisms in a population 8d: Students know reproductive or geographic isolation affects speciation Review Population: A collection of individuals of the same species in a given area Gene pool: The combined genetic information of all members of a particular population Relative frequency: Number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of time other alleles for the same gene occur Evolution involves a change in relative frequencies of alleles in a gene pool of a population. Gene Pools Sample Population 48% heterozygous black 16% homozygous black 36% homozygous brown Frequency of Alleles allele for brown fur allele for black fur Genetic Drift Remember that mutations always occur. Mutations do not always have to be beneficial in order for evolution to occur (ie: adaptation not always necessary) In other words, evolution can occur in the absence of natural selection Genetic drift: A random change in the frequency of a gene Genetic Drift Sample of Original Population Descendants Founding Population A Founding Population B Genetic Drift Sample of Original Population Descendants Founding Population A Founding Population B Genetic Drift Sample of Original Population Descendants Founding Population A Founding Population B Hardy Weinberg Founder Effect: change of allele frequency due to the migration of a small subgroup in a population. Hardy-Weinberg Principle: allele frequency will remain constant (genetic equilibrium) unless one or more factors cause frequencies to change. Genetic Equilibrium 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Five conditions are required to maintain genetic equilibrium Random mating Population must be large No movement in or out of population No mutations No natural selection But does this happen in real life? Directional Selection Key Directional Selection Low mortality, high fitness Food becomes scarce. High mortality, low fitness Stabilizing Selection Stabilizing Selection Key Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Birth Weight Selection against both extremes keep curve narrow and in same place. Disruptive Selection Disruptive Selection Low mortality, high fitness High mortality, low fitness Population splits into two subgroups specializing in different seeds. Beak Size Number of Birds in Population Key Number of Birds in Population Largest and smallest seeds become more common. Beak Size