* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Thermal shift assay wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
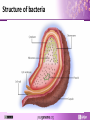
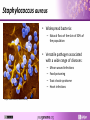
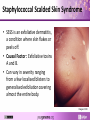
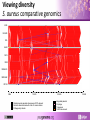
Staphylococcus aureus An introduction to the genetic features of MRSA What is a pathogen? • A pathogen is a disease causing agent Bacteria Fungus Protozoa Virus Images: Janice Carr; CDC/Dr. Godon Roberstad; Wellcome Images; Anna Tanczos, Wellcome Images Question Can you name a disease caused by bacteria? Structure of bacteria Staphylococcus aureus • Widespread bacteria: – Natural flora of the skin of 30% of the population • Versatile pathogen associated with a wide range of diseases: – – – – Image: Sharon Peacock, Oxford University Minor wound infections Food poisoning Toxic shock syndrome Heart infections How does S. aureus cause disease? • Bacteria have a range of molecular “weapons” to help them invade a host and evade detection. • What do you think these “weapons” are? The S. aureus arsenal Fibronectin binding protein Collagen binding protein Toxins Hemolysins Leukocidins Enterotoxins Exfoliative toxins Toxic shock syndrome toxin Clumping factor S. aureus Protein A Elastin binding protein Matrix adhesion factor Surface proteins Enzymes Lipases Esterases Nucleases Coagulases Phospholipase C Extracellular proteins What is a surface protein? • Surface proteins are found on the outside of S. aureus. • They enable it to attach to host cells aiding tissue invasion and colonisation. • Examples: – Elastin binding protein – Collagen binding protein What is a toxin? • A protein that has the ability to damage specific cells and cellular components. Q. Can anyone think of a disease or syndrome caused by bacterial toxins? Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome • SSSS is an exfoliative dermatitis, a condition where skin flakes or peels off. • Causal Factor : Exfoliative toxins A and B. • Can vary in severity ranging from a few localised blisters to generalised exfoliation covering almost the entire body. Images: CDC Toxic Shock Syndrome • Symptoms: sudden onset of fever, chills, vomiting, diarrhoea, muscle aches and rash. Can lead to hypotension and anaphylactic shock which can lead to organ failure. • Causal factor: S. aureus toxic shock syndrome toxin. • Associated with tampon use and also as a complication of skin abscesses or surgery. Strawberry tongue symptom of TSS Image: CDC What is an enzyme? • Enzymes break down organic compounds of cells and tissues, allowing the bacteria to absorb nutrients and also to spread through body tissues. • Examples: – Protease – Coagulase – Lipase How do you treat S. aureus infections? • Diseases caused by S. aureus are usually treated with bactericidal antibiotics and the patient is normally free of pathogenic bacteria within a month. • Antibiotics include: – penicillin – oxacillin – nafcillin Image: Bmramon/wikimedia commons Superbugs & antibiotic resistance • Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is termed a “superbug”. • Common cause of hospital acquired infection. • Hospital-acquired MRSA infections lead to: – prolonged hospital stay – increased costs to NHS How does resistance occur? • Use of antibiotics creates a selective pressure. • Only bacteria with genes that confer resistance can survive a treatment of antibiotics. • Eventually resistant bacteria can make up the majority of the population. Population after Before antibiotics Add antibiotics antibiotics Genetic diversity of bacteria • Bacteria are under continuous selection pressure and are constantly evolving to adapt to changes in their environment. • How? – Mutations occur within the genome during DNA copying and because of damage to DNA which confer a selective advantage. – Horizontal gene transfer (direct exchange of genes between individual bacteria). Horizontal transfer • New antibiotic genes can be acquired via horizontal transfer or conjugation. Images: Genome Research Limited Viewing diversity S. aureus comparative genomics 8325 USA300 COL Mu50 N315 MW2 MSSA476 MRSA252 RF122 0 Mb 1.0 Mb Staphylococcal cassette chromosome (SCC) element Genomic islands shared with other S. aureus strains Pathogenicity islands 2.0 Mb Integrated plasmid Prophage Transposon Tn916-like element 3.0 Mb