* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Enzymes - Net Start Class
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Lactoylglutathione lyase wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Beta-lactamase wikipedia , lookup
Transferase wikipedia , lookup
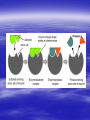
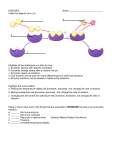
Enzymes Enzymes – special types of proteins Enzymes are proteins capable of increasing the rate of a reaction without being consumed in the process Types of reactions enzymes are involved in include: –Digestion –Synthesis of molecules –Storage and release of energy Enzymes have the ability to carry out reactions at lower temperatures that would normally require extremely high temperatures Activation Energy – the energy required to attach enzymes to substrates and cause a change Substrate – the molecule undergoing a change; also called the reactant. Section 2-4 Effect of Enzymes Enzymes/Catalyst lower the activation energy in order to speed up the chemical reaction Reaction pathway without enzyme Activation energy without enzyme Reactants Reaction pathway with enzyme Activation energy withProducts enzyme Active site – place on the enzyme where a specific substrate attaches Reactant – in a chemical equation, it is on the left side; what is added together to form products Product – the end result of the enzyme-substrate reaction; found on the right side of a chemical equation Optimum – the best conditions for a reaction to occur. In your body, optimum conditions are a pH of 7 and a temperature of 37oC Denature – to permanently change the shape of an enzyme due to pH or temperature extremes; can prevent the enzyme from functioning properly. Coenzyme – needs to be present in some enzymes to aid in the reaction. If it is missing the enzyme may not work; vitamins act as coenzymes. Inhibitors – things that prevent enzymes from working properly –Competitive inhibitors – compete with the substrate for binding sites on the enzyme; slows down the reaction; ex: ethanol and isopropanol –Noncompetitive inhibitors – irreversible binding to enzymes; stop the reaction permanently Ex: some heavy metals.