* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concise History Ch.1 – 5 POWERPOINT not 2007
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Sudan wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
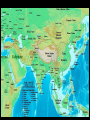
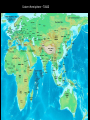
Chapters 1 – 5 REVIEW rihlah sa’idah, basi’ah tovah, safar be-khayr ….and may you have a fruitful intellectual journey Authors Approach • “From what we now know about Middle East history, we believe the most useful unit of study is not the dynasty or the nation-state but the civilization” (p.4) • “..this book…focuses on an interlocking complex of rulers and subjects, governments and laws, arts and letters, cultures and customs, cities and villages – in short, on a civilization that has prevailed in most of western Asia, and northern Africa since the 7th century, all tied together by the religion of Islam” (p.4) Geographic Topics • Coexistence in an arid environment • Natural crossroads of Euro-African landmass • OIL – a major resource – ECONOMIC ADVANTAGE • WATER – a limited resource – GEOPOLITICAL PROBLEM Middle East Before Muhammad Rise of Christianity • “If history can be defined as humanity’s recorded past, than the Middle East has had more history than any other part of the world” (p.15) • Under Roman rule, Christianity - which is based in the Middle East - becomes popular among Roman soldiers stationed at this far outpost of the empire • Roman emperor Constantine (313 – 337) adopts Christianity and builds new Roman capital at Constantinople (modern day Istanbul, Turkey) Dissident Christian Sects – What does it mean for future Arab Conquests? • Arians – argued that Christ was still not equivalent to God • Nestorians - saw Christ as two distinct persons; divine and human • Monophysites – believe Christ contained within him a single, wholly divine nature • All of these sects were persecuted by the Orthodox church. This policy turns dissenters against Constantinople. Why does this help the future Arab conquerors? Rome’s Persian Rival • Persian Empire included Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan and Central Asia • Zoroastrianism is state religion, BUT other religious groups could practice freely Arabs • Nobody is sure where the Arabs came from • Populated the dry and desolate Arabian Peninsula • Nomadic, following the seasonal availability of groundwater Arabian Culture * Arabs were warlike; hunger or habit led them to pray on one another or on outsiders * While the nomadic lifestyle gave them no chance to develop architecture, sculpture or painting – they did possess one highly portable form of artistic expression – poetry * Pre-Islamic poetry embodies the Arab Code of Virtue. These poems were recited by memory by tribal Arabs and their descendants * “Pre-Islamic poetry helped to shape the Arabic language, the literature and culture of the Arabs, and hence the thoughts and actions of Arabic-speaking peoples even now” (p.24) Arab Code of Virtue – “Muruwwah” (p.24) • • • • • • • • • Bravery in battle Patience in misfortune Persistence in revenge Protection of the weak Defiance toward the strong Hospitality to the visitor Generosity to the poor Loyalty to the tribe Fidelity in keeping promises Southern Arabia • The southern part of the Arabian peninsula has a moderate climate and environment and thus a different culture emerges there • Southern Arabia fought over by Ethiopians and Persians. Persians control the area from 575 - 625 Mecca and Muhammad Origins • Pre – Islamic Mecca was an important caravan station. Had spiritual importance due to nearby shrines in the mountains • Muhammad is born in Mecca in 570, he is part of the Quraysh tribe. Orphaned as child and cared for by his Uncle. Becomes a well respected merchant • MH upset that Meccan leaders were not upholding the code of virtue. Thought the Jews, Christians might have answers to problems (p.30-31) First Revelation & Early Muslims • In 610, Muhammad has first revelation when he is told by the angel, Gabriel, that he is the Lord’s Messenger. Muhammad now claims to be a prophet of God • First believers in Muhammad come from lower stratum of society – similar to so many other revolutions! • Muhammad’s early message is similar to Arab code of virtue Muslim – one who submits to God’s will Islam – the act of submission to God Meccan Opposition • Meccans of wealth and power feared MH’s influence. They made a lot of $$ from pilgrimages to Mecca’s many shrines • MH claims he made a pilgrimage in one night to Jerusalem on a winged horse • When MH’s influential Uncle dies, MH loses protection. He and his followers forced to leave Mecca for Medina Emigration to Medina (Hijra) • MH is welcomed into Medina as an arbitrator between quaraling Arab and Jewish tribes. In return for his work, MH and the Meccan Muslims are given sanctuary • MH soon becomes a leader of Medina. Is now both a spiritual and political leader • MH and the Muslims raid Meccan caravans and defeat a force of 1,000 sent from Mecca to bring him down Return to Mecca • In 628, MH makes a truce with Mecca. He returns a year later with a force 10,000 strong. Mecca falls under his control and embraces Islam • MH dies on June 8th, 632 What is Islam? • MH is the messenger of God (Allah) • Gabriel was the angel sent by Allah to reveal the Quran to MH • Quran is the record of God’s revelations to the angel Gabriel via MH. It is 114 chapters of hard reading. • Muslims recognize Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, Jonah, Job and Jesus as prophets. They deny, however, that Jesus was the “son of God” • There is a belief in a Judgment Day when all people will die. No prophets will return before this day Five Pillars of Islam • Believe that MH is the messenger of the one God, Allah • Pray five times a day towards Mecca • Fast during Ramadan • Almsgiving • Hajj – pilgramage to Mecca (takes place during December) Muhammad’s Successors • MH never chose a successor, nor ever mentioned a system to choose successors • His friend, and original convert, Abu-Bakr called himself the successor of the messenger of God. “Khalifat rasul Allah”, shortened to “Khalifa”, or in English, “Caliph”. Abu-Bakr is caliph from 632-634 Initial Arab Conquests • “The Caliph’s brilliant answer [to how to hold the Arab tribes together] was to turn the bedouin’s combative energies away from one another and toward conquering the settled lands to the North, the Roman and Persian empires” (p.55) • Rome’s Middle East holding (Palestine, Syria, Egypt) are captured in less than a decade • Persian Empire captured over a generation • “Within a century, Muslim soldiers would be stationed from Spain in the west, across North Africa and Middle East to the borders of China in the east” (p.55) Eastern Hemisphere – 700AD Five Reasons the Arabs Succeeded 1. Fought few, carefully chosen engagements in deserts mostly. Had small, but cohesive forces 2. Many non-Muslim Arabs joined the conquests (remember the code of virtue) 3. Years of warfare between Romans and Persians had weakened both 4. Many people living under both empires were discontented and welcomed the Arabs 5. Persian Empire underwent an internal collapse Beginnings of Islamic Government • Mostly Meccans and Medinians are sent to administer the newly conquered provinces. Jews, Christians and Zoroastrians were still allowed to practice • Ali, MH’s nephew, is fourth caliph. (656-661). He moves the capital to Kufa, Iraq • Mu’awiya is fifth caliphate. He moves capital to Damascus and launches attacks on Roman controlled Anatolia (Turkey) Husayn’s Rebellion – Emergence of Shi’ism • Husayn is MH’s grandson. He doesn’t recognize the caliphate of Mu’awiya and is therefore attacked and killed in Karbala, Iraq • Husayn’s supporters vow to never recognize the Umayyads (Mu’awiya’s tribe) as caliphs. They call themselves “Shi’at Ali” or “The Party of Ali” • Sunnis accept the ruling caliphs • Shiites have a separate pilgramage to Najaf and Karbala, the burial sites of Ali and Husayn. (Both of these are important cities in modern day Iraq)