* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jupiter - Department of Geology UPRM
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Eight Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
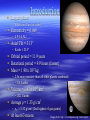
GEOL 3045: Planetary Geology Lysa Chizmadia Jupiter Largest planet Introduction – Fifth from Sun (or sixth) Eccentricity = 0.049 – 4.9-5.4 AU Axial Tilt = 3.13º – Earth = 23.5º Orbital period = 11.9 years Rotational period = 9.9 hours (fastest) Mass = 1.90 x 1027 kg – 2.5x more massive than all other planets combined – ~318 Earths Volume = 1.43 x 1015 km3 – ~1321 Earths Average = 1.33 g/cm3 – = 5.52 g/cm3 (2nd highest of gas giants) At least 63 moons Images from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter Internal Structure Atmosphere: – H & He ~ solar – ~27 km thick Metallic Hydrogen Mantle: – H2 upper mantle – Liquid H lower mantle H nuclei do not have lattice order Rocky Core: – From measurements: 3 - 15% of total mass 12 - 45x Earth’s mass Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter Atmosphere Pressure: ~70% of Earth Upper atmosphere: – ~90% H & ~10% He (~ solar) Bulk atmosphere: – 75% H & 24% He by mass With trace amounts of: – CH4, H2O, NH3, H2S, Ne, O2, PH3, S, & H-Cs Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter Clouds Ices in clouds: – H2O, NH3, NH4SH – Average cloud T: -121ºC Bands due to circulation zones – Tropical zones Colors due to UV light Winds up to 100 km/s Red Spot: – Rotates in 6 days – Counterclockwise – 2-3x larger than Earth Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter Rings Faintest of gas giants Three parts: – Halo – Bright main ring – Gossamer ring Image from: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/callisto/p48188.html Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter Composed of dust – Low albedo (0.05) – Compared to Saturn’s icy rings Produced from minor moons: – Main ring: Adrastea& Metis – Gossamer ring: Thebe & Amalthea Magnetosphere Auroral Borealis on Jupiter ~14x stronger than Earth’s Produced by eddys in metallic H liquid Image from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter Ionizes SO2 from Io Trapps ions from solar wind Causes radio emissions from polar regions Extends >650 x 109 km – Past Saturn’s orbit Image from: http://www.solarviews.com/eng/jupiter.htm Heat Output Radiates more Q than recieves from Sun – Due to contraction (shrinks ~2 cm/yr) Originally twice the size & much hotter Summary Largest planet in solar system – Very small axial tilt = no seasons – Fastest rotation (day) Atmosphere ~ solar = primordial Interior P & T high – Liquid metallic H mantle Rings have low albedo = rocky dust Radiates more heat than receives from Sun – Due to crystallization & contraction