* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PLANTS
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
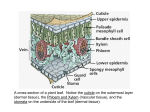
PLANTS I mean they do keep you alive! General Characteristics • • • • • Multicellular Photosynthesis aka Autotrophic Eukaryote All can reproduce sexually Have cell walls Fun Facts • The Energy most organisms needs comes directly or indirectly from plants • 12 phyla and more than 270,000 known species • Life cycles vary from a few weeks to 5,000 years • Some less than 1mm in width and some grow more than 328 feet tall. Review Photosynthesis • Carbon dioxide + water oxygen + sugar • Light is used as the energy source for the reaction. Evolution • Cyanobacteria endosymbiosis • All related to – green algae (multicellular photosynthetic plant-like protist) • Increased throughout time in the plants level of complexity • Could not grow until ozone formed (protected organisms from UV rays) Adaptation to Land • Aquatic environment to land (biggest goal: how to conserve water) – Thicker cell walls – Vascular tissue – Reproduction without water (spores and seeds) – Cuticle – Stomata Organization/Structures • 12 division/phylum classified into 2 groups • Vascular – True stems, leaves, and roots (think trees, flowers, pretty much all other plants) • Non Vascular – Short, no true stems, leaves or roots (think liverwart, moss, etc.) Nonvascular • 3 phyla are called bryophytes (16,600 species) • Usually grow near streams and rivers • Sexual reproduction needs water to reproduce (sperm and egg swim) • Asexual does not • Rhiziods instead of roots • Flat broad tissues instead of leaves Two types of vascular tissue • Xylem and Phloem • Xylem – carries WATER and inorganic nutrients in ONE direction from the roots to the stems and leaves • Phloem – carries ORGANIC compounds (carbohydrates) in ANY direction, depending on the plants needs. • Vascular Plants have three kinds of tissue (dermal, ground, and vascular) • Vascular tissue helps to provide support, aquatic plants use water as a support system. • Woody tissue – several layers of xylem • Non-woody = herbaceous Seedless or Seeds • Vascular Plants are broken down into 2 groups • Seedless – example ferns (produce spores) • Seeds Gymnosperm and Angiosperm • Seed plants are broken down into two groups • Gymnosperms – “Naked seed” ex pine trees : seeds are not in a fruit • Angiosperms – flowering plants: seeds are within a protective fruit Monocots and Dicots • Angiosperm breaks down into 2 classes • Monocots – embryo has 1 cotyledon, typically narrow leaves, long parallel veins, flowers in multiples of three (grasses, corn) • Dicots – embryo has 2 cotyledons, broad leaves with branching veins, flowers in multiples of four or five (beans, most trees) Functions Draw and label a picture of the types of tissue and general plant parts pg. 570 – Draw and label a woody stem pg. 575 – Draw and label simple and compound leaves pg. 576 – Draw and label the differences between monocot and dicot pg. 574 Use color and include all needed detail! (homework is not finished) Identifying Characteristics • Leaves • Monocot and Dicot • Stem types Basic Plant Reproduction Alternation of Generations All plants have a life cycle that involves two phases